|
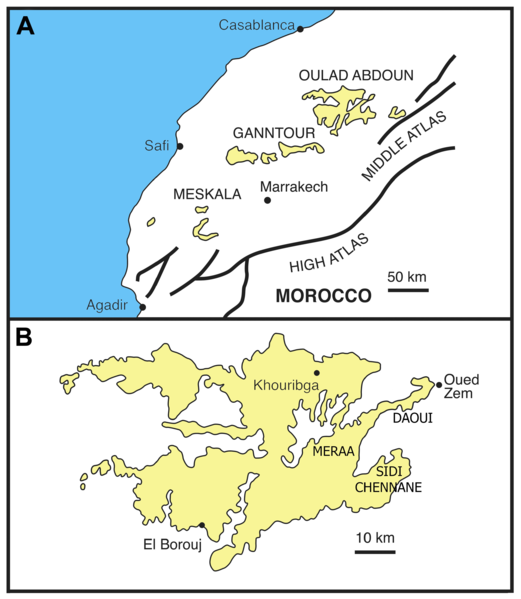
Ouled Abdoun Phosphatic Basin
The Oulad Abdoun Basin (also known as the Ouled Abdoun Basin or Khouribga Basin) is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years. Geography The Oulad Abdoun is located west of the Atlas Mountains, near the city of Khouribga. The Oulad Abdoun phosphate deposits encompass some , an area of . The Oulad Abdoun is the largest and northernmost of Morocco's major phosphate basins, which from northeast to southwest, include the Ganntour, Meskala, and Oued Eddahab (Laayoune-Baa) basins. Paleobiota The Oulad Abdoun Basin stretches from late Cretaceous to the Eocene, and contains abundant marine vertebrate fossils, including sharks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco Phosphate Basins
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bony Fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. The vast majority of fish are members of Osteichthyes, which is an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of 45 orders, and over 435 families and 28,000 species. It is the largest class of vertebrates in existence today. The group Osteichthyes is divided into the ray-finned fish ( Actinopterygii) and lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii). The oldest known fossils of bony fish are about 425 million years old, which are also transitional fossils, showing a tooth pattern that is in between the tooth rows of sharks and bony fishes. Osteichthyes can be compared to Euteleostomi. In paleontology the terms are synonymous. In ichthyology the difference is that Euteleostomi presents a cladistic view which includes the terrestrial tet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alepisauriformes
Aulopiformes is a diverse order of marine ray-finned fish consisting of some 15 extant and several prehistoric families with about 45 genera and over 230 species. The common names grinners, lizardfishes and allies, or aulopiforms are sometimes used for this group. The scientific name means "''Aulopus''-shaped", from ''Aulopus'' (the type genus) + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek ''aulós'' (αὐλός, "flute" or "pipe") + Latin ''forma'' ("external form"), the former in reference to the elongated shape of many aulopiforms.FishBase (2000) They are grouped together because of common features in the structure of their gill arches. Indeed, many authors have considered them so distinct as to warrant separation in a monotypic superorder of the Teleostei, under the name Cyclosquamata. However, monotypic taxa are generally avoided by modern taxonomists if not necessary, and in this case a distinct superorder seems indeed unwarranted: to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratodus
''Stratodus'' is a genus of giant prehistoric aulopiform fish found in Cretaceous-aged marine strata of Kansas, Alabama, Morocco, Israel, and Niger, South Dakota, Jordan. It has also been found in the Tamaguélelt Formation of Mali, dating to the Lower Eocene, indicating that ''Stratodus'' survived the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event. This sleek fish has an upper jaw filled with multiple rows of tiny teeth and was the largest aulopiform, reaching 5 meters in length. History of Discovery ''Stratodus'' was initially described by Edward Drinker Cope in Kansas during 1872, naming the type species ''S. apicalis'', and described a second species in 1877, ''S. oxypogon'', both species being assigned to the family Stratodontidae. ''S. oxypogon'' is now often considered a synonym of ''S. apicalis'', and the family was shifted from Stratodontidae to Dercetidae, but now has gone back to Stratodontidae. For the 19th and 20th centuries, ''Stratodus'' was only known from poor fossi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoegertonia
''Pseudoegertonia'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Maastrichtian age of the Cretaceous period and Danian age of the Paleocene epoch. See also * Prehistoric fish * List of prehistoric bony fish A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College Albert A. List College of Jewish Studies, known simply as List College, is the undergraduate school of the J ... References Paleocene fish of Asia Paleogene fish of North America {{paleo-bony-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnodontidae
Pycnodontidae is an extinct family of ray-finned fishes, ranging from the Triassic period until the Eocene. Genera * '' Acrotemnus'' Agassiz, 1843 * '' Anomoeodus'' Forir, 1887 * ''Athrodon'' Sauvage, 1880 * '' Callodus'' Thurmond, 1974 * ''Coccodus'' * '' Coelodus'' Haeckel * ''Gyrodus'' Agassiz, 1843 * '' Iemanja'' Wenz, 1989 * '' Macromesodon'' Blake, 1905 * '' Microdus'' * '' Micropycnodon'' Hibbard and Graffham, 1945 * '' Neoproscinetes'' De Figueiredo and Silva Santos, 1990 * '' Nonaphalagodus'' Thurmond, 1974 * '' Omphalodus'' von Meyer, 1847 * '' Paleobalistum'' * ''Paramicrodon'' Thurmond, 1974 * '' Polypsephis'' Hay, 1899 * ''Proscinetes'' Gistl, 1848 * '' Pycnodus'' Agassiz, 1835 * '' Pycnomicrodon'' Hibbard and Graffham, 1941 * '' Scalacurvichthys'' Cawley and Kriwet, 2017 * '' Sphaerodus'' Agassiz, 1843 * ''Stemmatodus ''Stemmatodus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish that lived in Europe during the Early Cretaceous approximately 129 to 125 milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enchodus Petrosus
''Enchodus'' (from el, ἔγχος , 'spear' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') is an extinct genus of aulopiform ray-finned fish related to lancetfish and lizardfish. Species of ''Enchodus'' flourished during the Late Cretaceous, and survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, persisting into the late Eocene. Taxonomy Species of ''Enchodus'' are generally classified into two different clades, the North American and the Mediterranean. It has been proposed that this distinction is the result of several isolated events between the two populations over the Late Cretaceous. Description ''Enchodus'' species were small to medium in size. One of the genus' most notable attributes are the large "fangs" at the front of the upper and lower jaws and on the palatine bones, leading to its misleading nickname among fossil hunters and paleoichthyologists, "the saber-toothed herring". These fangs, along with a long sleek body and large eyes, suggest ''Enchodus'' was a predatory specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulopiformes
Aulopiformes is a diverse order of marine ray-finned fish consisting of some 15 extant and several prehistoric families with about 45 genera and over 230 species. The common names grinners, lizardfishes and allies, or aulopiforms are sometimes used for this group. The scientific name means "''Aulopus''-shaped", from ''Aulopus'' (the type genus) + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek ''aulós'' (αὐλός, "flute" or "pipe") + Latin ''forma'' ("external form"), the former in reference to the elongated shape of many aulopiforms.FishBase (2000) They are grouped together because of common features in the structure of their gill arches. Indeed, many authors have considered them so distinct as to warrant separation in a monotypic superorder of the Teleostei, under the name Cyclosquamata. However, monotypic taxa are generally avoided by modern taxonomists if not necessary, and in this case a distinct superorder seems indeed unwarra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enchodus
''Enchodus'' (from el, ἔγχος , 'spear' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') is an extinct genus of aulopiform ray-finned fish related to lancetfish and lizardfish. Species of ''Enchodus'' flourished during the Late Cretaceous, and survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, persisting into the late Eocene. Taxonomy Species of ''Enchodus'' are generally classified into two different clades, the North American and the Mediterranean. It has been proposed that this distinction is the result of several isolated events between the two populations over the Late Cretaceous. Description ''Enchodus'' species were small to medium in size. One of the genus' most notable attributes are the large "fangs" at the front of the upper and lower jaws and on the palatine bones, leading to its misleading nickname among fossil hunters and paleoichthyologists, "the saber-toothed herring". These fangs, along with a long sleek body and large eyes, suggest ''Enchodus'' was a predatory spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bony Fish
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. The vast majority of fish are members of Osteichthyes, which is an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of 45 orders, and over 435 families and 28,000 species. It is the largest class of vertebrates in existence today. The group Osteichthyes is divided into the ray-finned fish ( Actinopterygii) and lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii). The oldest known fossils of bony fish are about 425 million years old, which are also transitional fossils, showing a tooth pattern that is in between the tooth rows of sharks and bony fishes. Osteichthyes can be compared to Euteleostomi. In paleontology the terms are synonymous. In ichthyology the difference is that Euteleostomi presents a cladistic view which includes the terrestrial tet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |