|
Outwood Academy Acklam
Outwood Academy Acklam (formerly Oakfields Community College) is a comprehensive secondary school with academy status, located in the Acklam area of Middlesbrough, England. It has a mixed intake of both boy and girls, ages 11–16, with over 1000 pupils on roll . The school is operated by Outwood Grange Academies Trust, and the current principal is Graham Skidmore. The school is designated as a National Support School - meaning that it is recognised as a high performing school able to provide support to other schools. History The school was first established as Oakfields Community College in September 2011, replacing Hall Garth Community Arts College and King's Manor School in Hall Drive, Acklam. The school then relocated to new building opened in September 2012 as part of Middlesbrough's £100 million Building Schools for the Future scheme. Oakfields Community College received its first Ofsted inspection report in February 2012, and was placed in special measures after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outwood Academy Acklam Logo
Outwood may refer to: Places in the United Kingdom *Outwood, Greater Manchester, formerly a civil parish *Outwood, Somerset, a List of United Kingdom locations: On-Oz, UK location *Outwood, Surrey *Outwood, Wakefield *Outwood, Worcestershire, a neighbourhood in Chaddesley Corbett See also * Outwood Grange Academies Trust, including a list of schools * {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoral Care
Pastoral care is an ancient model of emotional, social and spiritual support that can be found in all cultures and traditions. The term is considered inclusive of distinctly non-religious forms of support, as well as support for people from religious communities. Definition Modern context Pastoral care as a contemporary term is distinguished from traditional pastoral ministry, which is religious (primarily Christian) and historically tied to Christian beliefs. Institutional pastoral care departments in Europe are increasingly not only multi-faith but inclusive in particular of non-religious, humanist approaches to providing support and comfort. Just as the theory and philosophy behind modern pastoral care is not dependent on any one set of beliefs or traditions, so pastoral care is relating gently and skillfully, with the inner world of individuals from all walks of life, and the elements that go to make up that persons sense of self, their inner resources, resilience and capac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outwood Grange Schools
Outwood may refer to: Places in the United Kingdom *Outwood, Greater Manchester, formerly a civil parish * Outwood, Somerset, a UK location *Outwood, Surrey *Outwood, Wakefield * Outwood, Worcestershire, a neighbourhood in Chaddesley Corbett Chaddesley Corbett is a village and civil parish in the Wyre Forest District of Worcestershire, England. The Anglican and secular versions of the parish include other named neighbourhoods, once farmsteads or milling places: Bluntington, Brocken ... See also * Outwood Grange Academies Trust, including a list of schools * {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academies In Middlesbrough
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Schools In Middlesbrough
Secondary may refer to: Science and nature * Secondary emission, of particles ** Secondary electrons, electrons generated as ionization products * The secondary winding, or the electrical or electronic circuit connected to the secondary winding in a transformer * Secondary (chemistry), a term used in organic chemistry to classify various types of compounds * Secondary color, color made from mixing primary colors * Secondary mirror, second mirror element/focusing surface in a reflecting telescope * Secondary craters, often called "secondaries" * Secondary consumer, in ecology * An obsolete name for the Mesozoic in geosciences * Secondary feathers, flight feathers attached to the ulna on the wings of birds Society and culture * Secondary (football), a position in American football and Canadian football * Secondary dominant in music * Secondary education, education which typically takes place after six years of primary education ** Secondary school, the type of school at the secon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
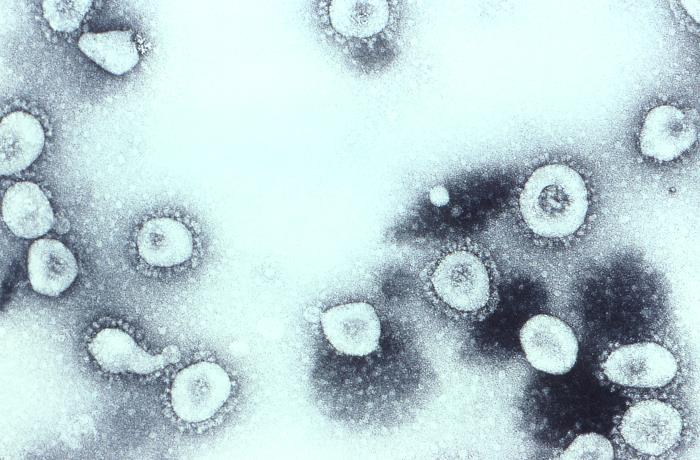
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family ''Coronaviridae'', order '' Nidovirales'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which in electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Punishment
School discipline relates to actions taken by teachers or school organizations toward students when their behavior disrupts the ongoing educational activity or breaks a rule created by the school. Discipline can guide the children's behavior or set limits to help them learn to take better care of themselves, other people and the world around them. School systems set rules, and if students break these rules they are subject to discipline. These rules may, for example, define the expected standards of school uniform, punctuality, social conduct, and work ethic. The term "discipline" is applied to the punishment that is the consequence of breaking the rules. The aim of discipline is to set limits restricting certain behaviors or attitudes that are seen as harmful or against school policies, educational norms, school traditions, etc. The focus of discipline is shifting and alternative approaches are emerging due to notably high dropout rates, disproportionate punishment upon minori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expulsion (academia)
Expulsion, also known as dismissal, withdrawal, or permanent exclusion (British English), is the permanent removal or banning of a student from a school, school district, college or university due to persistent violation of that institution's rules, or in extreme cases, for a single offense of marked severity. Colloquialisms for expulsion include being kicked out of school or sent down. Laws and procedures regarding expulsion vary between countries and states. The practice of pressuring parents to voluntarily withdraw their child from an educational institution, termed off-rolling in the UK, is comparable to expulsion. Rates of expulsion may be especially high for students of color, even when their behavioral infractions are the same as those of white children. Certain disabilities, such as autism and ADHD, also increases the risk of expulsion, despite the fact that this constitutes unlawful discrimination in many jurisdictions. By country Ireland In Ireland, a school must no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Discipline
School discipline relates to actions taken by teachers or school organizations toward students when their behavior disrupts the ongoing educational activity or breaks a rule created by the school. Discipline can guide the children's behavior or set limits to help them learn to take better care of themselves, other people and the world around them. School systems set rules, and if students break these rules they are subject to discipline. These rules may, for example, define the expected standards of school uniform, punctuality, social conduct, and work ethic. The term "discipline" is applied to the punishment that is the consequence of breaking the rules. The aim of discipline is to set limits restricting certain behaviors or attitudes that are seen as harmful or against school policies, educational norms, school traditions, etc. The focus of discipline is shifting and alternative approaches are emerging due to notably high dropout rates, disproportionate punishment upon minori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Bullying
School bullying, like bullying outside the school context, refers to one or more perpetrators who have greater physical strength or more social power than their victim repeatedly by acting aggressively toward their victim. Bullying can be verbal or physical. Bullying, with its ongoing character, is distinct from one-off types of peer conflict. Different types of school bullying include ongoing physical, emotional, and/or verbal aggression. Cyberbullying and sexual bullying are also types of bullying. Bullying even exists in higher education. There are warning signs that suggest that a child is being bullied, a child is acting as a bully, or a child has witnessed bullying at school. The cost of school violence is significant across many nations but there are educational leaders who have had success in reducing school bullying by implementing certain strategies. Some strategies used to reduce or prevent school bullying include educating the students about bullying, restricting o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, town, or neighbourhood) or in virtual space through communication platforms. Durable good relations that extend beyond immediate genealogical ties also define a sense of community, important to their identity, practice, and roles in social institutions such as family, home, work, government, society, or humanity at large. Although communities are usually small relative to personal social ties, "community" may also refer to large group affiliations such as national communities, international communities, and virtual communities. The English-language word "community" derives from the Old French ''comuneté'' (Modern French: ''communauté''), which comes from the Latin ''communitas'' "community", "public spirit" (from Latin '' communis'', "co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutor
TUTOR, also known as PLATO Author Language, is a programming language developed for use on the PLATO system at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign beginning in roughly 1965. TUTOR was initially designed by Paul Tenczar for use in computer assisted instruction (CAI) and computer managed instruction (CMI) (in computer programs called "lessons") and has many features for that purpose. For example, TUTOR has powerful answer-parsing and answer-judging commands, graphics, and features to simplify handling student records and statistics by instructors. TUTOR's flexibility, in combination with PLATO's computational power (running on what was considered a supercomputer in 1972), also made it suitable for the creation of games — including flight simulators, war games, dungeon style multiplayer role-playing games, card games, word games, and medical lesson games such as ''Bugs and Drugs'' (''BND''). TUTOR lives on today as the programming language for the Cyber1 PLATO Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |