|
Orthograde Posture
Orthograde is a term derived from Greek ὀρθός, ''orthos'' ("right", "true", "straight") + Latin ''gradi'' (to walk) that describes a manner of walking which is upright, with the independent motion of limbs. Both New and Old World monkeys are primarily arboreal, and they have a tendency to walk with their limbs swinging in parallel to one another. This differs from the manner of walking demonstrated by the apes. Chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans and humans, when walking, walk upright, and their limbs swing in opposition to one another for balance (unlike monkeys, apes lack a tail to use for balance). Disadvantages related to upright walking do exist for primates, since their primary mode of locomotion is quadrupedalism. This upright locomotion is called "orthograde posture". Orthograde posture in humans was made possible through millions of years of evolution. In order to walk upright with maximum efficiency, the skull, spine, pelvis, lower limbs, and feet all underwent evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propithecus Bipedal Gallop
A sifaka (; ) is a lemur of the genus ''Propithecus'' from the family Indriidae within the order Primates. The name of their family is an onomatopoeia of their characteristic "shi-fak" alarm call. Like all lemurs, they are found only on the island of Madagascar. All species of sifakas are threatened, ranging from endangered to critically endangered. Anatomy and physiology Sifakas are medium-sized indrids with a head and body length of and a weight of . Their tail is just as long as their body, which differentiates them from the Indri. Their fur is long and silky, with coloration varying by species from yellowish-white to blackish-brown. Their round, hairless face is always black. As with all lemurs, the sifaka has special adaptations for grooming, including a toilet-claw on its second toe and a toothcomb. Sifakas move by vertical clinging and leaping, meaning they maintain an upright position leaping from tree trunk to tree trunk and moving along branches. They are skillf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orrorin
''Orrorin tugenensis'' is a postulated early species of Homininae, estimated at and discovered in 2000. It is not confirmed how ''Orrorin'' is related to modern humans. Its discovery was used to argue against the hypothesis that australopithecines are human ancestors, although this remains the most prevalent hypothesis of human evolution as of 2012. The name of genus ''Orrorin'' (plural ''Orroriek'') means "original man" in Tugen, and the name of the only classified species, ''O. tugenensis'', derives from Tugen Hills in Kenya, where the first fossil was found in 2000. As of 2007, 20 fossils of the species have been found. Fossils The 20 specimens found as of 2007 are believed to be from at least five individuals. They include: the posterior part of a mandible in two pieces; a symphysis and several isolated teeth; three fragments of femora; a partial humerus; a proximal phalanx; and a distal thumb phalanx. ''Orrorin'' had small teeth relative to its body size. Its dentition d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronograde
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor'' for "four", and ''pes'', ''pedis'' for "foot"). Quadruped animals are found among both vertebrates and invertebrates. Quadrupeds vs. tetrapods Although the words ‘quadruped’ and ‘tetrapod’ are both derived from terms meaning ‘four-footed’, they have distinct meanings. A tetrapod is any member of the taxonomic unit Tetrapoda (which is defined by descent from a specific four-limbed ancestor), whereas a quadruped actually uses four limbs for locomotion. Not all tetrapods are quadrupeds and not all entities that could be described as ‘quadrupedal’ are tetrapods. This last meaning includes certain artificial objects; almost all quadruped ''organisms'' are tetrapods (with the exception of some raptorial arthropods adapted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipedalism
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' and ''pes'' 'foot'). Types of bipedal movement include walking, running, and hopping. Several groups of modern species are habitual bipeds whose normal method of locomotion is two-legged. In the Triassic period some groups of archosaurs (a group that includes crocodiles and dinosaurs) developed bipedalism; among the dinosaurs, all the early forms and many later groups were habitual or exclusive bipeds; the birds are members of a clade of exclusively bipedal dinosaurs, the theropods. Within mammals, habitual bipedalism has evolved multiple times, with the macropods, kangaroo rats and mice, springhare, hopping mice, pangolins and hominin apes ( australopithecines, including humans) as well as various other extinct groups evolving the tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spine. Similarly, kyphosis historically refers to ''abnormal'' convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacral regions is also termed ''kyphosis'' or ''kyphotic''. The term comes from the Greek lordōsis, from ''lordos'' ("bent backward"). Lordosis in the human spine makes it easier for humans to bring the bulk of their mass over the pelvis. This allows for a much more efficient walking gait than that of other primates, whose inflexible spines cause them to resort to an inefficient forward leaning "bent-knee, bent-waist" gait. As such, lordosis in the human spine is considered one of the primary physiological adaptations of the human skeleton that allows for human gait to be as energeticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of Zygapophysial joint, facets on the sides of the bodies for Articulation (anatomy), articulation with the head of rib, heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercle (rib), tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalization Quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed to predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regression on a range of reference species. It has been used as a proxy for intelligence and thus as a possible way of comparing the intelligences of different species. For this purpose it is a more refined measurement than the raw brain-to-body mass ratio, as it takes into account allometric effects. Expressed as a formula, the relationship has been developed for mammals and may not yield relevant results when applied outside this group. Perspective on intelligence measures Encephalization quotient was developed in an attempt to provide a way of correlating an animal's physical characteristics with perceived intelligence. It improved on the previous attempt, brain-to-body mass ratio, so it has persisted. Subsequent work, notably Roth, found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taung Child
