|
Optomechanics
Optomechanics is the manufacture and maintenance of optical parts and devices. This includes the design and manufacture of hardware used to hold and align elements in optical systems, such as: * Optical tables, breadboards, and rails * Mirror mounts * Optical mounts * Translation stages * Rotary stage * Optical fiber aligners * Pedestals and posts * Micrometers, screws and screw sets Optomechanics also covers the methods used to design and package compact and rugged optical trains, and the manufacture and maintenance of fiber optic An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ... materials References {{Reflist Optical devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optomechanics
Optomechanics is the manufacture and maintenance of optical parts and devices. This includes the design and manufacture of hardware used to hold and align elements in optical systems, such as: * Optical tables, breadboards, and rails * Mirror mounts * Optical mounts * Translation stages * Rotary stage * Optical fiber aligners * Pedestals and posts * Micrometers, screws and screw sets Optomechanics also covers the methods used to design and package compact and rugged optical trains, and the manufacture and maintenance of fiber optic An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ... materials References {{Reflist Optical devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Table
An optical table is a vibration control platform that is used to support systems used for laser- and optics-related experiments in science, engineering and manufacturing. The surfaces of these tables are designed to be very rigid with minimum deflection so that the alignment of optical elements remains stable over time. Many optical systems require that vibration of optical elements be kept small. As a result, optical tables are typically very heavy and incorporate vibration isolation and damping features in their structure. Many use pneumatic isolators that act as mechanical low-pass filters, reducing the ability of vibrations in the floor to cause vibrations in the tabletop. The surface of an optical table is typically stainless steel with a rectangular grid of tapped holes in either metric or imperial units: * metric: M6 on a 25 mm grid * imperial: ¼"-20 UNC on a 1" (25.4 mm) grid Optical breadboards, benches, and rails are simpler structures that perform a simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Mount
A mirror mount is a device that holds a mirror. In optics research, these can be quite sophisticated devices, due to the need to be able to tip and tilt the mirror by controlled amounts, while still holding it in a precise position when it is not being adjusted. An optical mirror mount generally consists of a movable front plate which holds the mirror, and a fixed back plate with adjustment screws. Adjustment screws drive the front plate about the axes of rotation in the pitch (vertical) and yaw (horizontal) directions. An optional third actuator often enables z-axis translation. Precision mirror mounts can be quite expensive, and a notable amount of engineering goes into their design. Such sophisticated mounts are often required for lasers, interferometers, and optical delay lines. Types of mirror mount The most common type of mirror mount is the kinematic mount. This type of mount is designed according to the principles of kinematic determinacy. Typically, the movable fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Mount
An optical mount is a device used to join a normal camera and another optical instrument, such as a microscope or telescope. The optical mount is generally attached to the camera as a lens would on one end, and fastened to the other instrument in a similar fashion. Optical mounts are used extensively in scientific imaging applications in biology and astronomy Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g .... Photography equipment Microscopy Astronomical instruments Optomechanics {{Photography-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
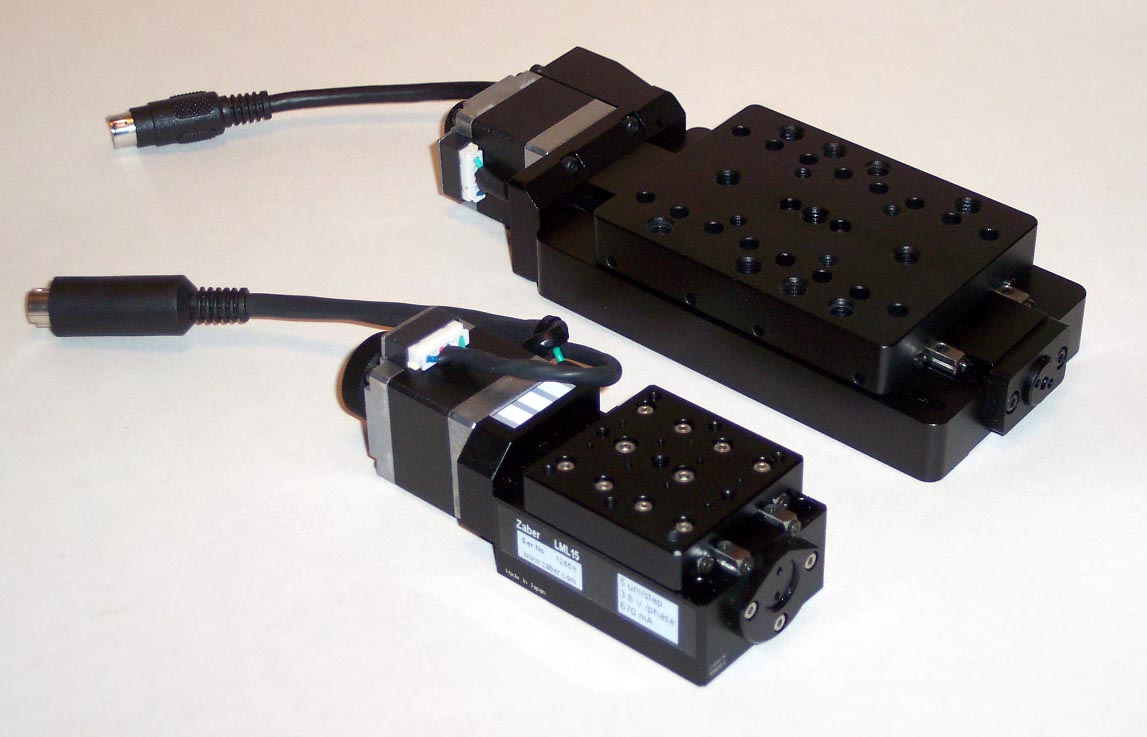
Translation Stage
A linear stage or translation stage is a component of a precise motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refers to a linear motion bearing, which is only a component of a linear stage. All linear stages consist of a platform and a base, joined by some form of guide or linear bearing in such a way that the platform is restricted to linear motion with respect to the base. In common usage, the term linear stage may or may not also include the mechanism by which the position of the platform is controlled relative to the base. Principle of operation In three-dimensional space, an object may either rotate about, or translate along any of three axes. Thus the object is said to have six degrees of freedom (3 rotational and 3 translational). A linear stage exhibits only one degree of freedom (translation along one axis). In other words, linear stages opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Stage
A rotary stage is a component of a motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of rotation. The terms rotary table or rotation stage are often used interchangeably with rotary stage. All rotary stages consist of a platform and a base, joined by some form of guide in such a way that the platform is restricted to rotation about a single axis with respect to the base. In common usage, the term rotary stage may or may not also include the mechanism by which the angular position of the platform is controlled relative to the base. Principle of operation In three-dimensional space, an object may either rotate about, or translate along, any of three axes. Thus, the object is said to have six degrees of freedom (3 rotational and 3 translational). A rotary stage exhibits only one degree of freedom (rotation about one axis). In other words, rotary stages operate by physically restricting 3 axes of translation and 2 axes of rotation. Bearing types Rotary stages consist of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical System
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Fiber
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data transfer rates) than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss; in addition, fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometer (device)
A micrometer, sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw widely used for accurate measurement of components in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier, and digital calipers. Micrometers are usually, but not always, in the form of calipers (opposing ends joined by a frame). The spindle is a very accurately machined screw and the object to be measured is placed between the spindle and the anvil. The spindle is moved by turning the ratchet knob or thimble until the object to be measured is lightly touched by both the spindle and the anvil. Micrometers are also used in telescopes or microscopes to measure the apparent diameter of celestial bodies or microscopic objects. The micrometer used with a telescope was invented about 1638 by William Gascoigne, an English astronomer. History The word ''micrometer'' is a neoclassical coinage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |