|
Oximes
In organic chemistry, an oxime is a organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula , where R is an organic side-chain and R’ may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides () with general structure . Oximes are usually generated by the reaction of hydroxylamine with aldehydes () or ketones (). The term ''oxime'' dates back to the 19th century, a combination of the words ''oxygen'' and ''imine''. Structure and properties If the two side-chains on the central carbon are different from each other—either an aldoxime, or a ketoxime with two different "R" groups—the oxime can often have two different geometric stereoisomeric forms according to the ''E''/''Z'' configuration. An older terminology of ''syn'' and ''anti'' was used to identify especially aldoximes according to whether the R group was closer or further from the hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descriptor (chemistry)
A descriptor is in chemical nomenclature a prefix placed before the systematic substance name, which describes the configuration or the stereochemistry of the molecule. Some listed descriptors are only of historical interest and should not be used in publications anymore as they do not correspond with the modern recommendations of the IUPAC. Stereodescriptors are often used in combination with locants to clearly identify a chemical structure unambiguously. The descriptors, usually placed at the beginning of the systematic name, are not taken into account in the alphabetical sorting. Configuration descriptors ''cis'', ''trans'' See: cis–trans isomerism The descriptors ''cis'' (lat. ''on this side of'') and ''trans'' (lat. ''over, beyond'') are used in various contexts for the description of chemical configurations: In organic structural chemistry, the configuration of a double bond can be described with ''cis'' and ''trans'', in case it has a simple substitution pattern w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions. Structure For ketimines and aldimines, respectively, the five core atoms (C2C=NX and C(H)C=NX, X = H or C) are coplanar. Planarity results from the sp2-hybridization of the mutually double-bonded carbon and the nitrogen atoms. The C=N distance is 1.29-1.31 Å for nonconjugated imines and 1.35 Å for conjugated imines. By contrast, C-N distances in amines and nitriles are 1.47 and 1.16 Å, respectively. Rotation about the C=N bond is slow. Using NMR spectroscopy, both E- and Z-isomers of aldimines have been detected. Owing to steric effects, the E isomer is favored. Nomenclature and classification The term "imine" was coine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. Fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Structure Of Oximes
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
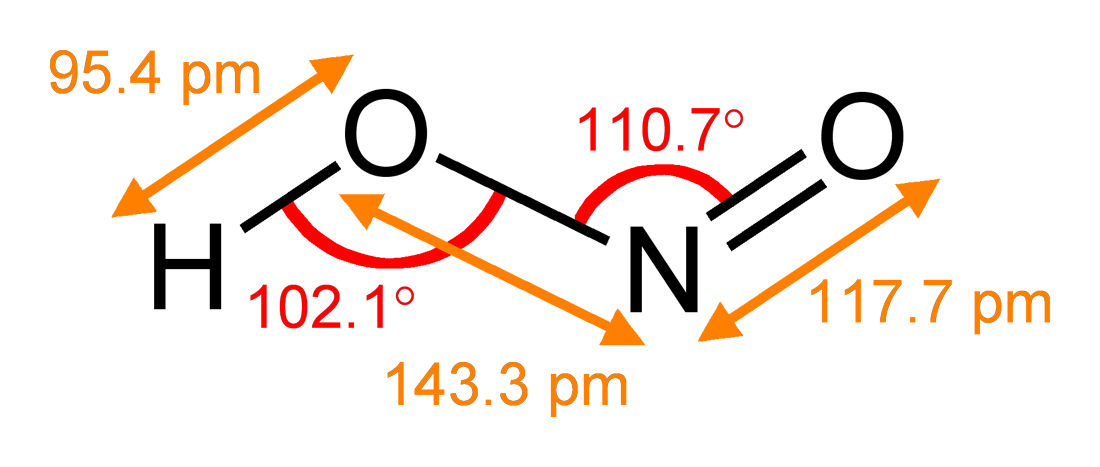
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoamyl Nitrite
Amyl nitrite is a chemical compound with the formula C5H11ONO. A variety of isomers are known, but they all feature an amyl group attached to the nitrite functional group. The alkyl group is unreactive and the chemical and biological properties are mainly due to the nitrite group. Like other alkyl nitrites, amyl nitrite is bioactive in mammals, being a vasodilator, which is the basis of its use as a prescription medicine. As an inhalant, it also has a psychoactive effect, which has led to its recreational use, with its smell being described as that of old socks or dirty feet. It is also referred to as ''banapple gas''. It was first documented in 1844 and came into medical use in 1867. Uses * Amyl nitrite is employed medically to treat heart diseases as well as angina. * Amyl nitrite is sometimes used as an antidote for cyanide poisoning. It can act as an oxidant, to induce the formation of methemoglobin. Methemoglobin in turn can sequester cyanide as cyanomethemoglobin. * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Acetoacetate
The organic compound ethyl acetoacetate (EAA) is the ethyl ester of acetoacetic acid. It is a colorless liquid. It is widely used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a wide variety of compounds. It is used as a flavoring for food. Preparation Ethyl acetoacetate is produced industrially by treatment of diketene with ethanol. The preparation of ethyl acetoacetate is a classic laboratory procedure. It is prepared via the Claisen condensation of ethyl acetate. Two moles of ethyl acetate condense to form one mole each of ethyl acetoacetate and ethanol. : Reactivity Acidity Ethyl acetoacetate is diprotic: :CH3C(O)CH2CO2Et + NaH → CH3C(O)CH(Na)CO2Et + H2 :CH3C(O)CH(Na)CO2Et + BuLi → LiCH2C(O)CH(Na)CO2Et + BuH Keto-enol tautomerism Ethyl acetoacetate is subject to keto-enol tautomerism. In the neat liquid at 33 °C, the enol consists of 15% of the total. Multicarbon building block Ethyl acetoacetic acid is a building block in organic synthesis since the protons alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Nitrite
Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite salt. It is a precursor to a variety of organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides, but it is probably best known as a food additive used in processed meats and (in some countries) in fish products. Uses Industrial chemistry The main use of sodium nitrite is for the industrial production of organonitrogen compounds. It is a reagent for conversion of amines into diazo compounds, which are key precursors to many dyes, such as diazo dyes. Nitroso compounds are produced from nitrites. These are used in the rubber industry. It is used in a variety of metallurgical applications, for phosphatizing and detinning. Sodium nitrite is an effective corrosion inhibitor and is used as an additive in industrial greases, as an aq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Nitrite
The chemical compound ethyl nitrite is an alkyl nitrite with a chemical formula C2H5NO2. It may be prepared from ethanol. : Uses It is used as a reagent with butanone to yield the dimethylglyoxime end product. Ethyl nitrite is the main ingredient in a traditional ethanol-based South African remedy for colds and flu known as ''Witdulsies'', which is sold in pharmacies. It is known as a traditional Afrikaans remedy; the same remedy is apparently made by the Amish The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churches ... in the US. However, FDA has blocked over-the-counter sales of this same remedy, known in the US as ''sweet nitrite'' or ''sweet spirit of nitre'', since 1980. Its use has been associated with fatal methemoglobinemia. Methemoglobinemia is the primary toxic effect of et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Ethyl Ketone
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts.Wilhelm Neier, Guenter Strehlke "2-Butanone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran. Production Butanone may be produced by oxidation of 2-butanol. The dehydrogenation of 2-butanol is catalysed by copper, zinc, or bronze: :CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 → CH3C(O)CH2CH3 + H2 This is used to produce approximately 700 million kilograms yearly. Other syntheses that have been examined but not implemented include Wacker oxidation of 2-butene and oxidation of isobutylbenzene, which is analogous to the industrial production of acetone. The cumene process ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |