|
Original Keetoowah Society
The Original Keetoowah Society is a 21st-century Cherokee religious organization dedicated to preserving the culture and teachings of the Keetoowah Nighthawk Society ( chr, ᎩᏚᏩ ᎤᎾᏙᏢᎯ) in Oklahoma. It has been described as the surviving core of the Cherokee movement of religious nationalism originally led by Redbird Smith in the mid-nineteenth century. After the Cherokee were forced to move to Indian Territory, various groups associated with the Keetoowah Society worked to preserve traditional culture and its teachings. The group now known as ''The Original Keetoowah Society'' is believed to have developed from an early 20th-century group known as the Keetoowah Nighthawk Society (or the Nighthawk Keetoowahs). One of the earliest records of the Keetoowah Movement post-Indian Removal is dated August 15, 1888. Origin of name The term Keetoowah has been applied to various groups of Cherokee, and is sometimes thought to be an alternative term that the early indigenou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
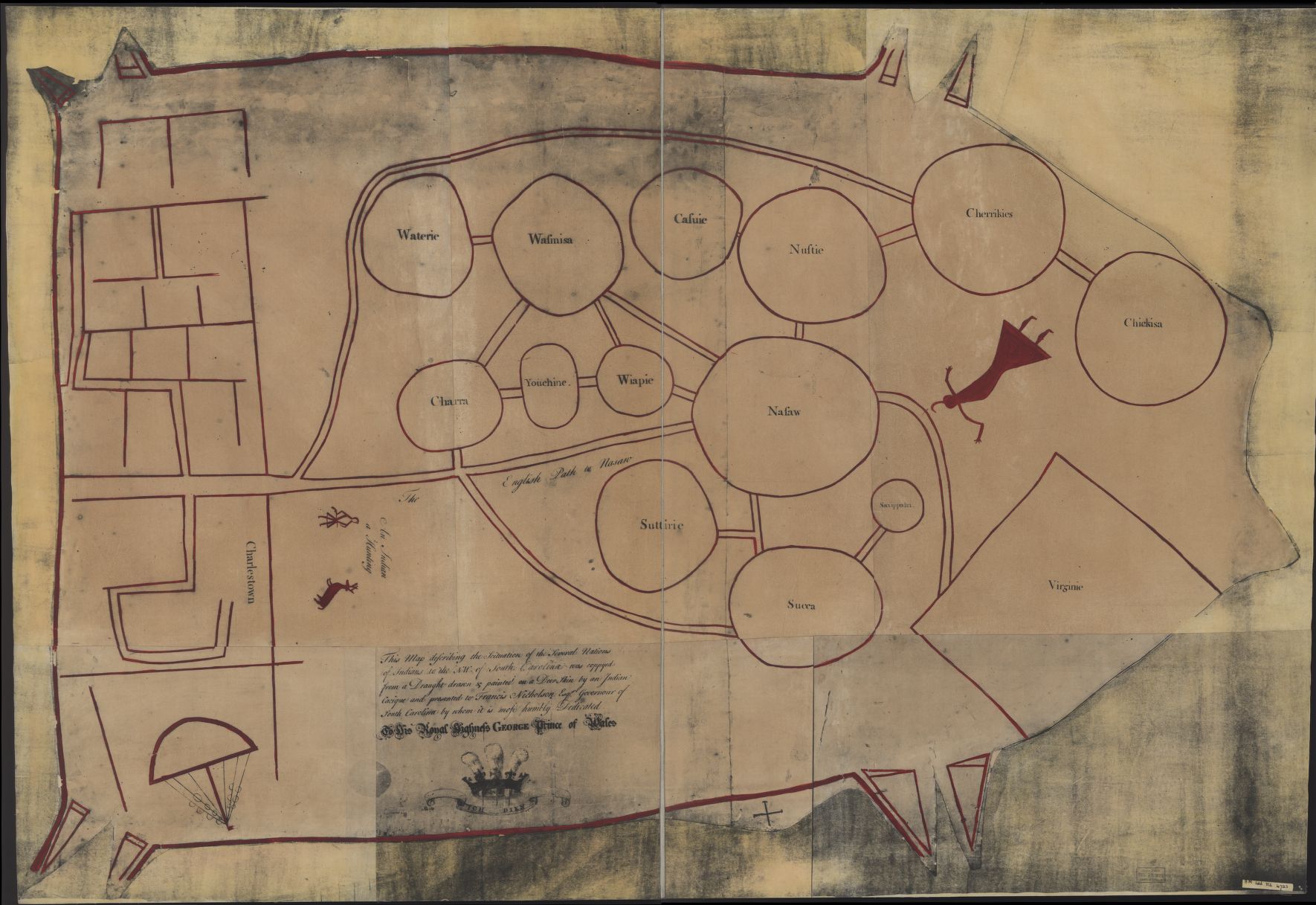
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia, and northeastern Alabama. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that the origin of the proto-Iroquoian language was likely the Appalachian region, and the split betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee Nation V
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia, and northeastern Alabama. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that the origin of the proto-Iroquoian language was likely the Appalachian region, and the split between North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee Culture
Cherokee society ( in the Cherokee language) is the culture and societal structures shared by the Cherokee Peoples. It can also mean the extended family or village. The Cherokee are Indigenous to the mountain and inland regions of the southeastern United States in the areas of present-day North Carolina, and historically in South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, and Georgia. The majority of the tribe was forcefully removed to Indian Territory in Oklahoma in the 1830s. The three federally recognized Cherokee tribes are: the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma (CNO), the United Keetoowah Band of Cherokee Indians (UKB) also in Oklahoma, and the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI) consisting of the Cherokee who remained in North Carolina. The three Tribes The community of the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians' headquarters are in the town of Cherokee, North Carolina, on the Qualla Boundary, while the Cherokee Nation and the United Keetoowah Band are both centered in Tahlequah, Oklaho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert J
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Richardson
William Blaine Richardson III (born November 15, 1947) is an American politician, author, and diplomat who served as the 30th governor of New Mexico from 2003 to 2011. He was also the U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations and Energy Secretary in the Clinton administration, a U.S. Congressman, chairman of the 2004 Democratic National Convention, and chairman of the Democratic Governors Association. In December 2008, Richardson was nominated for the cabinet-level position of Secretary of Commerce in the first Obama administration but withdrew a month later, as he was being investigated for possible improper business dealings in New Mexico. Although the investigation was later dropped, it was seen to have damaged Richardson's career as his second and final term as New Mexico governor concluded. Richardson has occasionally provided advice on diplomatic issues pertaining to North Korea and has visited the nation on several occasions, including efforts to release American detainee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reorganization Act
The Indian Reorganization Act (IRA) of June 18, 1934, or the Wheeler–Howard Act, was U.S. federal legislation that dealt with the status of American Indians in the United States. It was the centerpiece of what has been often called the "Indian New Deal". The major goal was to reverse the traditional goal of cultural assimilation of Native Americans into American society and to strengthen, encourage and perpetuate the tribes and their historic Native American cultures in the United States. The Act also restored to Indians the management of their assets—land and mineral rights—and included provisions intended to create a sound economic foundation for the residents of Indian reservations. The law did not apply to the territories—including what would become the state of Hawaii, and the state of Alaska—nor did they apply to the state of Oklahoma, which until McGirt v. Oklahoma, the McGirt case was regarded as having dissolved its reservations. In 1936 however, the rights of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, meaning that their members can marry one another. Clans preceded more centralized forms of community organization and government, and exist in every country. Members may identify with a coat of arms or other symbol to show that they are an . Kinship-based groups may also have a symbolic ancestor, whereby the clan shares a "stipulated" common ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Etymology The English word "clan" is derived from old Irish meaning "children", "offspring", "progeny" or "descendants"; it is not from the word for "family" or "clan" in either Irish or Scottish Gaelic. According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the word "clan" was introduced into English in around 1425, as a descriptive label for the organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oneida People
The Oneida people (autonym: Onʌyoteˀa·ká·, Onyota'a:ka, ''the People of the Upright Stone, or standing stone'', ''Thwahrù·nęʼ'' in Tuscarora) are a Native American tribe and First Nations band. They are one of the five founding nations of the Iroquois Confederacy in the area of upstate New York, particularly near the Great Lakes. Originally the Oneida lived in what is now central New York, particularly around Oneida Lake and Oneida County. Today the Oneida have four federally recognized nations: the Oneida Indian Nation in New York, the Oneida Nation in and around Green Bay, Wisconsin, in the United States; and two in Ontario, Canada: Oneida at Six Nations of the Grand River and Oneida Nation of the Thames in Southwold. People of the Standing Stone The name Oneida is derived from the English pronunciation of ''Onyota'a:ka'', the people's name for themselves. ''Onyota'a:ka'' means "People of the Standing Stone". This identity is based on an ancient legend. The One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester Polk Cornelius
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Locality"; downloaded froCheshire West and Chester: Population Profiles, 17 May 2019 it is the most populous settlement of Cheshire West and Chester (a unitary authority which had a population of 329,608 in 2011) and serves as its administrative headquarters. It is also the historic county town of Cheshire and the second-largest settlement in Cheshire after Warrington. Chester was founded in 79 AD as a " castrum" or Roman fort with the name Deva Victrix during the reign of Emperor Vespasian. One of the main army camps in Roman Britain, Deva later became a major civilian settlement. In 689, King Æthelred of Mercia founded the Minster Church of West Mercia, which later became Chester's first cathedral, and the Angles extended and stren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawes Commission
The United States, American Dawes Commission, named for its first chairman Henry L. Dawes, was authorized under a rider to an Indian Office appropriation bill, March 3, 1893. Its purpose was to convince the Five Civilized Tribes to agree to cede tribal title of Native Americans in the United States, Indian lands, and adopt the policy of dividing tribal lands into individual allotments that was enacted for other tribes as the Dawes Act of 1887. In November 1893, President Grover Cleveland appointed Dawes as chairman, and Meridith H. Kidd and Archibald S. McKennon as members. During this process, the Indian nations were stripped of their communally held national lands, which was divided into single lots and allotted to individual members of the nation. The Dawes Commission required that individuals claim membership in only one tribe, although many people had more than one line of ancestry. Registration in the national registry known as the Dawes Rolls has come to be critical in issues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawes Act
The Dawes Act of 1887 (also known as the General Allotment Act or the Dawes Severalty Act of 1887) regulated land rights on tribal territories within the United States. Named after Senator Henry L. Dawes of Massachusetts, it authorized the President of the United States to subdivide Native American tribal communal landholdings into allotments for Native American heads of families and individuals. This would convert traditional systems of land tenure into a government-imposed system of private property by forcing Native Americans to "assume a capitalist and proprietary relationship with property" that did not previously exist in their cultures. The act allowed tribes the option to sell the lands that remained after allotment to the federal government. Before private property could be dispensed, the government had to determine "which Indians were eligible" for allotments, which propelled an "official search for a federal definition of Indian-ness." Although the act was passed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keetoowah Nighthawk Society
The Keetoowah Nighthawk Society was a Cherokee organisation formed ''ca.'' 1900 that intended to preserve and practice traditional "old ways" of tribal life, based on religious nationalism. It was led by Redbird Smith, a Cherokee National Council and original Keetoowah Society member. It formed in the Indian Territory that was superseded by admission of Oklahoma as a state, during the late-nineteenth century period when the federal government was breaking up tribal governments and communal lands under the Dawes Act and Curtis Act. The Nighthawks arose in response to weakening resolve on the part of Cherokee leaders—including the original Keetoowah Society (Cherokee: ᎩᏚᏩ ᎤᎾᏙᏢᎯ), a political organization created by Cherokee Native American full bloods, in or about 1859—to continue their resistance on behalf of the Cherokee after the Dawes Commission began forcing the transfer of Oklahoma tribal lands in the Indian Territory to individual ownership in the 1890s (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |