|
Organologist
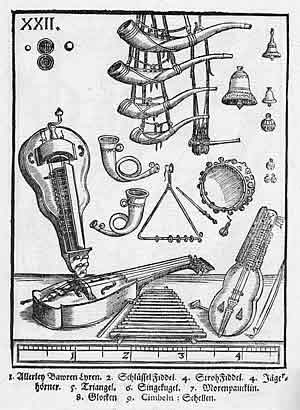
Organology (from Ancient Greek () 'instrument' and (), 'the study of') is the science of musical instruments and their classifications. It embraces study of instruments' history, instruments used in different cultures, technical aspects of how instruments produce sound, and musical instrument classification. There is a degree of overlap between organology, ethnomusicology (being subsets of musicology) and the branch of the science of acoustics devoted to musical instruments. History A number of ancient cultures left documents detailing the musical instruments used and their role in society; these documents sometimes included a classification system. The first major documents on the subjects from the west, however, date from the 16th century, with works such as Sebastian Virdung's ''Musica getuscht und ausgezogen'' (1511), and Martin Agricola's ''Musica instrumentalis deudsch'' (1529). One of the most important organologists of the 17th century is Michael Praetorius. His ''Syntag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Praetorius
Michael Praetorius (probably 28 September 1571 – 15 February 1621) was a German composer, organist, and music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant hymns. Life Praetorius was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in Creuzburg, in present-day Thuringia. After attending school in Torgau and Zerbst, he studied divinity and philosophy at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). He was fluent in a number of languages. After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He served in the duke's State Orchestra, first as organist and later (from 1604) as ''Kapellmeister'' (court music director). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Baines
Anthony Cuthbert Baines (1912–1997) was an English organologist who produced a wide variety of works on the history of musical instruments, and was a founding member of the Galpin Society. He attended Westminster School and then read for a degree in chemistry at Christ Church, Oxford. He subsequently won a scholarship to the Royal College of Music as a bassoon player, and went on to perform with the London Philharmonic Orchestra.A. C. Baines (ed.): ''Musical Instruments Through the Ages'' (Harmondsworth: Pelican Books, 1961), cover text. Selected publications * ''Woodwind Instruments and their History'' (London: Faber & Faber, 1957; reprinted 1962, 1967, 1991) * ''Bagpipes'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1960; reprinted 1979, 1995), * ''Musical Instruments Through the Ages'' (Harmondsworth: Pelican, 1961; revised edition, London: Faber, 1966), * ''European and American Musical Instruments'' (London: B. T. Batsford, 1966; London: Chancellor, 1983) * ''Brass Instruments: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Waterhouse (bassoonist)
William Waterhouse (18 February 1931 – 5 November 2007) was an English bassoonist and musicologist. He played with notable orchestras, was a member of the Melos Ensemble, professor at the Royal Northern College of Music, author of the ''Yehudi Menuhin Music Guide "Bassoon"'', of ''The New Langwill Index'', and contributor to the ''New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians''. Biography and career as a performer Born in London, Waterhouse studied at the Royal College of Music, specifically the bassoon with Archie Camden, viola with Cecil Aronowitz, and harmony with the composer Gordon Jacob. From 1953 to 1955, he was second bassoonist in the orchestra of the Royal Opera at Covent Garden at the time of Maria Callas, Tito Gobbi, and Kirsten Flagstad. Later he stated that his most valuable lessons in phrasing were actually learned playing in the pit while accompanying opera singers. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon Theremin
Leon Theremin (born Lev Sergeyevich Termen rus, Лев Сергеевич Термéн, p=ˈlʲef sʲɪrˈɡʲejɪvʲɪtɕ tɨrˈmʲen; – 3 November 1993) was a Russian and USSR, Soviet inventor, most famous for his invention of the theremin, one of the first electronic musical instruments and the first to be mass-produced. He also worked on early television research. His listening device, "The Thing (listening device), The Thing", hung for seven years in plain view in the List of ambassadors of the United States to Russia, United States Ambassador's Embassy of the United States, Moscow, Moscow office and enabled Soviet agents to eavesdrop on secret conversations. Early life Leon Theremin was born in Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire in 1896. His father was Sergei Emilievich Theremin of French Huguenot descent. His mother was Yevgenia Antonova Orzhinskaya and of German ancestry. He had a sister named Helena. In the seventh class of his high school before an audience of studen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Partch
Harry Partch (June 24, 1901 – September 3, 1974) was an American composer, music theorist, and creator of unique musical instruments. He composed using scales of unequal intervals in just intonation, and was one of the first 20th-century composers in the West to work systematically with microtonal scales, alongside Lou Harrison. He built custom-made instruments in these tunings on which to play his compositions, and described the method behind his theory and practice in his book '' Genesis of a Music'' (1947). Partch composed with scales dividing the octave into 43 unequal tones derived from the natural harmonic series; these scales allowed for more tones of smaller intervals than in standard Western tuning, which uses twelve equal intervals to the octave. To play his music, Partch built many unique instruments, with such names as the Chromelodeon, the Quadrangularis Reversum, and the Zymo-Xyl. Partch described his music as corporeal, and distinguished it from abs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Moog
Robert Arthur Moog ( ; May 23, 1934 – August 21, 2005) was an American engineer and electronic music pioneer. He was the founder of the synthesizer manufacturer Moog Music and the inventor of the first commercial synthesizer, the Moog synthesizer, which debuted in 1964. In 1970, Moog released a more portable model, the Minimoog, described as the most famous and influential synthesizer in history. Among Moog's honors are a Technical Grammy Award, received in 2002, and an induction into the National Inventors Hall of Fame. By 1963, Moog had been designing and selling theremins for several years, while working towards a PhD in engineering physics at Cornell University. He developed his synthesizer in response to demand for more practical and affordable electronic music equipment, guided by suggestions and requests from composers. Moog's principal innovation was the voltage-controlled oscillator, which uses voltage to control pitch. He also introduced fundamental synthesizer conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor-Charles Mahillon
Victor-Charles Mahillon (March 10, 1841 in Brussels – June 17, 1924 in Saint-Jean-Cap-Ferrat, France) was a Belgian musician, instrument builder and writer on musical topics. He was the founder and first curator of the Musée instrumental du Conservatoire Royal de Musique, known today as the Musical Instrument Museum. He built, collected, and described more than 1500 musical instruments. Biography Early life and family Born in a family of instrument makers and music publishers, son of Charles Mahillon (1813-1887), and brother of Joseph-Jean Mahillon (1848-1923, Adolphe Désiré Mahillon (1851-1906) and Ferdinand-Charles-Eugène Mahillon (1855-1948). His uncle Barthelemi and his son Fernand-Charles-Henri had the same profession. Partly self-taught, Mahillon studied Musical Acoustics and Organology and started working at his father's factory of musical instruments in 1865. In 1869, he started the musical journal ''L'Echo musical'', which ran until 1886. Brussels Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Musical Instruments
''Experimental Musical Instruments'' was a periodical edited and published by Bart Hopkin, an instrument builder and writer about 20th century experimental music design and custom made instrument construction. Though no longer in print, back issues are still available. The material and approach of EMI can now be found electronically on their site hosted by Bart Hopkin. This site is, together with www.oddmusic.com the main source on the internet for experimental musical instrumentalism.https://www.google.com/search?hl=en&client=safari&rls=nl-nl&q=experimental+musical+instrument&btnG=Zoeken&lr= Although only old editions of the magazine are still available and no newer editions appear, the name is still in use as the publisher for many of the book written by Bart Hopkin and co-writers. Publications *''Experimental Musical Instruments'', magazine, 70 issues appeared as a printed publication between 1985 and 1999, later on re-issued as well on CD-ROM. It was first headquartered in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bart Hopkin
Bart Hopkin is a builder of experimental musical instruments and a writer and publisher on the subject. Hopkin runs the website windworld.com, which provides resources regarding unusual instruments. Hopkin published the magazine ''Experimental Musical Instruments'' for 15 years and published several books and CDs specialized in a specialisation of certain types of instruments, such as wind chimes, plosive aerophones and marimbas. For these publications, Hopkin regularly asks experts on the subject to co-write the books, such as Carl Dean for the book about how to build and tune marimbas. ''Getting a Bigger Sound'' is a book Bart Hopkin wrote with Robert Cain and Jason Lollar about amplification of sound sources with several types of pickups ranging from piezo disc pickups to common pickups often used in electric guitars. Jason Lollar is a known builder of hand-wound electro-magnetic pickups. Besides writing, he has also built several experimental musical instruments such as wood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Fender
Clarence Leonidas Fender (August 10, 1909 – March 21, 1991) was an American inventor known for designing the Fender Stratocaster. He also founded the Fender Musical Instruments Corporation. In January 1965, he sold Fender to CBS, and later founded two other musical instrument companies, Music Man (company), Music Man and G&L Musical Instruments. The guitars, basses, and amplifiers he designed from the 1940s on are still widely used: the Fender Telecaster (1950) was the first mass-produced solid-body electric guitar; the Fender Stratocaster (1954) is among the most iconic electric guitars; the Fender Precision Bass (1951) set the standard for electric basses, and the Fender Bassman amplifier, popular in its own right, became the basis for later amplifiers (notably by Marshall Amplification, Marshall and Mesa Boogie) that dominated rock and roll music. Leo Fender was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1992. His instruments were played by many Rock and Roll Hall of Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |