|
Oregon Lakes
Oregon Lakes is a freshwater ecoregion in the western United States. It includes several closed basins in southern-central Oregon and adjacent parts of California and Nevada, including the Harney Basin, Warner Valley, and the basins of Lake Abert and Summer Lake."Oregon Lakes". Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Accessed 18 September 2021/ref> Geography The ecoregion includes several closed, or endorheic, basins. The ecoregions's streams empty into alkaline lakes or onto playas. The ecoregion is bounded on the north and east by the Columbia River basin, on the west by the upper basin of the Klamath River, on the southwest by the upper Sacramento River watershed, and on the south and southeast by the closed Lahontan Basin.Howard, J., and C. Revenga (2009). "California’s freshwater biodiversity in a continental context". Science for Conservation Technical Brief Series. The Nature Conservancy of California. San Francisco, CA. 29 pp + Appendices. Accessed 18 September 2021/ref> Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades. The small part of the range in British Columbia is referred to as the Canadian Cascades or, locally, as the Cascade Mountains. The latter term is also sometimes used by Washington residents to refer to the Washington section of the Cascades in addition to North Cascades, the more usual U.S. term, as in North Cascades National Park. The highest peak in the range is Mount Rainier in Washington at . part of the Pacific Ocean's Ring of Fire, the ring of volcanoes and associated mountains around the Pacific Ocean. All of the eruptions in the contiguous United States over the last 200 years have been from Cascade volcanoes. The two most recent were Lassen Peak from 1914 to 1921 and a major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregions Of California
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic framework is optimal for all taxa. Ecoregions reflect the best compromise for as many taxa as possible. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Ecoregions
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic framework is optimal for all taxa. Ecoregions reflect the best compromise for as many taxa as possible. Sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warner Lakes
The Warner Lakes are a chain of shallow lakes and marshes in the Warner Valley of eastern Lake County, Oregon, United States. The lakes extend the length of the valley, covering approximately . The lakes are named in honor of Captain William H. Warner, a topographical engineer who explored Warner Valley before being killed by Native Americans in 1849. The Warner Lakes and surrounding wetlands support a wide variety of birds and other wildlife. Much of the land surrounding the lakes is owned by the public and is administered by the Bureau of Land Management. These public lands provide recreational opportunities including hunting, fishing, bird watching, and camping. Warner Valley The Warner Valley is in south-central Oregon. It is approximately long and wide. Most of the valley is in Lake County, however the north end of the valley extends about into Harney County. It is an alluvial basin containing numerous lakes, remnants of a single great lake that covered the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warner Sucker
The Warner sucker (''Catostomus warnerensis'') is a rare species of freshwater ray-finned fish in the family Catostomidae. Native to Oregon in the United States and found only in the Warner Lakes, Warner Basin, its distribution extends just into Nevada''Catostomus warnerensis''. The Nature Conservancy. and California.USFWS ''Catostomus warnerensis'' Five-year Review. August 2010. It is a federally listed threatened species. Its other common name is redhorse.Williams, J. E. (1995) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borax Lake (Oregon)
Borax Lake is a alkaline lake in the Alvord Desert of southeastern Oregon in the United States. The lake is fed by geothermal springs below the surface that range in temperature from . Surface water temperatures usually range from but occasionally go higher. The springs lie along the Steens fault zone, which runs north–south through the Alvord Valley east of Steens Mountain. The lake contains high concentrations of borax (sodium borate), as well as arsenic and lead. Despite this, it is home to a unique species of fish, known as the Borax Lake chub. The species was formerly threatened by development of geothermal energy in the vicinity. However, in 1993 The Nature Conservancy bought of private land, including the lake, in order to protect it; the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has designated near the lake as critical habitat, and the Steens Mountain Cooperative Management and Protection Act of 2000 put the area around the lake off-limits to geothermal exploration and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borax Lake Chub
The Borax Lake chub (''Siphateles boraxobius'') is a rare cyprinid fish found only in outflows and pools around Borax Lake, a small lake of the Alvord basin, Harney County, Oregon. This species typically reaches only in length, although some are as long as . The back is generally a dark olive green, while the sides are silvery, with a dark line extending from gill cover to tail, and a scattering of dark melanophores. The fins are colorless, with more melanophores on the rays of the dorsal fin and tail, as well as on the first four rays of the pectoral fins. Similar in many ways to the Alvord chub, the Borax Lake species has a longer, wider, and deeper head, and larger eyes, and the caudal peduncle is more slender. The Borax Lake chub eats a variety of foods, including midge larvae, diatoms, copepods, ostracod Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 70,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake–Columbia Shrub Steppe
The Snake–Columbia shrub steppe is an ecoregion defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). This ecoregion receives little precipitation because it is within the rain shadow of the Cascade Range. It takes in a western portion of the Columbia Basin in Washington, and extends south along the Deschutes River Basin, expanding to cover most of southeast Oregon including the Oregon Lakes region. This ecoregion reaches south from Oregon into northern Nevada and the northeast corner of California. It also connects east onto the Snake River Plain, which it follows east from Hells Canyon to the continental divide in eastern Idaho. Information about this ecoregion is covered by two articles that follow the ecoregion definitions of the United States Environmental Protection Agency: * Columbia Plateau (ecoregion) * Snake River Plain (ecoregion) See also *List of ecoregions in the United States (WWF) The following is a list of ecoregions in the United States as identified by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing some precipitation, and temperatures are not moderated by oceans. Continental climates occur mostly in the Northern Hemisphere due to the large landmasses found there. Most of northern and northeastern China, eastern and southeastern Europe, Western and north western Iran, central and southeastern Canada, and the central and northeastern United States have this type of climate. Continentality is a measure of the degree to which a region experiences this type of climate. In continental climates, precipitation tends to be moderate in amount, concentrated mostly in the warmer months. Only a few areas—in the mountains of the Pacific Northwest of North America and in Iran, northern Iraq, adjacent Turkey, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Central Asia� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
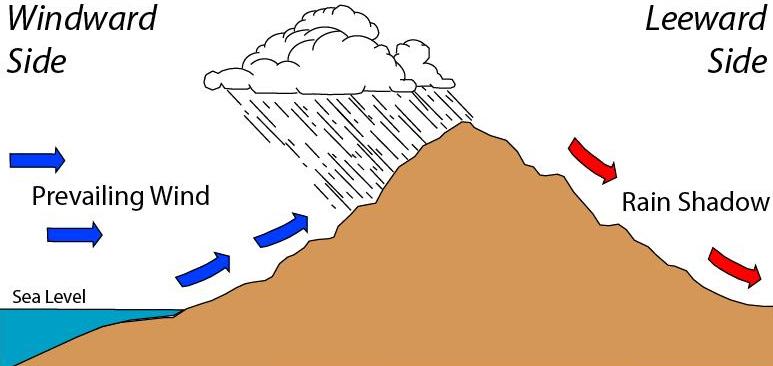
Rain Shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side. Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carried by the prevailing onshore breezes towards the drier and hotter inland areas. When encountering elevated landforms, the moist air is driven upslope towards the peak, where it expands, cools, and its moisture condenses and starts to precipitate. If the landforms are tall and wide enough, most of the humidity will be lost to precipitation over the windward side (also known as the ''rainward'' side) before ever making it past the top. As the air descends the leeward side of the landforms, it is compressed and heated, producing foehn winds that ''absorb'' moisture downslope and cast a broad "shadow" of dry climate region behind the mountain crests. This climate typically takes the form of shrub–steppe, xeric shrublands or even deserts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorheic Basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. They are also called closed or terminal basins, internal drainage systems, or simply basins. Endorheic regions contrast with exorheic regions. Endorheic water bodies include some of the largest lakes in the world, such as the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water. Basins with subsurface outflows which eventually lead to the ocean are generally not considered endorheic; they are cryptorheic. Endorheic basins constitute local base levels, defining a limit of erosion and deposition processes of nearby areas. Etymology The term was borrowed from French ''endor(rh)éisme'', coined from the combining form ''endo-'' (from grc, ἔνδον ''éndon'' 'wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |