|
Ottoman Gendarmerie
The Ottoman Gendarmerie ( tr, Jandarma), also known as ''zaptı'', was a security and public order organization (a precursor to law enforcement) in the 19th-century Ottoman Empire. The first official gendarmerie organization was founded in 1869. History After the abolition of the Janissary corps of the Ottoman Empire in 1826, military organizations called ''Asâkir-i Muntazâma-i Mansûre'', ''Asâkir-i Muntazâma-i Hâssa'', and, in 1834, ''Asâkir-i Redîfe'' were established to deliver security and public order services in Anatolia and in some provinces of Rumelia. Since the term Gendarmerie was noticed only in the Assignment Decrees published in the years following the declaration of Tanzimat in 1839, it is assumed that the Gendarmerie organization was founded after that year, but the exact date of foundation has not yet been determined. Therefore, taking the June 14 of "June 14, 1869", on which ''Asâkir-i Zaptiye Nizâmnâmesi'' was adopted, June 14, 1839 was accepted as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa, Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the Ottoman wars in Europe, conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman Anatolian beyliks, beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Sule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auspicious Incident
The Auspicious Incident (or EventGoodwin, pp. 296–299.) (Ottoman Turkish: ''Vaka-i Hayriye'', "Fortunate Event" in Constantinople; ''Vaka-i Şerriyye'', "Unfortunate Incident" in the Balkans) was the forced disbandment of the centuries-old Janissary corps by Sultan Mahmud II on 15 June 1826.Kinross, pp. 456–457Shaw, pp. 19–20 Most of the 135,000 Janissaries revolted against Mahmud II, and after the rebellion was suppressed, most of them were executed, exiled or imprisoned. The disbanded Janissary corps was replaced with a more modern military force. Background The Janissaries were first created by the Ottoman Sultans in the late 14th century and were employed as household troops. Janissaries began as an elite corps made up through the devşirme system of child slavery, by which young Christian boys, notably Serbs, Albanians, Bosnians, Bulgarians, Croats, Greeks, Macedonians, Slovenians and Romanians, Armenians were taken from the Balkans, forcibly circumcised and forcibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janissary
A Janissary ( ota, یڭیچری, yeŋiçeri, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman Sultan's household troops and the first modern standing army in Europe. The corps was most likely established under sultan Orhan (1324–1362), during the Viziership of Alaeddin. Janissaries began as elite corps made up through the devşirme system of child levy, by which Christian Albanians, Romanians, Armenians, Bulgarians, Croats, Greeks and Serbs were taken, levied, subjected to circumcision and conversion to Islam, and incorporated into the Ottoman army. They became famed for internal cohesion cemented by strict discipline and order. Unlike typical slaves, they were paid regular salaries. Forbidden to marry before the age of 40 or engage in trade, their complete loyalty to the Sultan was expected. By the seventeenth century, due to a dramatic increase in the size of the Ottoman standing army, the corps' initially strict recruitment policy was relaxed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
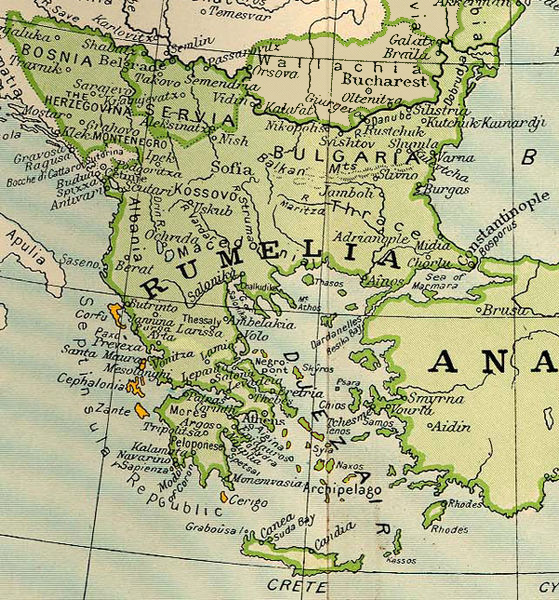
Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edict Of Gülhane
The Gülhane Hatt-ı Şerif ("Supreme Edict of the Rosehouse"; french: Hatti-Chérif de Gulhané) or Tanzimât Fermânı ("Imperial Edict of Reorganization") was a proclamation by Ottoman Sultan Abdülmecid I in 1839 that launched the Tanzimât period of reforms and reorganization in the Ottoman Empire. The 125th anniversary of the edict was depicted on a former Turkish postcard stamp. The proclamation was issued at the behest of reformist Grand Vizier Mustafa Reşid Pasha. It promised reforms such as the abolition of tax farming, reform of conscription, and guarantee of rights to all Ottoman citizens regardless of religion or ethnic group. The goal of the decree was to help modernize the empire militarily and socially so that it could compete with the Great Powers of Europe. It also was hoped the reforms would win over the disaffected parts of the empire, especially in the Ottoman controlled parts of Europe, which were largely Christian. At the time of the edict, mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzimat
The Tanzimat (; ota, تنظيمات, translit=Tanzimāt, lit=Reorganization, ''see'' nizām) was a period of reform in the Ottoman Empire that began with the Gülhane Hatt-ı Şerif in 1839 and ended with the First Constitutional Era in 1876. The Tanzimat era began with the purpose, not of radical transformation, but of modernization, desiring to consolidate the social and political foundations of the Ottoman Empire. It was characterised by various attempts to modernise the Ottoman Empire and to secure its territorial integrity against internal nationalist movements and external aggressive powers. The reforms encouraged Ottomanism among the diverse ethnic groups of the Empire and attempted to stem the tide of the rise of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire. Historian Hans-Lukas Kieser has argued that the reforms led to "the rhetorical promotion of equality of non-Muslims with Muslims on paper vs. the primacy of Muslims in practice"; other historians have argued that the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878 ( tr, 93 Harbi, lit=War of ’93, named for the year 1293 in the Islamic calendar; russian: Русско-турецкая война, Russko-turetskaya voyna, "Russian–Turkish war") was a conflict between the Ottoman Empire and a coalition led by the Russian Empire, and including Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, and Montenegro. Fought in the Balkans and in the Caucasus, it originated in emerging 19th century Balkan nationalism. Additional factors included the Russian goals of recovering territorial losses endured during the Crimean War of 1853–56, re-establishing itself in the Black Sea and supporting the political movement attempting to free Balkan nations from the Ottoman Empire. The Russian-led coalition won the war, pushing the Ottomans back all the way to the gates of Constantinople, leading to the intervention of the western European great powers. As a result, Russia succeeded in claiming provinces in the Caucasus, namely Kars and Batum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed Said Pasha
Mehmed Said Pasha ( ota, محمد سعيد پاشا ; 1838–1914), also known as Küçük Said Pasha ("Said Pasha the Younger") or Şapur Çelebi or in his youth as Mabeyn Başkatibi Said Bey, was an Ottoman monarchist, senator, statesman and editor of the Turkish newspaper ''Jerid-i-Havadis''. He was among the statesmen who were disliked by the CUP, the political party which came to power after the Ottoman coup d'état of 1913. Biography According to his contemporary Petre Kharischirashvili, he was of Georgian descent. He became first secretary to Sultan Abdul Hamid II shortly after the Sultan's accession, and is said to have contributed to the realizations of his majesty's design of concentrating power in his own hands; later he became successively minister of the interior and then governor of Bursa, reaching the high post of grand vizier in 1879. He was grand vizier seven more times under Abdul Hamid II, and once under his successor, Mehmed V. He was known for hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Turk Revolution
The Young Turk Revolution (July 1908) was a constitutionalist revolution in the Ottoman Empire. The Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), an organization of the Young Turks movement, forced Sultan Abdul Hamid II to restore the Ottoman Constitution and recall the parliament, which ushered in multi-party politics within the Empire. From the Young Turk Revolution to the Empire's end marks the Second Constitutional Era of the Ottoman Empire's history. More than three decades earlier, in 1876, constitutional monarchy had been established under Abdul Hamid during a period of time known as the First Constitutional Era, which lasted for only two years before Abdul Hamid suspended it and restored autocratic powers to himself. The revolution began with CUP member Ahmed Niyazi's flight into the Albanian highlands. He was soon joined by İsmail Enver and Eyub Sabri. They networked with local Albanians and utilized their connections within the Salonica based Third Army to instigat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the Spanish flu, 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising French Third Republic, France, Russia, and British Empire, Britain) and the Triple A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish War Of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by the Turkish National Movement after parts of the Ottoman Empire were occupied and partitioned following its defeat in World War I. These campaigns were directed against Greece in the west, Armenia in the east, France in the south, loyalists and separatists in various cities, and British and Ottoman troops around Constantinople (İstanbul). The ethnic demographics of the modern Turkish Republic were significantly impacted by the earlier Armenian genocide and the deportations of Greek-speaking, Orthodox Christian Rum people. The Turkish nationalist movement carried out massacres and deportations to eliminate native Christian populations—a continuation of the Armenian genocide and other ethnic cleansing operations during World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |