|
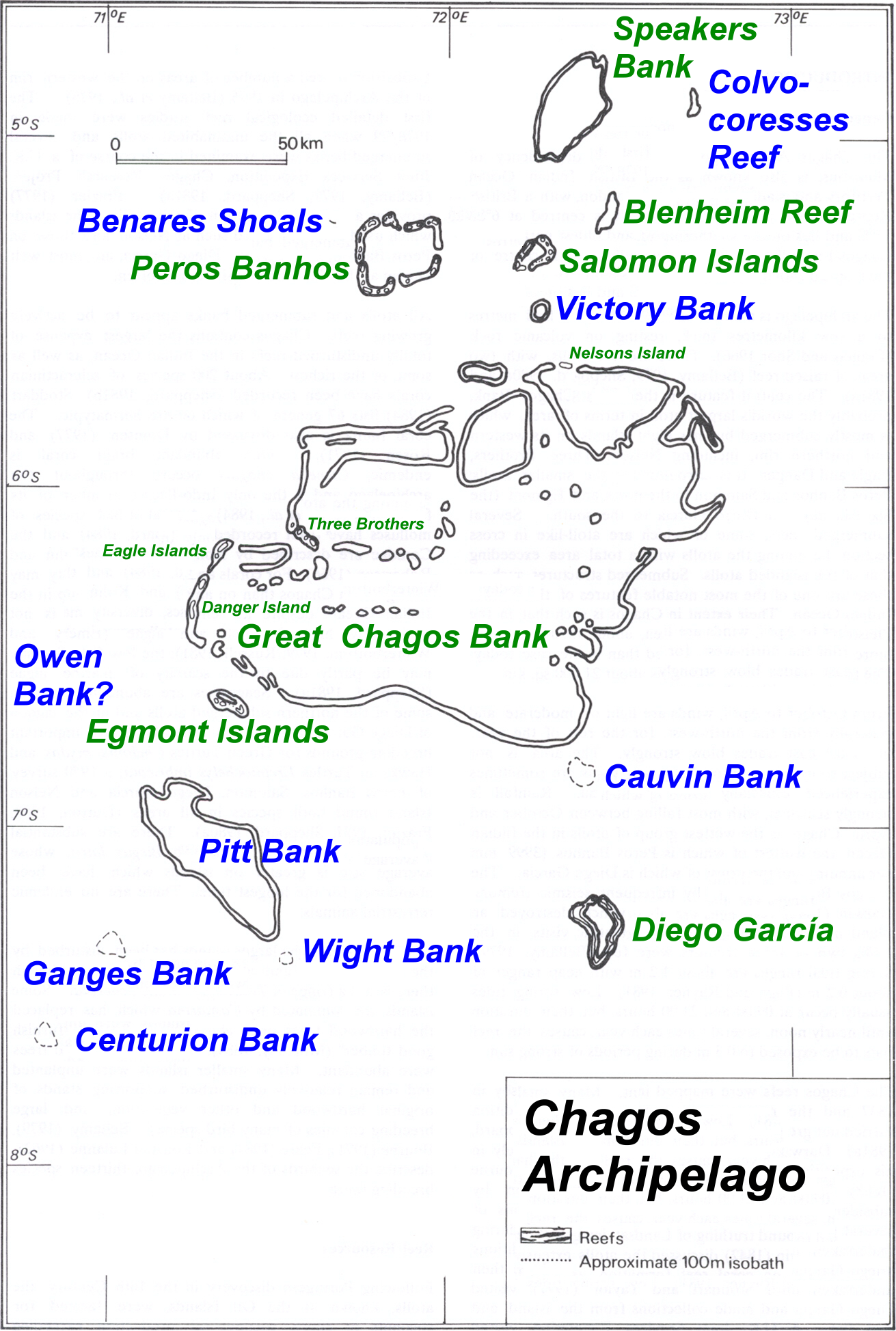
Owen Bank
Owen Bank is a wholly submerged atoll structure in the Chagos Archipelago, Indian Ocean. The reported location is 06°47'S, 070°14'E to 06°48'S, 070°15'E, thus the bank is the westernmost feature of the Chagos group. The closest islands are Danger Island on the Great Chagos Bank, and Île Sipaille in the Egmont Atoll, both located about East-North-East of Owen Bank. This geographic feature is not mentioned in the current Indian Ocean Pilot, but it appears in the British Admiralty nautical charts. British Admiralty nautical chart A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land ( topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the co ...s BA4071 - Indian Ocean Northern Part & BA4072 - Indian Ocean Western Part, Scale 1:10000000 References External linksIndian Ocean Pilot (download PDF) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can grow. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean. Two different, well-cited models, the subsidence and antecedent karst models, have been used to explain the development of atolls.Droxler, A.W. and Jorry, S.J., 2021. ''The Origin of Modern Atolls: Challenging Darwin's Deeply Ingrained Theory.'' ''Annual Review of Marine Science'', 13, pp.537-573. According to Charles Darwin's ''subsidence model'', the formation of an atoll is explained by the subsidence of a volcanic island around which a coral fringing reef has formed. Over geologic time, the volcanic island becomes extinct and eroded as it subsides completely beneath the surface of the ocean. As the volcanic island subsides, the coral fringing reef becomes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagos Archipelago
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelson's Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont and Danger Island(s); southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. The Chagos Islands had been home to the native Chagossians, a Bourbonnais Creole-speaking people, until the United Kingdom expelled them from the archipelago at the request of the United States between 1967 and 1973 to allow the United States to build a military base on Diego Garcia. Since 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danger Island, Great Chagos Bank
Danger Island is the westernmost and the southernmost island of the Great Chagos Bank, which is the world's largest coral atoll structure, located in the Chagos Archipelago in the Indian Ocean. Description It is a 2 km (1.24 m) long and flat island with a maximum width of , covered with tall coconut trees. Its name in all likelihood derives from the lack of a safe anchorage, which rendered every visit to this island dangerous for the ship and crew. The closest land is Sea Cow Island, the southernmost of the Eagle Islands which lies to the NNE. History There was never a permanent settlement on Danger Island, even at the time that the Chagos were inhabited (between the mid-18th and mid-20th centuries). However, occasionally plantation workers from other islands would be brought to this island to collect coconuts. In 1975 there was an expedition to Danger Island by the Joint Services (JSDI). The expedition members were taken by RFA Resurgent to Eagle Islands and then by ketch an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Chagos Bank
The Great Chagos Bank, in the Chagos Archipelago, about south of Maldives, is the largest atoll structure in the world, with a total area of . The atoll is administered by the United Kingdom through the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT). Islands Despite its enormous size, the Great Chagos Bank is largely a submarine structure. There are only four emerging reefs, mostly located on the western rim of the atoll, except for lonely Nelson Island, which lies wholly isolated in the middle of the northern fringe. These reefs have eight individual low and sandy islands, with a total land area of about . All islands and their surrounding waters are a Strict Nature Reserve since 1998. The total length of the eastern and southern expanses of the bank, as well as the reefs in its central area are wholly submerged. The islands of the Great Chagos Bank, starting clockwise from the south, are: * Danger Island (slightly more than long from North to South, by wide, land area , vege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egmont Atoll
Egmont Islands (also known as Egmont Atoll, or Six Iles) is an uninhabited atoll administered by the United Kingdom. They are one of the few emerged coral atolls that make up the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory. This small atoll lies less than 10km south of the southwestern rim of the Great Chagos Bank submerged coral reef. Its total size is 29km², including the lagoon and the fringing coral reef. The land area totals about 4km². The nearest island is Danger Island on the Great Chagos Bank, less than 30km due north. There are two passages into the lagoon along the Northern Rim, Fausse Passe in the northeast and a wider passage in the northwest. The Egmont Islands are one of the favorite anchoring spots for itinerant yachtsmen passing through the Chagos. Islands The largest island is "Île Sud-Est" (Eastern Egmont), where the settlement was located, with an area of 1.5km². While "Île Lubine" is similar in size, the other islets are smaller. All islands are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautical Chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land (topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the coastline, navigational hazards, locations of natural and human-made aids to navigation, information on tides and currents, local details of the Earth's magnetic field, and human-made structures such as harbours, buildings, and bridges. Nautical charts are essential tools for marine navigation; many countries require vessels, especially commercial ships, to carry them. Nautical charting may take the form of charts printed on paper (raster navigational charts) or computerized electronic navigational charts. Recent technologies have made available paper charts which are printed "on demand" with cartographic data that has been downloaded to the commercial printing company as recently as the night before printing. With each daily download, critica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |