|
Owlfly
Ascalaphidae is a family of insects in the order Neuroptera, commonly called owlflies; there are some 450 extant species. They are fast-flying crepuscular or diurnal predators of other flying insects, and have large bulging eyes and strongly knobbed antennae. The larvae are ambush predators; some of them make use of self-decoration camouflage. Description Owlflies are readily distinguished from the superficially similar dragonflies by their long, clubbed antennae; dragonflies have short, bristle-like antennae. The closely related antlions (family Myrmeleontidae) have short, weakly clubbed antennae, smaller eyes, and reticulate wing venation. All but one species of Ascalaphidae have long antennae, easily distinguishing them. The sole exception is the Brazilian '' Albardia furcata'', the only living member of the subfamily Albardiinae, which has short antennae, but these are strongly clubbed (compared to myrmeleontids), and its wing venation is reticulate, typical of ascalaph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owlfly
Ascalaphidae is a family of insects in the order Neuroptera, commonly called owlflies; there are some 450 extant species. They are fast-flying crepuscular or diurnal predators of other flying insects, and have large bulging eyes and strongly knobbed antennae. The larvae are ambush predators; some of them make use of self-decoration camouflage. Description Owlflies are readily distinguished from the superficially similar dragonflies by their long, clubbed antennae; dragonflies have short, bristle-like antennae. The closely related antlions (family Myrmeleontidae) have short, weakly clubbed antennae, smaller eyes, and reticulate wing venation. All but one species of Ascalaphidae have long antennae, easily distinguishing them. The sole exception is the Brazilian '' Albardia furcata'', the only living member of the subfamily Albardiinae, which has short antennae, but these are strongly clubbed (compared to myrmeleontids), and its wing venation is reticulate, typical of ascalaph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
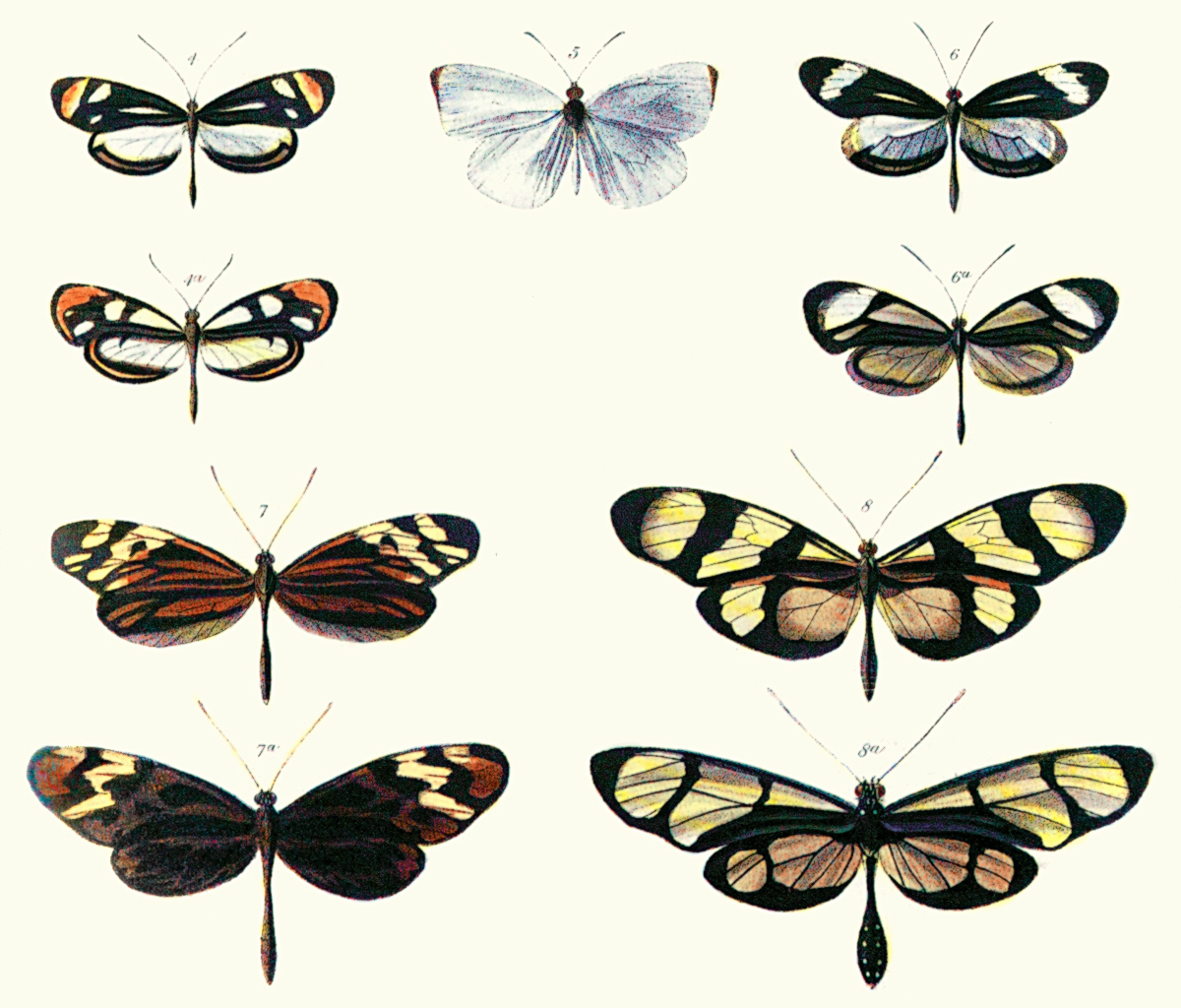
Libelloides Macaronius
''Libelloides macaronius'' is a day-flying owlfly species of Europe and Asia. The genus belongs to the family Ascalaphidae, subfamily Ascalaphinae. The species has appeared on postage stamps of Moldova and Ukraine. Description The adult is a large insect somewhat resembling a dragonfly. Its body, eyes, and long clubbed antennae are black; the wings are bright yellow, spotted with black, the forewings being partly transparent near the wingtips. The abdomen ends with a pair of hooked claspers in the male, a short ovipositor in the female. At rest, adults often perch like dragonflies with their wings outspread. They fly rapidly and rather straight over grass or bushes. The species has the excellent eyesight of predatory day-flying insects, though the large eyes are of the superposition type normally found in nocturnal insects. Distribution and ecology The species occurs in central, eastern, and southern Europe, and Palearctic Asia. They live in relatively open areas such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ululodes
''Ululodes'' is a genus of owlflies Ascalaphidae is a family of insects in the order Neuroptera, commonly called owlflies; there are some 450 extant species. They are fast-flying crepuscular or diurnal predators of other flying insects, and have large bulging eyes and strongly ... in the tribe Ululodini. There are 26 described species in ''Ululodes''. Species * '' Ululodes apollinaris'' * '' Ululodes arizonensis'' * '' Ululodes banksi'' * '' Ululodes bicolor'' * '' Ululodes brachycerus'' * '' Ululodes cajennensis'' ** ''U. c. cajennensis'' ** ''U. c. nanus'' * '' Ululodes costanus'' * '' Ululodes flavistigma'' * '' Ululodes floridanus'' * '' Ululodes heterocerus'' * '' Ululodes macleayanus'' ** ''U. m. macleayanus'' ** ''U. m. sanctaeluciae'' * '' Ululodes mexicanus'' * '' Ululodes nigripes'' * '' Ululodes oppositus'' * '' Ululodes paleonesius'' * '' Ululodes pilosus'' * '' Ululodes quadripunctatus'' * '' Ululodes roseni'' * '' Ululodes sanctidoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
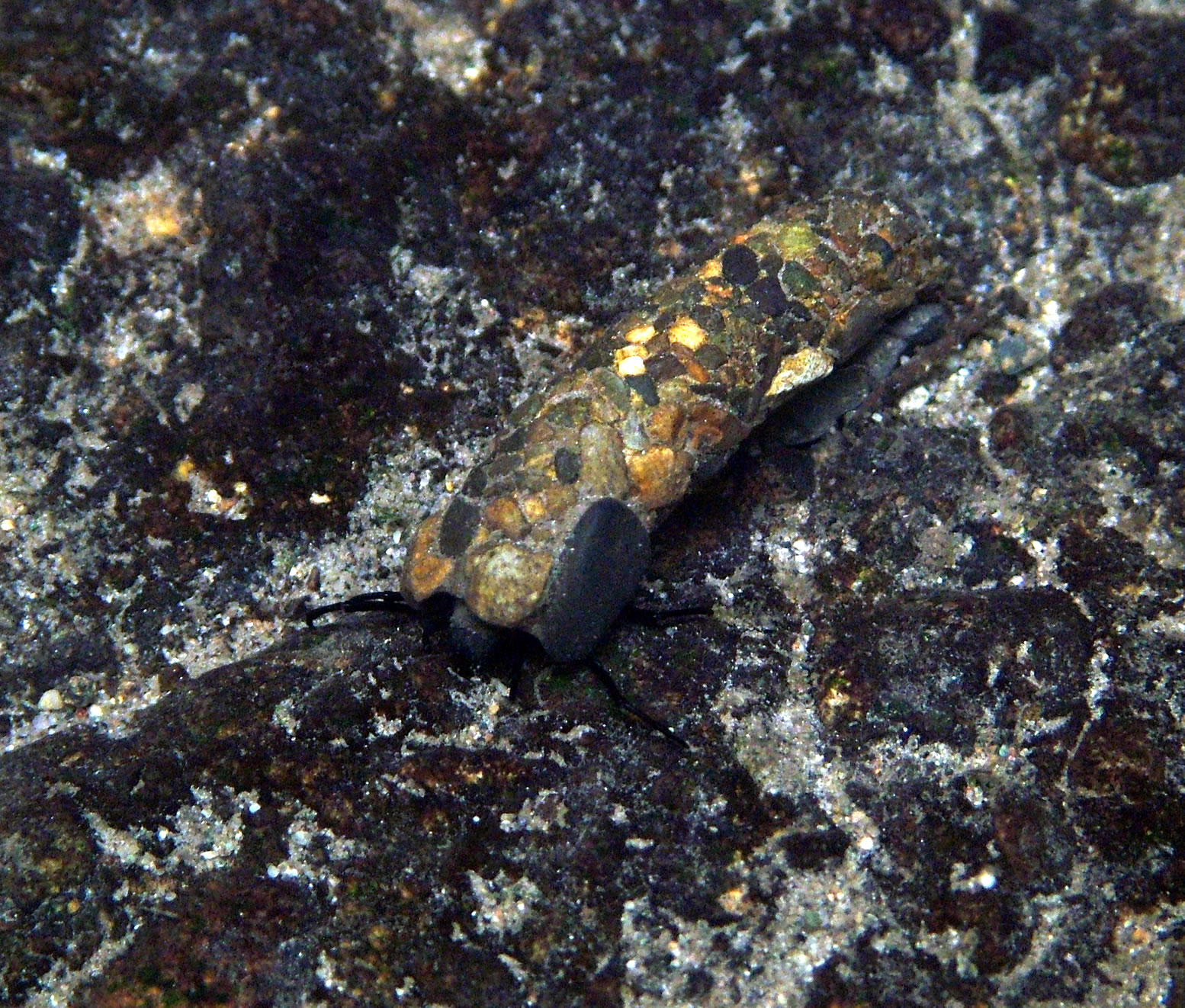
Self-decoration Camouflage
Self-decoration camouflage is a method of camouflage in which animals or soldiers select materials, sometimes living, from the environment and attach these to themselves for concealment. The method was described in 1889 by William Bateson, who observed '' Stenorhynchus'' decorator crabs. It was classified as "adventitious protection" by Edward Bagnall Poulton in 1890, and as "adventitious concealing coloration" or "adventitious resemblance" by Hugh Bamford Cott in 1940, who compared it to the way Australian aborigines stalked waterfowl, covering their faces with water lily leaves. Among animals, self-decoration is found in decorator crabs, some insects such as caddis flies and the masked hunter bug, and occasionally also in octopuses. In military camouflage, it is seen in the use of ghillie suits by snipers and the helmet nets of soldiers more generally, when these are camouflaged by inserting grass and other local plant materials, and in a more general way by the use of decora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascalaphini
Ascalaphini is the type subfamily of the neuropteran owlfly family. Most species are found in the tropics. Their characteristic apomorphy , shared with the Ululodini, is the ridge which divides each of their large compound eyes; both groups are thus sometimes known as split-eyed owlflies. The group has been alternatly treated as a subfamily of Ascalaphidae, when the family is treated separate from Myrmelontidae, or as a tribe, when the ascalaphids are treated as a subfamily in an expanded Myrmelontidae. Like the other owlflies, they are insectivores. Imagines are cumbersome fliers and lack the strong mouthparts of dragonflies (which owlflies resemble at first glance, despite being not at all closely related insects) or other decidedly predatory insects, they are restricted to small and defenseless prey. The larvae on the other hand resemble antlions in appearance and habits and are voracious ambush predators, able to tackle prey like ants that will not be eaten without a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Venation
Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to flight, fly. They are found on the second and third Thorax (insect anatomy), thoracic segments (the mesothorax and metathorax), and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane (extreme examples include the Odonata, dragonflies and Neuroptera, lacewings). The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family (biology), family or even genus level in many order (biology), orders of insects. Physically, some insects move their flight muscles directly, others indirectly. In insects with direct flight, the wing muscles directly attach to the wing base, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver (such as a predator) perceives the similarity between a mimic (the organism that has a resemblance) and a model (the organism it resembles) and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen (insect Anatomy)
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between L5 and S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at front and to the sides, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musk
Musk (Persian: مشک, ''Mushk'') is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial substances with similar odors. ''Musk'' was a name originally given to a substance with a strong odor obtained from a gland of the musk deer. The substance has been used as a popular perfume fixative since ancient times and is one of the most expensive animal products in the world. The name originates from the Late Greek μόσχος 'moskhos', from Persian 'mushk', similar to Sanskrit मुष्क muṣka ("testicle"), derived from Proto-Indo-European noun ''múh₂s'' meaning "mouse". The deer gland was thought to resemble a scrotum. It is applied to various plants and animals of similar smell (e.g. muskox) and has come to encompass a wide variety of aromatic substances with similar odors, despite their often differing chemical structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clemson University
Clemson University () is a public land-grant research university in Clemson, South Carolina. Founded in 1889, Clemson is the second-largest university in the student population in South Carolina. For the fall 2019 semester, the university enrolled a total of 20,195 undergraduate students and 5,627 graduate students, and the student/faculty ratio was 18:1. Clemson's 1,400-acre campus is in the foothills of the Blue Ridge Mountains. The campus now borders Lake Hartwell, which was formed by the dam completed in 1962. The university manages the nearby 17,500-acre Clemson Experimental Forest that is used for research, education, and recreation. Clemson University consists of seven colleges: Agriculture, Forestry and Life Sciences; Architecture, Arts and Humanities; The Wilbur O. and Ann Powers College of Business; Behavioral, Social and Health Sciences; Education; Engineering, Computing and Applied Sciences; and Science. '' U.S. News & World Report'' ranks Clemson University 77th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg , image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg , anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland") , image_map = , map_caption = , capital = Zagreb , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Croatian , languages_type = Writing system , languages = Latin , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2021 , religion = , religion_year = 2021 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Zoran Milanović , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Andrej Plenković , leader_title3 = Speaker of Parliament , leader_name3 = Gordan Jandroković , legislature = Sabor , sovereignty_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

_with_its_prey.jpg)