The Taung Child (or Taung Baby) is the fossilised skull of a young ''Australopithecus africanus''. It was discovered in 1924 by quarrymen working for the Northern Lime Company in Taung, South Africa. Raymond Dart described it as a new species in the journal ''Nature'' in 1925. The Taung skull is in repository at the University of Witwatersrand. Dean Falk, a specialist in brain evolution, has called it "the most important anthropological fossil of the twentieth century." History Background In the early 20th century, the workers at limestone quarries in Southern Africa routinely uncovered fossils from the tufa formations that they mined. The tufa did not form consistently, and over time cavities were left open and they became beneficial areas for animals to take shelter in. As a result, many bones began to build up in these areas. These areas were mostly sandstone, and they stood in the way of successful mining. So, miners would use explosives to clear these areas, and disca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rib Cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the human skeleton. A typical human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. Together with the skin and associated fascia and muscles, the thoracic cage makes up the thoracic wall and provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back. The rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration ( diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
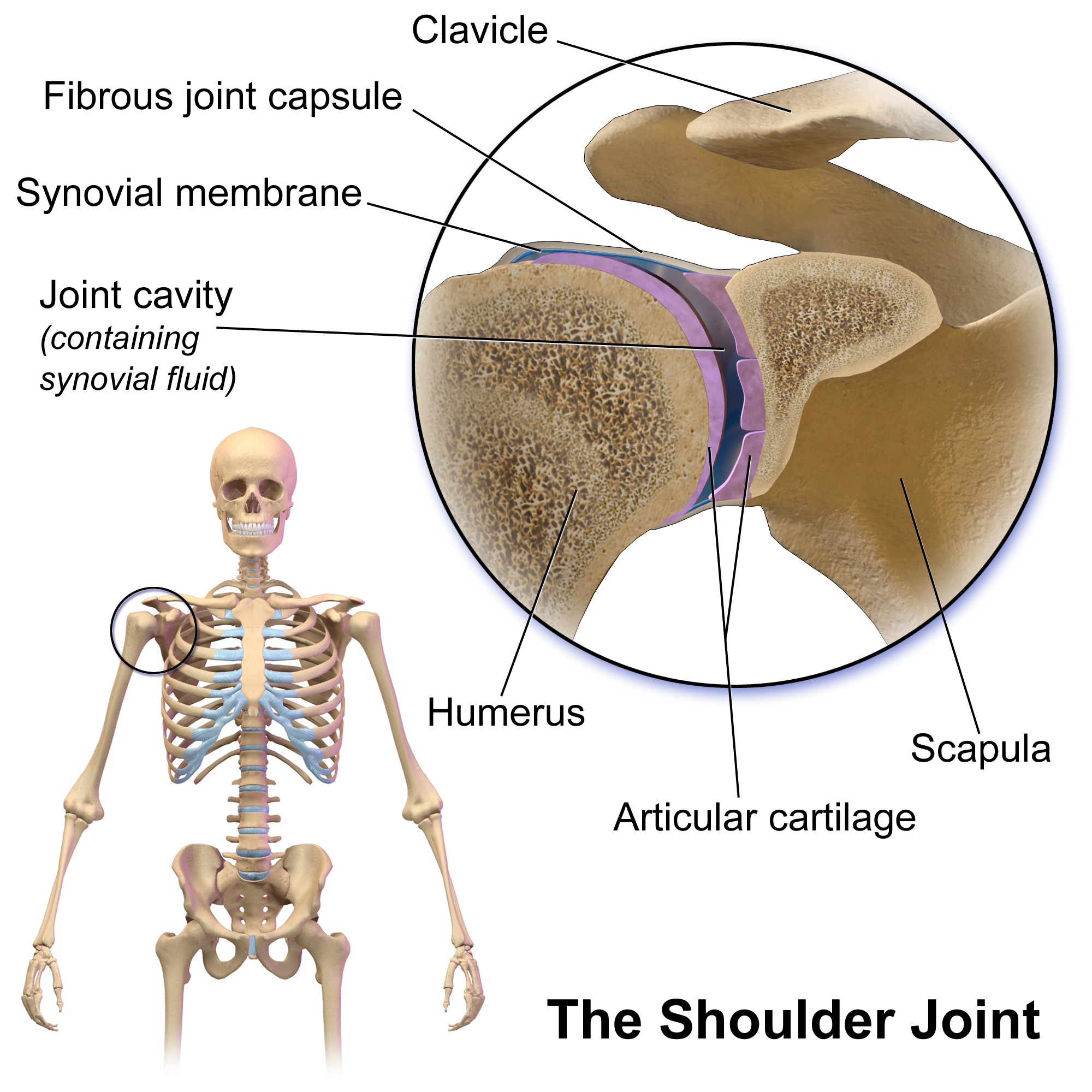
Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hominini
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas). The term was originally introduced by Camille Arambourg (1948). Arambourg combined the categories of ''Hominina'' and ''Simiina'' due to Gray (1825) into his new subtribe. Traditionally, chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans were grouped together as pongids. Since Gray's classification, evidence has accumulated from genetic phylogeny confirming that humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas are more closely related to each other than to the orangutan. The former pongids were reassigned to the subfamily Hominidae ("great apes"), which already included humans, but the details of this reassignment remain contested; within Hominini, not every source excludes gorillas, and not every source includes chimpanzees. Humans are the only extant species in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardipithecus
''Ardipithecus'' is a genus of an extinct hominine that lived during the Late Miocene and Early Pliocene epochs in the Afar Depression, Ethiopia. Originally described as one of the earliest ancestors of humans after they diverged from the chimpanzees, the relation of this genus to human ancestors and whether it is a hominin is now a matter of debate. Two fossil species are described in the literature: '' A. ramidus'', which lived about 4.4 million years ago during the early Pliocene, and '' A. kadabba'', dated to approximately 5.6 million years ago (late Miocene). Initial behavioral analysis indicated that ''Ardipithecus'' could be very similar to chimpanzees, however more recent analysis based on canine size and lack of canine sexual dimorphism indicates that ''Ardipithecus'' was characterised by reduced aggression, and that they more closely resemble bonobos. Some analyses describe ''Australopithecus'' as being sister to ''Ardipithecus ramidus'' specifically. This mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |