|
Organozinc Compound
Organozinc compounds in organic chemistry contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds. Organozinc chemistry is the science of organozinc compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions.The Chemistry of Organozinc Compounds' (Patai Series, (Eds. Z. Rappoport and I. Marek), John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2006, .''Organozinc reagents – A Practical Approach'', (Eds. P. Knochel and P. Jones), Oxford Medical Publications, Oxford, 1999, . Organozinc compounds were among the first organometallic compounds made. They are less reactive than many other analogous organometallic reagents, such as Grignard and organolithium reagents. In 1848 Edward Frankland prepared the first organozinc compound, diethylzinc, by heating ethyl iodide in the presence of zinc metal.E. Frankland, Liebigs Ann. Chem.,1849, 71, 171 This reaction produced a volatile colorless liquid that spontaneous combusted upon contact with air. Due to their pyrophoric nature, organozinc compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, astatide, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX (X = F, Cl, Br or I). Many salts are halides; the ''hal-'' syllable in ''halide'' and ''halite'' reflects this correlation. All Group 1 metals form halides that are white solids at room temperature. A halide ion is a halogen atom bearing a negative charge. The halide anions are fluoride (), chloride (), bromide (), iodide () and astatide (). Such ions are present in all ionic halide salts. Halide minerals contain halides. All these halides are colourless, high melting crystalline solids having high negative enthalpies of format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Hybridisation
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital combines with three valence-shell p orbitals to form four equivalent sp3 mixtures in a tetrahedral arrangement around the carbon to bond to four different atoms. Hybrid orbitals are useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Usually hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing atomic orbitals of comparable energies. History and uses Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the hybridisation theory in 1931 to explain the structure of simple molecules such as methane (CH4) using atomic orbitals. Pauling pointed out that a carbon atom forms fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are precursors to nylon. Cyclohexyl () is the alkyl substituent of cyclohexane and is abbreviated Cy. Production Modern On an industrial scale, cyclohexane is produced by hydrogenation of benzene in the presence of a Raney nickel catalyst. Producers of cyclohexane account for approximately 11.4% of global demand for benzene. The reaction is highly exothermic, with ΔH(500 K) = -216.37 kJ/mol. Dehydrogenation commenced noticeably above 300 °C, reflecting the favorable entropy for dehydrogenation. : Early Unlike benzene, cyclohexane is not found in natural resources such as coal. For this reason, early investigators synthesized their cyclohexa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
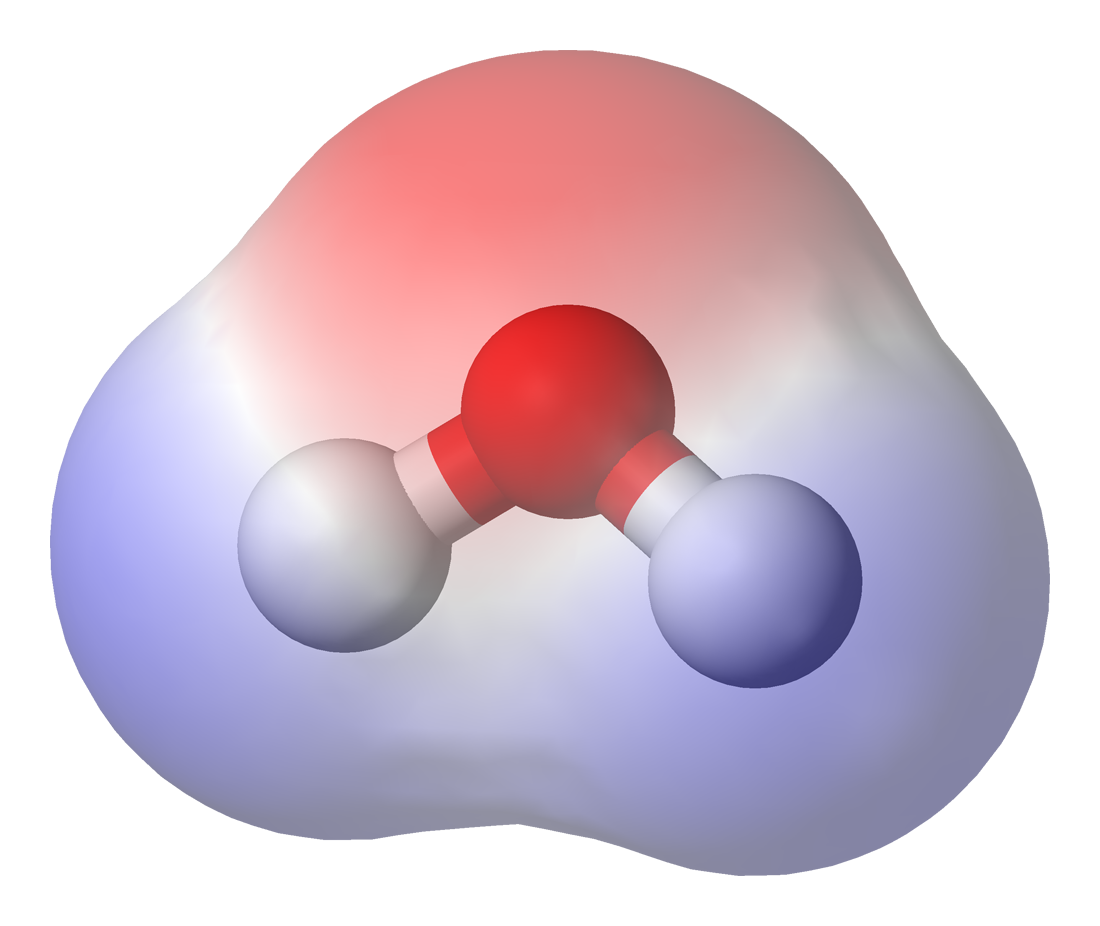
Molecular Dipole Moment
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: *An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) *A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precise: for the definition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Covalent Bond
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angewandte Chemie International Edition
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-length reviews, short highlights, research communications, minireviews, essays, book reviews, meeting reviews, correspondences, corrections, and obituaries. This journal contains review articles covering all aspects of chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2021 impact factor of 16.823. Editions The journal appears in two editions with separate volume and page numbering: a German edition, ''Angewandte Chemie'' ( (print), (online)), and a fully English-language edition, ''Angewandte Chemie International Edition'' ( (print), (online)). The editions are identical in content with the exception of occasional reviews of German-language books or German translations of IUPAC recommendations. Business model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand Field
Ligand field theory (LFT) describes the bonding, orbital arrangement, and other characteristics of coordination complexes. It represents an application of molecular orbital theory to transition metal complexes. A transition metal ion has nine valence atomic orbitals - consisting of five ''n''d, one (''n''+1)s, and three (''n''+1)p orbitals. These orbitals are of appropriate energy to form bonding interaction with ligands. The LFT analysis is highly dependent on the geometry of the complex, but most explanations begin by describing octahedral complexes, where six ligands coordinate to the metal. Other complexes can be described by reference to crystal field theory.G. L. Miessler and D. A. Tarr "Inorganic Chemistry" 3rd Ed, Pearson/Prentice Hall publisher, . History Ligand field theory resulted from combining the principles laid out in molecular orbital theory and crystal field theory, which describes the loss of degeneracy of metal d orbitals in transition metal complexes. John Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is , meaning that the 1s, 2s and 2p subshells are occupied by 2, 2 and 6 electrons respectively. Electronic configurations describe each electron as moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions. According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, a level of energy is associated with each electron configuration and in certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedral
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)