|
Operation Skyshield
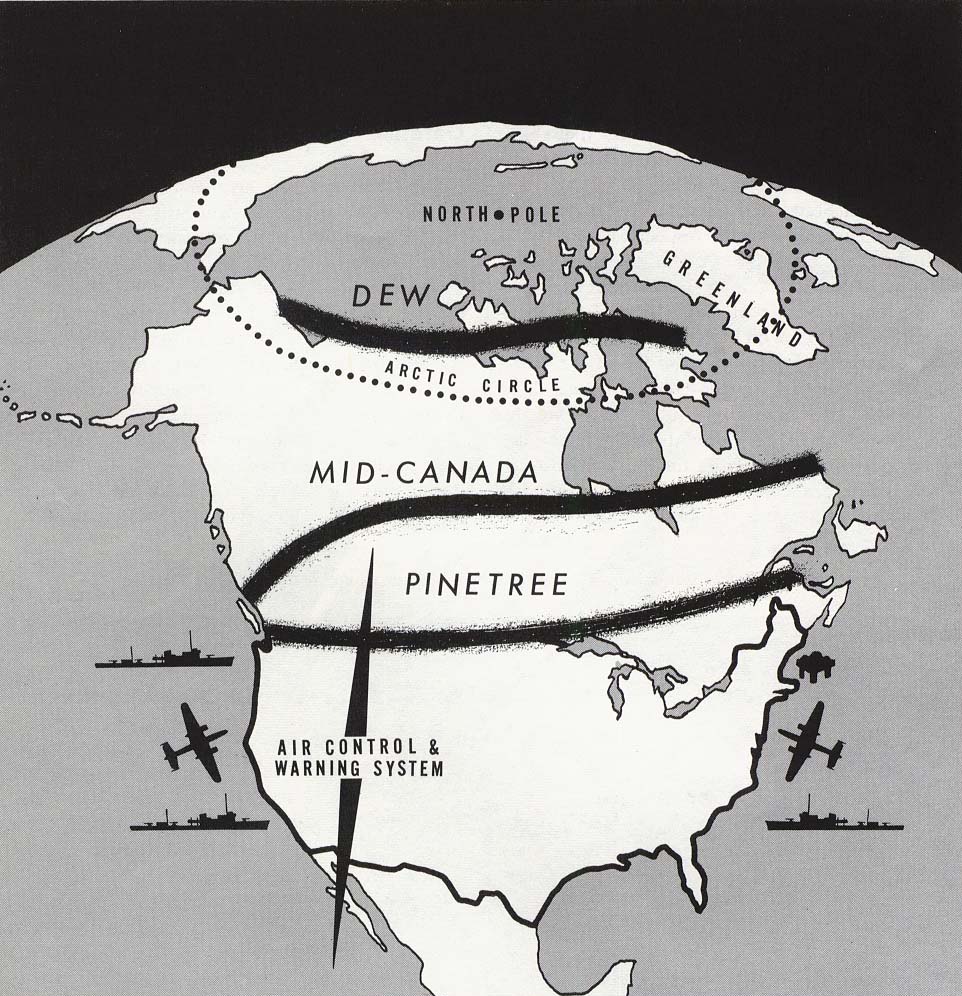
Operation Sky Shield, sometimes known as Exercise Skyshield, was a series of three large-scale military exercises conducted in the United States in 1960, 1961, and 1962 by the North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) and the Strategic Air Command (SAC) to test defenses against an air attack from the Soviet Union. The tests were intended to ensure that any attacks over the American–Canadian border or coastlines would be detected and then stopped. The operations involved 6,000 sorties flown by aircraft of the United States Air Force, British Royal Air Force (RAF) and Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), simulating Soviet fighter and bomber attacks against New York, Chicago, San Diego, Los Angeles, Washington and more. It was among the largest military aviation exercises ever held. The United States and Canada assured citizens that their defenses were "99 percent effective," but the results showed how unsuccessful the defense would be against a Soviet air attack. No more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Nike
Project Nike (Greek: Νίκη, "Victory") was a U.S. Army project, proposed in May 1945 by Bell Laboratories, to develop a line-of-sight anti-aircraft missile system. The project delivered the United States' first operational anti-aircraft missile system, the Nike Ajax, in 1953. A great number of the technologies and rocket systems used for developing the Nike Ajax were re-used for a number of functions, many of which were given the "Nike" name (after Nike, the goddess of victory from Greek mythology). The missile's first-stage solid rocket booster became the basis for many types of rocket including the Nike Hercules missile and NASA's Nike Smoke rocket, used for upper-atmosphere research. History Project Nike began during 1944 when the War Department demanded a new air defense system to combat new jet aircraft, as existing gun-based systems proved largely incapable of dealing with the speeds and altitudes at which jet aircraft operated. Two proposals were accepted. Bell La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Transport Association
Airlines for America (A4A), formerly known as Air Transport Association of America (ATA), is an American trade association and lobbying group based in Washington, D.C. that represents major North American airlines. Profile Mission A4A's stated purpose is to "foster a business and regulatory environment that ensures safe and secure air transportation and enables U.S. airlines to flourish, stimulating economic growth locally, nationally and globally". A4A advocates on behalf of participating regularly scheduled airline corporations to the U.S. Congress, state legislatures, the U.S. Department of Transportation, including the Federal Aviation Administration, and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, including the Transportation Security Administration and Customs and Border Protection. Since its founding in 1936, A4A has played a major role in all government decisions concerning aviation, including the creation of the Civil Aeronautics Board, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kindley Air Force Base
Kindley Air Force Base was a United States Air Force base in Bermuda from 1948–1970, having been operated from 1943 to 1948 by the United States Army Air Forces as ''Kindley Field''. History World War II Prior to American entry into the Second World War, the governments of the United Kingdom and the US led by Prime Minister Winston Churchill and President Roosevelt came to an agreement exchanging a number of obsolete ex-US Naval destroyers for 99-year base rights in a number of British Empire West Indian territories. Bases were also granted in Bermuda and Newfoundland, though Britain received no loans in exchange for these. This was known as the destroyers for bases deal. As the government of Bermuda had not been party to the agreement, the arrival of US engineers in 1941 came as rather a surprise to many in Bermuda. The US engineers began surveying the colony for the construction of an airfield that was envisioned as taking over most of the West End of the Island. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Military Aircraft Serials
United Kingdom military aircraft serial numbers are aircraft registration numbers used to identify individual military aircraft in the United Kingdom (UK). All UK military aircraft are allocated and display a unique registration number. A unified registration number system, maintained initially by the Air Ministry (AM), and its successor the Ministry of Defence (MoD), is used for aircraft operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF), Fleet Air Arm (FAA), and Army Air Corps (AAC). Military aircraft operated by government agencies and civilian contractors (for example QinetiQ) are also assigned registration numbers from this system. When the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was formed in 1912, its aircraft were identified by a letter/number system related to the manufacturer. The prefix 'A' was allocated to balloons of No.1 Company, Air Battalion, Royal Engineers, the prefix 'B' to aeroplanes of No.2 Company, and the prefix 'F' to aeroplanes of the Central Flying School.Bruce 1956, p.922 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas F4D Skyray
The Douglas F4D Skyray (later redesignated F-6 Skyray) is an American carrier-based fighter/ interceptor built by the Douglas Aircraft Company. Although it was in service for a relatively short time (1956–1964) and never entered combat, it was the first carrier-launched aircraft to hold the world's absolute speed record, at 752.943 mph,Angelluci 1987, p. 92. (1211.744 km/h) and was the first United States Navy and United States Marine Corps fighter that could exceed Mach 1 in level flight.Francillon 1979, p. 480. It was the last fighter produced by the Douglas Aircraft Company before it merged with McDonnell Aircraft and became McDonnell Douglas. The F5D Skylancer was an advanced development of the F4D Skyray that did not go into service. Design and development The Skyray was designed to meet a Navy requirement issued in 1947 for a fighter aircraft that could intercept and destroy an enemy aircraft at an altitude of 50,000 ft (15,240 m) within five minu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop F-89 Scorpion
The Northrop F-89 Scorpion was an American all-weather, twin-engined interceptor aircraft built during the 1950s, the first jet-powered aircraft designed for that role from the outset to enter service. Though its straight wings limited its performance, it was among the first United States Air Force (USAF) jet fighters equipped with guided missiles and notably the first combat aircraft armed with air-to-air nuclear weapons (the unguided Genie rocket). Design and development The Scorpion stemmed from a United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) Air Technical Service Command specification ("Military Characteristics for All-Weather Fighting Aircraft") for a night fighter to replace the P-61 Black Widow. The preliminary specification, sent to aircraft manufacturers on 28 August 1945, required two engines and an armament of six guns, either machine guns or autocannon. The revised specification was issued on 23 November; it did not specify jet propulsion, but the desired maximum speed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed F-104 Starfighter
The Lockheed F-104 Starfighter is an American single-engine, supersonic air superiority fighter which was extensively deployed as a fighter-bomber during the Cold War. Created as a day fighter by Lockheed as one of the "Century Series" of fighter aircraft for the United States Air Force (USAF), it was developed into an all-weather multirole aircraft in the early 1960s and produced by several other nations, seeing widespread service outside the United States. After a series of interviews with Korean War fighter pilots in 1951, Kelly Johnson, then lead designer at Lockheed, opted to reverse the trend of ever-larger and more complex fighters and produce a simple, lightweight aircraft with maximum altitude and climb performance. On 4 March 1954, the Lockheed XF-104 took to the skies for the first time, and on 26 February 1958 the production fighter was activated by the USAF. Only a few months later it was pressed into action during the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, when it was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair F-102 Delta Dagger
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was an American interceptor aircraft designed and manufactured by Convair. Built as part of the backbone of the United States Air Force's air defenses in the late 1950s, it entered service in 1956. Its main purpose was to intercept invading Soviet strategic bomber fleets (primarily the Tupolev Tu-95) during the Cold War. A total of 1,000 F-102s were built. A member of the Century Series, the F-102 was the USAF's first operational supersonic interceptor and delta-wing fighter. It used an internal weapons bay to carry both guided missiles and rockets. As originally designed, it could not achieve Mach 1 supersonic flight until redesigned with area ruling. The F-102 replaced subsonic fighter types such as the Northrop F-89 Scorpion, and by the 1960s, it saw limited service in the Vietnam War in bomber escort and ground-attack roles. It was supplemented by McDonnell F-101 Voodoos and, later, by McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom IIs. Many of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor in U.S. Air Force service to date. It was gradually retired during the 1980s, with the QF-106 drone conversions of the aircraft being used until 1998 under the ''Pacer Six'' program.Winchester 2006, p. 55. Development Antecedents The F-106 was the ultimate development of the USAF's 1954 interceptor program of the early 1950s. The initial winner of this competition had been the F-102 Delta Dagger, but early versions of this aircraft had demonstrated extremely poor performance, limited to subsonic speeds and relatively low altitudes. During the testing program the F-102 underwent numerous changes to improve its performance, notably the application of the area rule to the fuselage shaping and a change of engine, and the dropping of the advanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell F-101 Voodoo
The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo is a supersonic jet fighter which served the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF). Initially designed by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation as a long-range bomber escort (known as a ''penetration fighter'') for the USAF's Strategic Air Command (SAC), the Voodoo was instead developed as a nuclear-armed fighter-bomber for the USAF's Tactical Air Command (TAC), and as a photo reconnaissance aircraft based on the same airframe. An F-101A set a number of world speed records for jet-powered aircraft, including fastest airspeed, attaining per hour on 12 December 1957. They operated in the reconnaissance role until 1979. Delays in the 1954 interceptor project led to demands for an interim interceptor aircraft design, a role that was eventually won by the B model of the Voodoo. This required extensive modifications to add a large radar to the nose of the aircraft, a second crew member to operate it, and a new weapons bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot (UK Magazine)
''Pilot'' is a monthly general aviation magazine based in the United Kingdom. It is "Britain's best selling GA magazine" and the only one still in print. History and profile ''Pilot'' was launched in 1966. The former publisher was Lernhurst Publications Limited. The magazine is a part of Archant Specialist, from Archant. The headquarters is in Norwich. The editor since 2011 is Philip Whiteman, who was deputy editor under James Gilbert, who served as editor and publisher before the magazine was acquired by Archant. Philip owns and operates a Piper Cub. The magazine also operates PilotWeb, on which there is news, overviews of the magazine, forums and information for beginners in aviation. The editor between 2005 and 2011 was Nick Bloom who still regularly writes for the magazine. In February 2022, ''Pilot'' was sold to Kelsey Media. Content The magazine typically contains a news section, a number of flight tests and buyers guides, a section detailing what is involved in vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Owners And Pilots Association
The Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) is a Frederick, Maryland-based American non-profit political organization that advocates for general aviation. AOPA's membership consists mainly of general aviation pilots in the United States. AOPA exists to serve the interests of its members as aircraft owners and pilots and to promote the economy, safety, utility, and popularity of flight in general aviation aircraft. With 384,915 members in 2012, AOPA is the largest aviation association in the world, although it had decreased in membership from 414,224 in 2010, a loss of 7% in two years. AOPA is affiliated with other similar organizations in other countries through membership in the International Council of Aircraft Owner and Pilot Associations (IAOPA). In 2015, AOPA was inducted into the International Air & Space Hall of Fame at the San Diego Air & Space Museum. History The organization started at Wings Field in Blue Bell, Pennsylvania. On 24 April 1932, The Philadel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




%2C_in_October_1953.jpg)

.jpg)


