|
Otto Wilhelm Madelung
Otto Wilhelm Madelung (May 15, 1846 – July 22, 1926) was a German surgeon who was a native of Gotha Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the .... His son, physicist Erwin Madelung (1881–1972), discovered the Madelung constant. Academic career Madelung was born in Gotha. In 1869 he received his medical doctorate from the University of Tübingen, afterwards being assigned to a military hospital during the Franco-Prussian War. He later served as a surgical assistant in Bonn, and in 1873–74 worked as an assistant at the pathology, pathological clinic of Eduard von Rindfleisch, Georg Eduard von Rindfleisch (1836–1908). In 1874 he visited Great Britain and the United States. In 1881 he became an assistant professor of surgery at the University of Bonn, followed by profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Wilhelm Madelung
Otto Wilhelm Madelung (May 15, 1846 – July 22, 1926) was a German surgeon who was a native of Gotha Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the .... His son, physicist Erwin Madelung (1881–1972), discovered the Madelung constant. Academic career Madelung was born in Gotha. In 1869 he received his medical doctorate from the University of Tübingen, afterwards being assigned to a military hospital during the Franco-Prussian War. He later served as a surgical assistant in Bonn, and in 1873–74 worked as an assistant at the pathology, pathological clinic of Eduard von Rindfleisch, Georg Eduard von Rindfleisch (1836–1908). In 1874 he visited Great Britain and the United States. In 1881 he became an assistant professor of surgery at the University of Bonn, followed by profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Symmetric Lipomatosis
Benign symmetric lipomatosis is a skin condition characterized by extensive symmetric fat deposits in the head, neck, and shoulder girdle area. The German surgeon Otto Wilhelm Madelung was the first to give a detailed description of the disorder. This condition is very rare, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 25,000, and affects males up to 30 times more frequently than females. Cause The cause of the disease remains unknown, but its incidence strongly correlates with alcohol use disorder; abstinence from alcohol prevents disease progression. Defects in the adrenergic-stimulated lipolysis and accumulation of embryological brown fat have also been reported. Cosmetic disfigurement due to the fat deposition in the cervicothoracic region results in a "pseudoathletic appearance", resembling the Italian statue ''Warrior of Capestrano'' and carvings of Queen of Punt (Egypt). Treatment Traditionally the treatment is mainly surgical, consisting of the removal of the lipomas, although rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Girdle
The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species (such as the dog and the horse) have only the scapula. The pectoral girdles are to the upper limbs as the pelvic girdle is to the lower limbs; the girdles are the parts of the appendicular skeleton that anchor the appendages to the axial skeleton. In humans, the only true anatomical joints between the shoulder girdle and the axial skeleton are the sternoclavicular joints on each side. No anatomical joint exists between each scapula and the rib cage; instead the muscular connection or physiological joint between the two permits great mobility of the shoulder girdle compared to the compact pelvic girdle; because the upper limb is not usually involved in weight bearing, its stabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipose
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body. Far from being hormonally inert, adipose tissue has, in recent years, been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is also implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndrome, a constellation of diseases including, but not limited to, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipomatosis
Lipomatosis is believed to be an autosomal dominant condition in which multiple lipomas are present on the body. Many discrete, encapsulated lipomas form on the trunk and extremities, with relatively few on the head and shoulders. In 1993, a genetic polymorphism within lipomas was localized to chromosome 12q15, where the HMGIC gene encodes the high-mobility-group protein isoform I-C. This is one of the most commonly found mutations in solitary lipomatous tumors but lipomas often have multiple mutations. Reciprocal translocations involving chromosomes 12q13 and 12q14 have also been observed within. Although this condition is benign, it can sometimes be very painful depending on location of the lipomas. Some patients who are concerned with cosmetics seek removal of individual lipomas. Removal can include simple excision, endoscopic removal, or liposuction. Other entities which are accompanied by multiple lipomas include Proteus syndrome, Cowden syndrome and related disorders due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-François Malgaigne
Joseph-François Malgaigne (14 February 1806 – 17 October 1865) was a French surgeon and medical historian born in Charmes-sur-Moselle, Vosges. He studied medicine in Paris, and was later a surgeon of Parisian hospitals, including Hôpitals Saint-Louis, Charité and Beaujon. At the Hôpital Saint-Louis he was a colleague of Auguste Nélaton (1807-1873). Malgaigne was father-in-law to surgeon Léon Clément Le Fort (1829-1893). In 1846 he became a member of the Académie de Médecine. Malgaigne is known for his work with bone fractures and dislocations, specializing in orthopedic surgery of the knee, hip and shoulder. In 1834 he published ''Manuel de medecine operatoire'', an influential work on surgical techniques. This book was later translated into several languages. In 1843 Malgaigne, together with Germanicus Mirault designed a flap transposition procedure to close cleft lips.Mirault G. Deux lettres sur l'operation du bec-delievre. J Chir. 1844;2:257. As an advocate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Nélaton
Auguste Nélaton (17 June 1807 – 21 September 1873) was a French physician and surgeon. Born in Paris, he began studying medicine in 1828 and graduated as an MD in 1836 with a thesis on the effects of tuberculosis on the bones. Three years later, he became an '' agrégé'' at the Hôpital Saint-Louis after his publication of ''On the treatment of breast tumors''. From 1851 to 1867, he was a full professor, a post he abandoned when he became the personal surgeon of Napoleon III. Ramón Emeterio Betances— Puerto Rican pro-independence leader, surgeon and Légion d'honneur laureate—was one of Nélaton's prominent students.Ojeda Reyes, Félix (2001) ''El Desterrado de París'', Ediciones Puerto, , pp. 20, 29–30 In 1867, Nélaton was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. In 1868, Nélaton was appointed Imperial Senator. Nélaton worked in plastic surgery. He was the first to re-emphasize ligature of the two ends of arteries in hemorrhages first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume Dupuytren
Baron Guillaume Dupuytren (; 5 October 1777 – 8 February 1835) was a French anatomist and military surgeon. Although he gained much esteem for treating Napoleon Bonaparte's hemorrhoids, he is best known today for his description of Dupuytren's contracture which is named after him and on which he first operated in 1831 and published—in ''The Lancet'', in 1834. Birth and education Guillaume Dupuytren was born in the town of Pierre-Buffière in the present-day department of Haute-Vienne. He studied medicine in Paris at the newly established École de Médecine and was appointed prosector, by competition, when only eighteen years of age. His early studies were directed chiefly to anatomical pathology. In 1803 he was appointed assistant surgeon at the Hôtel-Dieu and in 1811 he became professor of operative surgery in succession to Raphael Bienvenu Sabatier. In 1816 he was appointed to the Read chair of clinical surgery and became head surgeon at general the Hôtel-Dieu. He held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
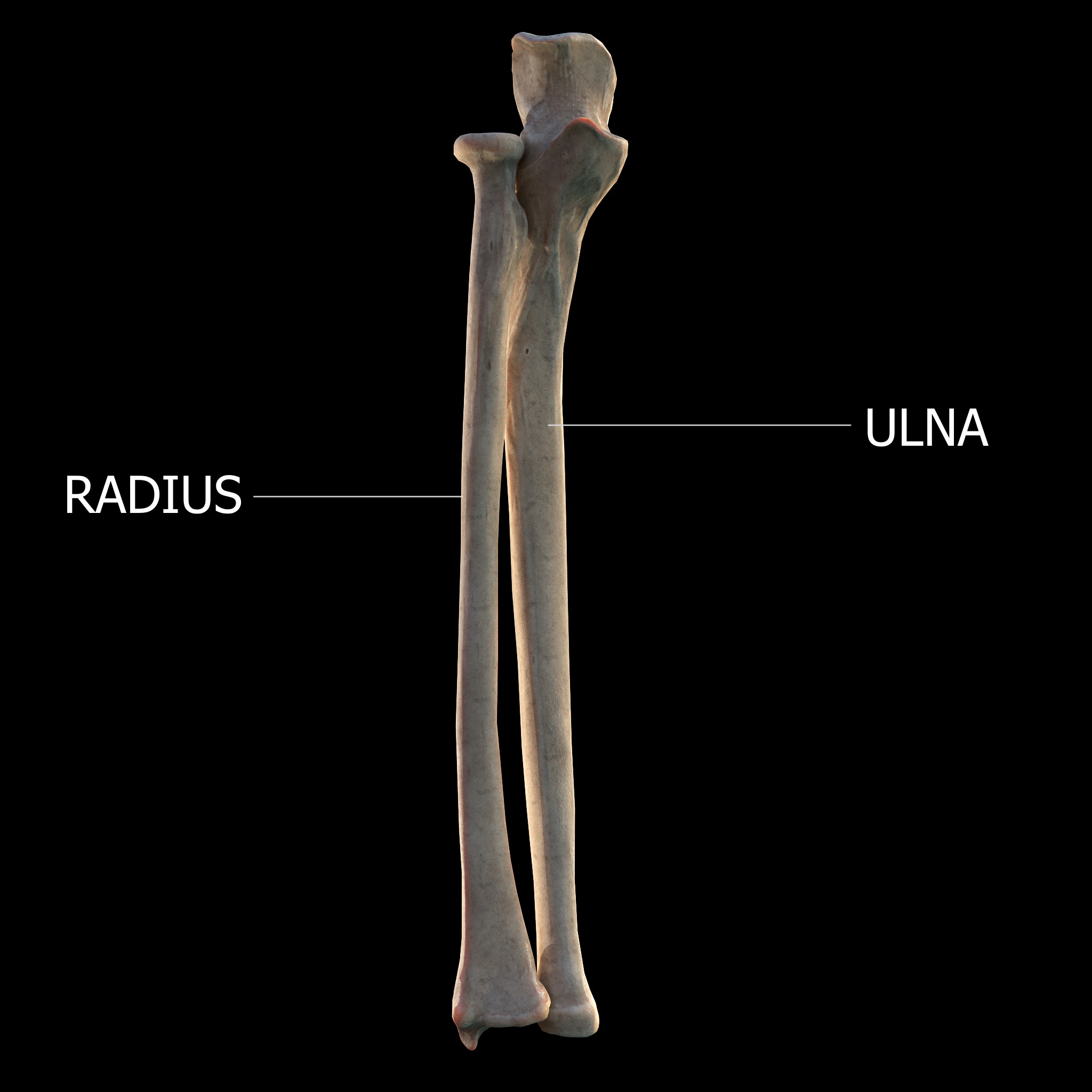
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The trabeculae of the spongy tissue are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |