|
Ophiuchus (astrology)
Ophiuchus (; grc, Ὀφιοῦχος, , Serpent-bearer; astrological symbol 16px, ⛎&xFE0E;) has sometimes been suggested in sidereal astrology as a 13th astrological sign in addition to the 12 signs of the tropical zodiac. The constellation Ophiuchus, as defined by the 1930 International Astronomical Union's constellation boundaries, is situated behind the sun from November 29 to December 18. The idea appears to have originated in 1970 with Steven Schmidt's suggestion of a 14-sign zodiac, also including Cetus as a sign. A 13-sign zodiac has been promulgated by Walter Berg and by Mark Yazaki in 1995, a suggestion that achieved some popularity in Japan, where Ophiuchus is known as . However, in sidereal and tropical astrology (including sun sign astrology), a 12-sign zodiac is based on dividing the ecliptic into 12 equal parts rather than the IAU constellation boundaries. That is, astrological signs do not correspond to the constellations which are their namesakes, partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
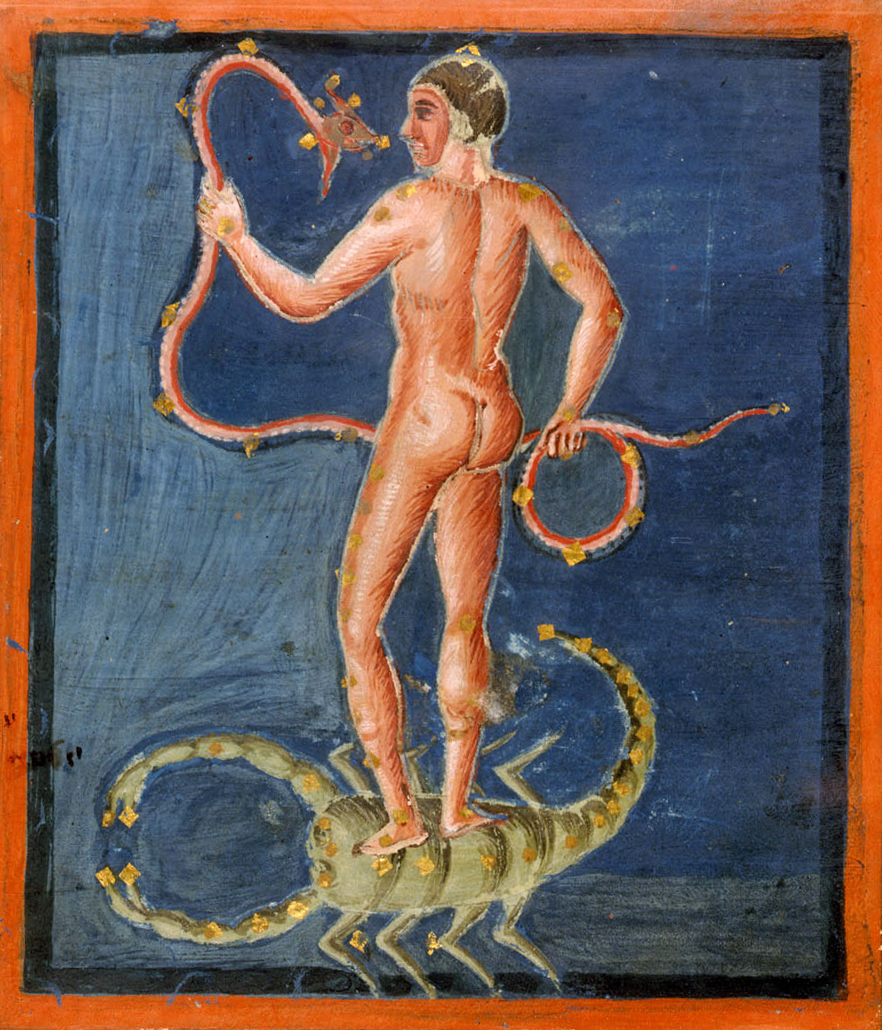
Aratea 10v
''Phaenomena Aratea'' may refer to: *A work by Aratus (3rd century BC) based on the above: *a work by Cicero (1st century BC) *a work by Germanicus Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ... (1st century BC or 1st century AD) **famously, Germanicus, Aratea (Leiden, Universiteitsbibliotheek, Voss. lat. Q 79) *the Carolingian De ordine ac positione stellarum in signis {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
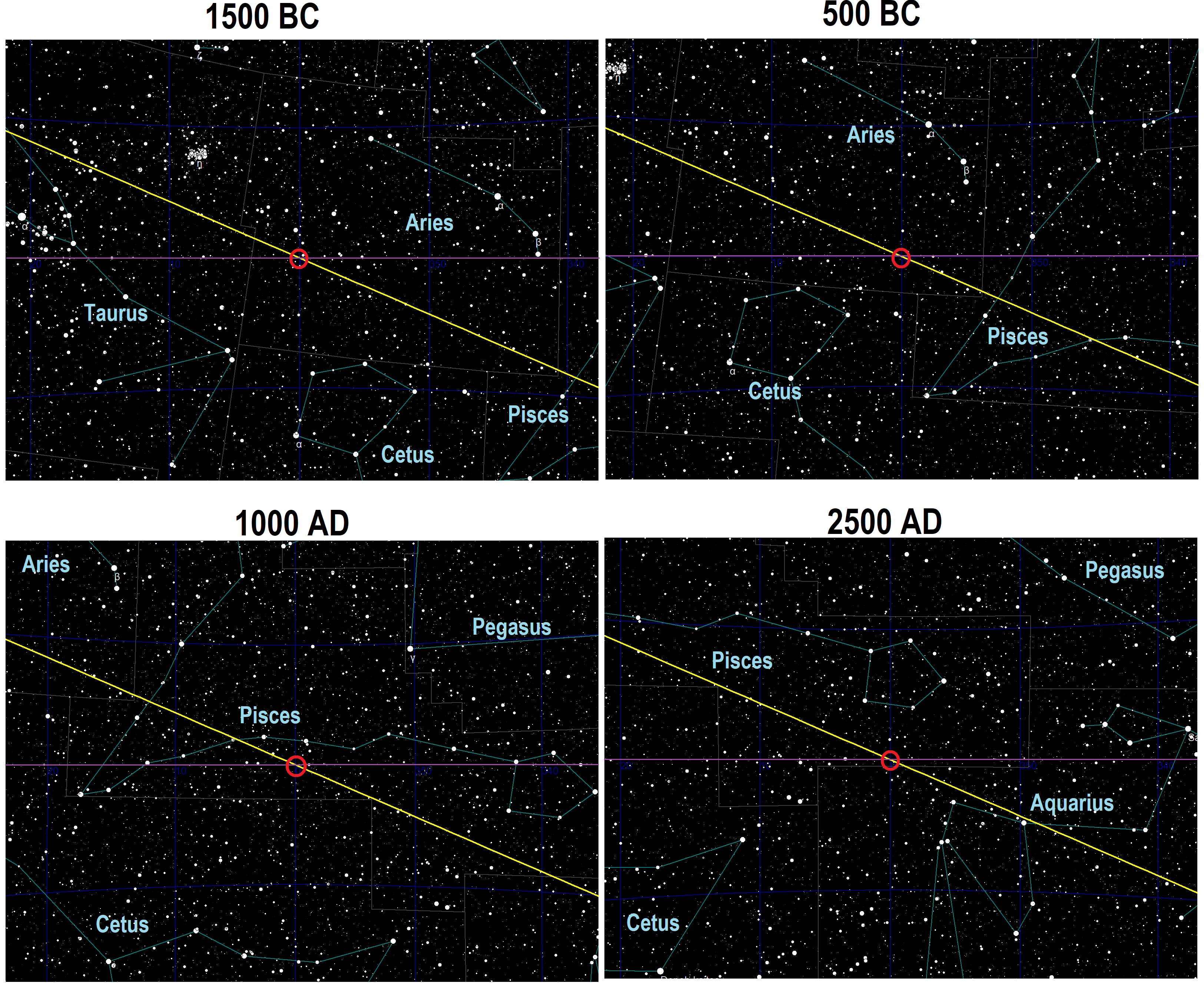
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Sun's apparent motion The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly north or south of) the Sun about four minutes later each day than it would if Earth did not orbit; a day on Earth is therefore 24 hours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Magazine
''Time'' (stylized in all caps) is an American news magazine based in New York City. For nearly a century, it was published weekly, but starting in March 2020 it transitioned to every other week. It was first published in New York City on March 3, 1923, and for many years it was run by its influential co-founder, Henry Luce. A European edition (''Time Europe'', formerly known as ''Time Atlantic'') is published in London and also covers the Middle East, Africa, and, since 2003, Latin America. An Asian edition (''Time Asia'') is based in Hong Kong. The South Pacific edition, which covers Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands, is based in Sydney. Since 2018, ''Time'' has been published by Time USA, LLC, owned by Marc Benioff, who acquired it from Meredith Corporation. History ''Time'' has been based in New York City since its first issue published on March 3, 1923, by Briton Hadden and Henry Luce. It was the first weekly news magazine in the United States. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard G
Howard is an English language, English-language given name originating from Old French Huard (other), Huard (or Houard) from a Germanic source similar to Old High German ''*Hugihard'' "heart-brave", or ''*Hoh-ward'', literally "high defender; chief guardian". It is also probably in some cases a confusion with the Old Norse cognate ''Haward'' (''Hávarðr''), which means "high guard" and as a surname also with the unrelated Hayward. In some rare cases it is from the Old English ''eowu hierde'' "ewe herd". In Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman the French digram ''-ou-'' was often rendered as ''-ow-'' such as ''tour'' → ''tower'', ''flour'' (western variant form of ''fleur'') → ''flower'', etc. (with svarabakhti). A diminutive is "Howie" and its shortened form is "Ward" (most common in the 19th century). Between 1900 and 1960, Howard ranked in the U.S. Top 200; between 1960 and 1990, it ranked in the U.S. Top 400; between 1990 and 2004, it ranked in the U.S. Top 600. Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesota Planetarium Society
The Minnesota Planetarium Society (MNPS) was a Minnesota-based organization for the promotion of and education in astronomy. In September 2011, it was absorbed by the Bell Museum of Natural History and the society no longer exists. ''Bell Museum and Planetarium Society Integrate Programming'', retrieved 2014 08 03 The Minnesota Planetarium operated from 1960 until it was closed in 2002. Government funding for a new planetarium was cancelled in 2011. History In 1889 the Minnesota Academy of Science was granted space in the Minneapolis Public Library for a science museum. When the Academy disbanded in 1929, the Library assumed responsibility for the science museum in a partnership that has evolved and endured for almost 80 years. In 1960, the City of Minneapolis built a new central downtown library and, to honor its partnership with science, a planetarium was included within it, the only library outside of Alexandria, Egypt, to contain such a feature. 170,000 visitors came to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereal Astrology
'' Sidereal'' and ''tropical'' are terms used to describe two different definitions of a year, applied in sidereal solar calendars or tropical solar calendars. In astrology, they refer to two different systems of ecliptic coordinates used to divide the ecliptic into twelve "signs". Each sign is divided into 30 degrees, making a total of 360 degrees. While sidereal systems of astrology define the signs relative to the apparent backwards movement of fixed stars of about 1 degree every 72 years from the perspective of the Earth, tropical systems define 0 degrees of Aries to coincide with the vernal point or vernal equinox (also known as the March equinox in the Northern hemisphere), and define the rest of the zodiac from this point. Sidereal astrology maintains the alignment between signs and constellations via corrective systems known as ayanamsas (Sanskrit: '''ayana''' "movement" + '''aṃśa "component"), to allow for the observed precession of equinoxes, whereas tropical astr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation Boundaries
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellations in the far southern sky were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |