|
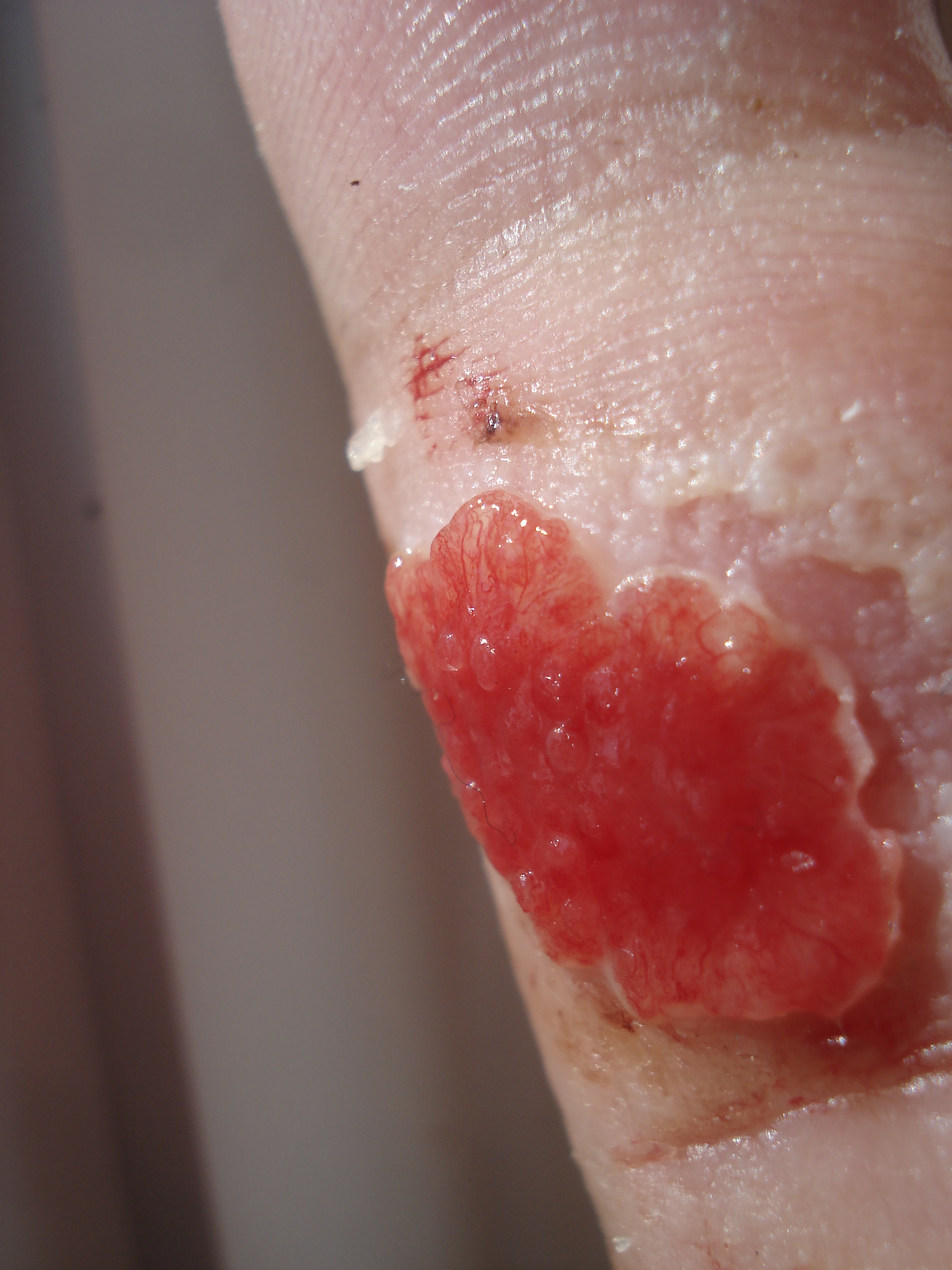
Otic Polyp
An otic polyp is a benign proliferation of chronic inflammatory cells associated with granulation tissue, in response to a longstanding inflammatory process of the middle ear. Signs and symptoms Patients usually present with otorrhea, conductive hearing loss, and otalgia, while bleeding and a sensation of a mass are much less common. Diagnosis Imaging Although imaging is not required to yield a diagnosis, it may be obtained to exclude other disorders, such as a concurrent cholesteatoma. Pathology By gross description, there is usually a solitary, polypoid, reddish mass behind an intact ear drum (tympanic membrane). The tissue is often friable, measuring <2 cm in most cases. All tissue should be processed in order to exclude a concurrent cholesteatoma. By microscopic exam, the polypoid appearance is maintained, showing a granulation-type tissue reaction with edematous stroma and a rich investment by capillaries. The surface of the polyp is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ENT Surgery
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ''rhino-'' + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulation Tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in pyogenic granulomas and pulp polyps. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and new thin-walled, delicate capillaries (angiogenesis), infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix. Appearance During the migratory phase of wound healing, granulation tissue is: * light red or dark pink, being perfused with new capillary loops or "buds"; * soft to the touch; * moist; * bumpy (granular) in appearance, due to punctate hemorrhages; * pulsatile on palpation; * painless when healthy; Structure Granulation tissue is composed of tissue matrix supporting a variety of cell types, most of which can be associated with one of the following functions: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear). The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the fluid and membranes of the inner ear. The hollow space of the middle ear is also known as the tympanic cavity and is surrounded by the tympanic part of the temporal bone. The auditory tube (also known as the Eustachian tube or the pharyngotympanic tube) joins the tympanic cavity with the nasal cavity (nasopharynx), allowing pressure to equalize between the middle ear and throat. The primary function of the middle ear is to efficiently transfer acoustic energy from compression waves in air to fluid–membrane waves within the cochlea. Structure Ossicles The middle ear contains three tiny bones known as the ossicles: '' malleus'', '' incus'', and ''stapes''. The ossicles were given their Latin names for their distinctive shapes; they ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otorrhea
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. The other main type is otitis media with effusion (OME), typically not associated with symptoms, although occasionally a feeling of fullness is described; it is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear which may persist for weeks or months often after an episode of acute otitis media. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation that results in a perforated tympanic membrane with discharge from the ear for more than six weeks. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three types of otitis media may be associated with hearing loss. If children with hearing loss due to OME do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to Hearing, hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to Language acquisition, acquire spoken language, and in adults it can create difficulties with social interaction and at work. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Presbycusis, Hearing loss related to age usually affects both ears and is due to cochlear hair cell loss. In some people, particularly older people, hearing loss can result in loneliness. Deafness, Deaf people usually have little to no hearing. Hearing loss may be caused by a number of factors, including: genetics, ageing, Noise-induced hearing loss, exposure to noise, some infections, birth complications, trauma to the ear, and certain medications or toxins. A common condition that results in hearing loss is chronic ear infections. Certain infections during pregnancy, such as cyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otalgia
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is felt. Most causes of ear pain are non-life-threatening. Primary ear pain is more common than secondary ear pain, and it is often due to infection or injury. The conditions that cause secondary (referred) ear pain are broad and range from temporomandibular joint syndrome to inflammation of the throat. In general, the reason for ear pain can be discovered by taking a thorough history of all symptoms and performing a physical examination, without need for imaging tools like a CT scan. However, further testing may be needed if red flags are present like hearing loss, dizziness, ringing in the ear or unexpected weight loss. Management of ear pain depends on the cause. If there is a bacterial infection, antibiotics are sometimes recommended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process. Cholesteatomas are not cancerous as the name may suggest, but can cause significant problems because of their erosive and expansile properties. This can result in the destruction of the bones of the middle ear ( ossicles), as well as growth through the base of the skull into the brain. They often become infected and can result in chronically draining ears. Treatment almost always consists of surgical removal. Signs and symptoms Other more common conditions (e.g. otitis externa) may also present with these symptoms, but cholesteatoma is much more serious and should not be overlooked. If a patient presents to a doctor with ear discharge and hearing loss, the doctor should consider cholesteatoma until the disease is definitely excluded. Other less common symptoms (all less than 15%) of cholesteatoma may include pain, balance disruption, tinnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * '' Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts. There are four subtypes – embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, and spindle cell/sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma. Embryonal, and alveolar are the main groups, and these types are the most common soft tissue sarcomas of childhood and adolescence. The pleomorphic type is usually found in adults. It is generally considered to be a disease of childhood, as the vast majority of cases occur in those below the age of 18. It is commonly described as one of the small-blue-round-cell tumors of childhood due to its appearance on an H&E stain. Despite being relatively rare, it accounts for approximately 40% of all recorded soft tissue sarcomas. RMS can occur in any soft tissue site in the body, but is primarily found in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extramedullary Plasmacytoma
Plasmacytoma is a plasma cell dyscrasia in which a plasma cell tumour grows within soft tissue or within the axial skeleton. The International Myeloma Working Group lists three types: solitary plasmacytoma of bone (SPB); extramedullary plasmacytoma (EP), and multiple plasmacytomas that are either primary or recurrent. The most common of these is SPB, accounting for 3–5% of all plasma cell malignancies. SPBs occur as lytic lesions within the axial skeleton and extramedullary plasmacytomas most often occur in the upper respiratory tract (85%), but can occur in any soft tissue. Approximately half of all cases produce paraproteinemia. SPBs and extramedullary plasmacytomas are mostly treated with radiotherapy, but surgery is used in some cases of extramedullary plasmacytoma. The skeletal forms frequently progress to multiple myeloma over the course of 2–4 years. Due to their cellular similarity, plasmacytomas have to be differentiated from multiple myeloma. For SPB and extramedul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Adenoma Middle Ear
Neuroendocrine adenoma middle ear (NAME) is a tumor which arises from a specific anatomic site: middle ear. NAME is a benign glandular neoplasm of middle ear showing histologic and immunohistochemical neuroendocrine and mucin-secreting differentiation (biphasic or dual differentiation). Classification Neuroendocrine adenoma of the middle ear has gone by several different names, including middle ear adenoma, carcinoid tumor, amphicrine adenoma, adenocarcinoid, and adenomatoid tumor of middle ear. The various names have created some confusion about this uncommon middle ear tumor. Regardless of the name applied, the ''middle ear'' anatomic site must be known or confirmed. Signs and symptoms This uncommon tumor accounts for less than 2% of all ear tumors. While patients present with symptoms related to the middle ear cavity location of the tumor, the tumor may expand into the adjacent structures (external auditory canal, mastoid bone, and eustachian tube). Patients come to clinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |