|
Optical Add-drop Multiplexer
An optical add-drop multiplexer (OADM) is a device used in wavelength-division multiplexing systems for multiplexing and routing different channels of light into or out of a single mode fiber (SMF). This is a type of optical node, which is generally used for the formation and the construction of optical telecommunications networks. "Add" and "drop" here refer to the capability of the device to add one or more new wavelength channels to an existing multi-wavelength WDM signal, and/or to drop (remove) one or more channels, passing those signals to another network path. An OADM may be considered to be a specific type of optical cross-connect. A traditional OADM consists of three stages: an optical demultiplexer, an optical multiplexer, and between them a method of reconfiguring the paths between the demultiplexer, the multiplexer and a set of ports for adding and dropping signals. The demultiplexer separates wavelengths in an input fiber onto ports. The reconfiguration can be ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconfigurable Optical Add-drop Multiplexer
In fiber optics, a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) is a form of optical add-drop multiplexer that adds the ability to remotely switch traffic from a wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) system at the wavelength layer. This is achieved through the use of a wavelength selective switching module. This allows individual or multiple wavelengths carrying data channels to be added and/or dropped from a transport fiber without the need to convert the signals on all of the WDM channels to electronic signals and back again to optical signals. The main advantages of the ROADM are: * The planning of entire bandwidth assignment need not be carried out during initial deployment of a system. The configuration can be done as and when required without affecting traffic already passing the ROADM. * ROADM allows for remote configuration and reconfiguration. * In ROADM, as it is not clear beforehand where a signal can be potentially routed, there is a necessity of power balancing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Mesh Network
An optical mesh network is a type of optical telecommunications network employing wired fiber-optic communication or wireless free-space optical communication in a mesh network architecture. Most optical mesh networks use fiber-optic communication and are operated by internet service providers in metropolitan and regional but also national and international scenarios. They are faster and less error prone than other network architectures and support backup and recovery plans for established networks in case of any disaster, damage or failure. Currently planned satellite constellations aim to establish optical mesh networks in space by using wireless laser communication. History of transport networks Transport networks, the underlying optical fiber-based layer of telecommunications networks, have evolved from Digital cross connect system (DCS)-based mesh architectures in the 1980s, to SONET/SDH (Synchronous Optical Networking/Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) ring architectures in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicast Lightpaths
A multicast session requires a "point-to-multipoint" connection from a source node to multiple destination nodes. The source node is known as the ''root''. The destination nodes are known as ''leaves''. In the modern era, it is important to protect multicast connections in an optical mesh network. Recently, multicast applications have gained popularity as they are important to protecting critical sessions against failures such as fiber cuts, hardware faults, and natural disasters. Multicast applications Multicast applications include multimedia, medical imaging, digital audio, HDTV, video conferencing, interactive distance learning, and distributed games. Multi-casting switch architecture In order to support multi-casting, the WDM network requires multicast-capable wavelength-routing switches at the network node. These switches are capable of replicating data streams from one input port to multiple output ports. There are two types of switch architectures that are usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization. SONET and SDH, which are essentially the same, were originally designed to transport circuit mode communications (e.g., DS1, DS3) from a variety of different sources, but they were primarily designed to support real-time, uncompressed, circuit-switched voice encoded in PCM format. The primary difficulty in doing this prior to SONET/SDH was that the synchronization sources of these various circuits were different. This meant that each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Add-drop Multiplexer
An add-drop multiplexer (ADM) is an important element of an optical fiber network. A multiplexer combines, or multiplexes, several lower-bandwidth streams of data into a single beam of light. An ''add-drop'' multiplexer also has the capability to ''add'' one or more lower-bandwidth signals to an existing high-bandwidth data stream, and at the same time can extract or ''drop'' other low-bandwidth signals, removing them from the stream and redirecting them to some other network path. This is used as a local "on-ramp" and "off-ramp" to the high-speed network. ADMs can be used both in long-haul core networks and in shorter-distance "metro" networks, although the former are much more expensive due to the difficulty of scaling the technology to the high data rates and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) used for long-haul communications. The main optical filtering technology used in add-drop multiplexers is the Fabry–Pérot etalon. Newer "multi-service SONET/SDH" (als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave intensities decrease according to the inverse square law as they expand into three-dimensional space. There are different types of waveguides for different types of waves. The original and most common meaningInstitute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. d. Standards Coordinating Committee 10, Terms and Definitions; Jane Radatz, (chair)/ref> is a hollow conductive metal pipe used to carry high frequency radio waves, particularly microwaves. Dielectric waveguides are used at higher radio frequencies, and transparent dielectric waveguides and optical fibers serve as waveguides f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
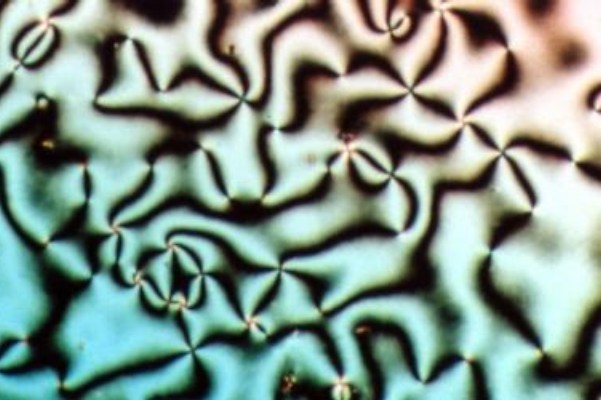
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microelectromechanical Systems
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), also written as micro-electro-mechanical systems (or microelectronic and microelectromechanical systems) and the related micromechatronics and microsystems constitute the technology of microscopic devices, particularly those with moving parts. They merge at the nanoscale into nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) and nanotechnology. MEMS are also referred to as micromachines in Japan and microsystem technology (MST) in Europe. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometers in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre (i.e., 0.02 to 1.0 mm), although components arranged in arrays (e.g., digital micromirror devices) can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data (an integrated circuit chip such as microprocessor) and several components that interact with the surroundings (such as microsensors). Because of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrayed Waveguide Grating
{{Unreferenced, date=April 2019 Arrayed waveguide gratings (AWG) are commonly used as optical (de)multiplexers in wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) systems. These devices are capable of multiplexing many wavelengths into a single optical fiber, thereby increasing the transmission capacity of optical networks considerably. The devices are based on a fundamental principle of optics that light waves of different wavelengths do not interfere linearly with each other. This means that, if each channel in an optical communication network makes use of light of a slightly different wavelength, then the light from many of these channels can be carried by a single optical fiber with negligible crosstalk between the channels. The AWGs are used to multiplex channels of several wavelengths onto a single optical fiber at the transmission end and are also used as demultiplexers to retrieve individual channels of different wavelengths at the receiving end of an optical communication network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Circulator
An optical circulator is a three- or four-port optical device designed such that light entering any port exits from the next. This means that if light enters port 1 it is emitted from port 2, but if some of the emitted light is reflected back to the circulator, it does not come out of port 1 but instead exits from port 3. This is analogous to the operation of an electronic circulator. Fiber-optic circulators are used to separate optical signals that travel in opposite directions in an optical fiber, for example to achieve bi-directional transmission over a single fiber. Because of their high isolation of the input and reflected optical powers and their low insertion loss, optical circulators are widely used in advanced communication systems and fiber-optic sensor applications. Optical circulators are ''non-reciprocal'' optics, which means that changes in the properties of light passing through the device are not reversed when the light passes through in the opposite direction. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |