|
Orffyreus
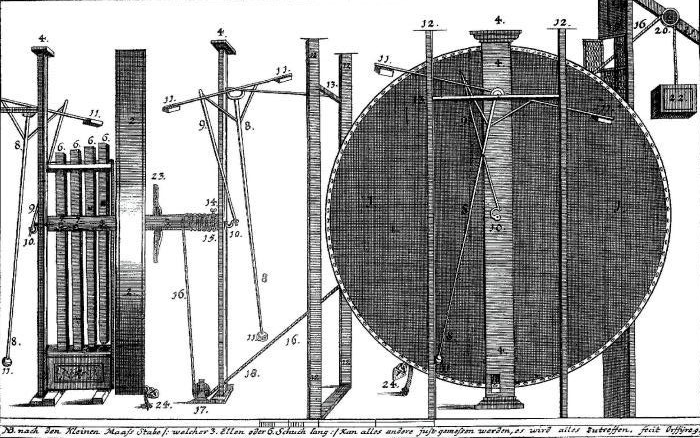
Johann Ernst Elias Bessler (''ca''. 1680 – 30 November 1745), known as Orffyreus or Orffyré, was a German entrepreneur who claimed to have built several perpetual motion machines. Those claims generated considerable interest and controversy among some of the leading natural philosophers of the day, including Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Johann Bernoulli, John Theophilus Desaguliers, and Willem 's Gravesande. The modern scientific consensus is that Bessler perpetrated a deliberate fraud, although the details of this have not been satisfactorily explained. Life and career Bessler was born to a peasant family in Upper Lusatia, in the German Electorate of Saxony, ''circa'' 1680. He went to school in Zittau, where (according to his own account) he excelled in his studies and became a favorite of Christian Weise, the rector of the local ''Gymnasium''. After he left school he began to travel widely, seeking his fortune. Having saved an alchemist from drowning in a well, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Bessler
Johann Ernst Elias Bessler (''ca''. 1680 – 30 November 1745), known as Orffyreus or Orffyré, was a German entrepreneur who claimed to have built several perpetual motion machines. Those claims generated considerable interest and controversy among some of the leading Natural philosophy, natural philosophers of the day, including Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Johann Bernoulli, John Theophilus Desaguliers, and Willem 's Gravesande. The modern scientific consensus is that Bessler perpetrated a deliberate fraud, although the details of this have not been satisfactorily explained. Life and career Bessler was born to a peasant family in Lusatia, Upper Lusatia, in the German Electorate of Saxony, ''circa'' 1680. He went to school in Zittau, where (according to his own account) he excelled in his studies and became a favorite of Christian Weise, the rector of the local Gymnasium (Germany), ''Gymnasium''. After he left school he began to travel widely, seeking his fortune. Having saved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willem 's Gravesande
Willem Jacob 's Gravesande (26 September 1688 – 28 February 1742) was a Dutch mathematician and natural philosopher, chiefly remembered for developing experimental demonstrations of the laws of classical mechanics and the first experimental measurement of kinetic energy. As professor of mathematics, astronomy, and philosophy at Leiden University, he helped to propagate Isaac Newton's ideas in Continental Europe. Life Born in 's-Hertogenbosch, 's Gravesande studied law at Leiden University, where he defended a thesis on suicide and earned a doctorate in 1707. He then practised law in The Hague while also participating in intellectual discussions and cultivating his interest in the mathematical sciences. His ''Essai de perspective'' ("Essay on Perspective"), published in 1711, was praised by the influential Swiss mathematician Johann Bernoulli. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ROT13
ROT13 ("rotate by 13 places", sometimes hyphenated ROT-13) is a simple letter substitution cipher that replaces a letter with the 13th letter after it in the alphabet. ROT13 is a special case of the Caesar cipher which was developed in ancient Rome. Because there are 26 letters (2×13) in the basic Latin alphabet, ROT13 is its own inverse; that is, to undo ROT13, the same algorithm is applied, so the same action can be used for encoding and decoding. The algorithm provides virtually no cryptographic security, and is often cited as a canonical example of weak encryption. ROT13 is used in online forums as a means of hiding spoilers, punchlines, puzzle solutions, and offensive materials from the casual glance. ROT13 has inspired a variety of letter and word games online, and is frequently mentioned in newsgroup conversations. Description Applying ROT13 to a piece of text merely requires examining its alphabetic characters and replacing each one by the letter 13 places further al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gera
Gera is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cities consisting of the six largest Thuringian cities from Eisenach in the west, via Gotha, Erfurt, Weimar and Jena to Gera in the east. Gera is the largest city in the Vogtland, and one of its historical capitals along with Plauen, Greiz and Weida. The city lies in the East Thuringian Hill Country, in the wide valley of the White Elster, between Greiz (upstream) and Leipzig (downstream). Gera is located in the Central German Metropolitan Region, approximately south of Saxony's largest city of Leipzig, east of Thuringia's capital Erfurt, west of Saxony's capital Dresden and 90 km (56 miles) north of Bavaria's city of Hof (Saale). First mentioned in 995 and developing into a city during the 13th century, Gera has historical significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassel
Kassel (; in Germany, spelled Cassel until 1926) is a city on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel and the district of the same name and had 201,048 inhabitants in December 2020. The former capital of the state of Hesse-Kassel has many palaces and parks, including the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Kassel is also known for the '' documenta'' exhibitions of contemporary art. Kassel has a public university with 25,000 students (2018) and a multicultural population (39% of the citizens in 2017 had a migration background). History Kassel was first mentioned in 913 AD, as the place where two deeds were signed by King Conrad I. The place was called ''Chasella'' or ''Chassalla'' and was a fortification at a bridge crossing the Fulda river. There are several yet unproven assumptions of the name's origin. It could be derived from the ancient ''Castellum Cattorum'', a castle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landgrave
Landgrave (german: Landgraf, nl, landgraaf, sv, lantgreve, french: landgrave; la, comes magnus, ', ', ', ', ') was a noble title used in the Holy Roman Empire, and later on in its former territories. The German titles of ', ' ("margrave"), and ' ("count palatine") are in the same class of ranks as ' ("duke") and above the rank of a ' ("count"). Etymology The English language, English word landgrave is the equivalent of the German language, German ''Landgraf'', a compound (linguistics), compound of the words ''Land'' and ''Graf'' (German: Count). Description The title referred originally to a count who had imperial immediacy, or feudal duty owed directly to the Holy Roman Emperor. His jurisdiction stretched over a sometimes quite considerable territory, which was not subservient to an intermediate power, such as a duke, a bishop or count palatine. The title survived from the times of the Holy Roman Empire (first recorded in Lower Lotharingia from 1086: Henry III, Count of Lou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I, Landgrave Of Hesse-Kassel
Charles of Hesse-Kassel (german: Karl von Hessen-Kassel; 3 August 1654 – 23 March 1730), of the House of Hesse, was the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel from 1670 to 1730. Childhood Charles was the second son of William VI, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, and Hedwig Sophia of Brandenburg (1623–1683). Until 1675 his mother ruled as his guardian and regent before Charles was old enough to take over the administration for the next 5 years. His older brother, William VII, had died in 1670 shortly after reaching adulthood, even before he had had the chance to make any changes with the administration. Policies Under the reign of Charles, the consequences of the Thirty Years' War in the agricultural county could be overcome more quickly than they were in the more industrialized regions of the Holy Roman Empire. He pushed for the recreation of a large army and put it in the service of other countries in the War of Spanish Succession. His soldiers, he gave, as well as other princes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landgraviate Of Hesse-Kassel
The Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel (german: Landgrafschaft Hessen-Kassel), spelled Hesse-Cassel during its entire existence, was a state in the Holy Roman Empire that was directly subject to the Emperor. The state was created in 1567 when the Landgraviate of Hesse was divided upon the death of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse. His eldest son William IV inherited the northern half of the Landgraviate and the capital of Kassel. The other sons received the Landgraviate of Hesse-Marburg, the Landgraviate of Hesse-Rheinfels and the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt. During the Napoleonic reorganisation of the Empire in 1803, the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel was elevated to an Electorate and Landgrave William IX became an Imperial Elector. Many members of the Hesse-Kassel House served in the Danish military gaining high ranks and power in the Oldenburg realm due to the fact that many Landgraves were married to Danish princesses. Members of the family who are known to have served Denmark-Norwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merseburg
Merseburg () is a town in central Germany in southern Saxony-Anhalt, situated on the river Saale, and approximately 14 km south of Halle (Saale) and 30 km west of Leipzig. It is the capital of the Saalekreis district. It had a diocese founded by Archbishop Adalbert of Magdeburg. The University of Merseburg is located within the town. Merseburg has around 33,000 inhabitants. Names * cs, Merseburk, Meziboř * french: Mersebourg * german: Merseburg * la, Merseburga * pl, Międzybórz * wen, Mjezybor Geography The town Merseburg consists of Merseburg proper and the following four ''Ortschaften'' or municipal divisions:Hauptsatzung der Stadt Merseburg § 15, April 2019. * |
Joseph Emanuel Fischer Von Erlach
Joseph Emanuel Fischer von Erlach, also ''Fischer von Erlach the younger'' (13 September 1693 in Vienna – 29 June 1742 in Vienna) was an Austrian architect of the Baroque, Rococo, and Baroque- Neoclassical. Biography Joseph Emanuel was the son of Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach. He first developed his skills in his father's workshop. In 1711, he worked on several of his father's commissions (e.g. Palais Dietrichstein, Palais Trautson, Bohemian Court Chancellery, Schwarzenberg Palace) and also helped complete the publication ''"Draft of a historical architecture"''; whose four volumes inspired many later designs. Through this work, Joseph Emanuel came into contact both with the architecture of his and earlier times and with Berne, his father's noble order. His father also involved Joseph Emanuel in the writing of ''"Folders and Outlines of some buildings of Vienna, self-drawn from J.E.F.v.E.,"'' with a preface by the court antiquarian Carl Gustav Heraeus. This publication w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1572.jpg)

