|
Operation Moked
Operation Focus ( he, מבצע מוקד, ''Mivtza Moked'') was the opening airstrike by Israel at the start of the Six-Day War in 1967. It is sometimes referred to as the "Sinai Air Strike". At 07:45 on 5 June 1967, the Israeli Air Force (IAF) under Maj. Gen. Mordechai Hod launched a massive airstrike that destroyed the majority of the Egyptian Air Force on the ground. Following Syrian and Jordanian attacks in retaliation, the Israeli Air Force proceeded to bomb air bases in those countries. By noon, the Egyptian, Jordanian and Syrian Air Forces, with about 450 aircraft, were destroyed. It was also very successful in disabling 18 airfields in Egypt, hindering Egyptian Air Force operations for the duration of the war, and remains one of the most successful air attack campaigns in military history. Summary The IAF launched all but 12 of its nearly 200 operational jets in three main waves of aerial attacks, and several smaller waves in the days following the operation. A total of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
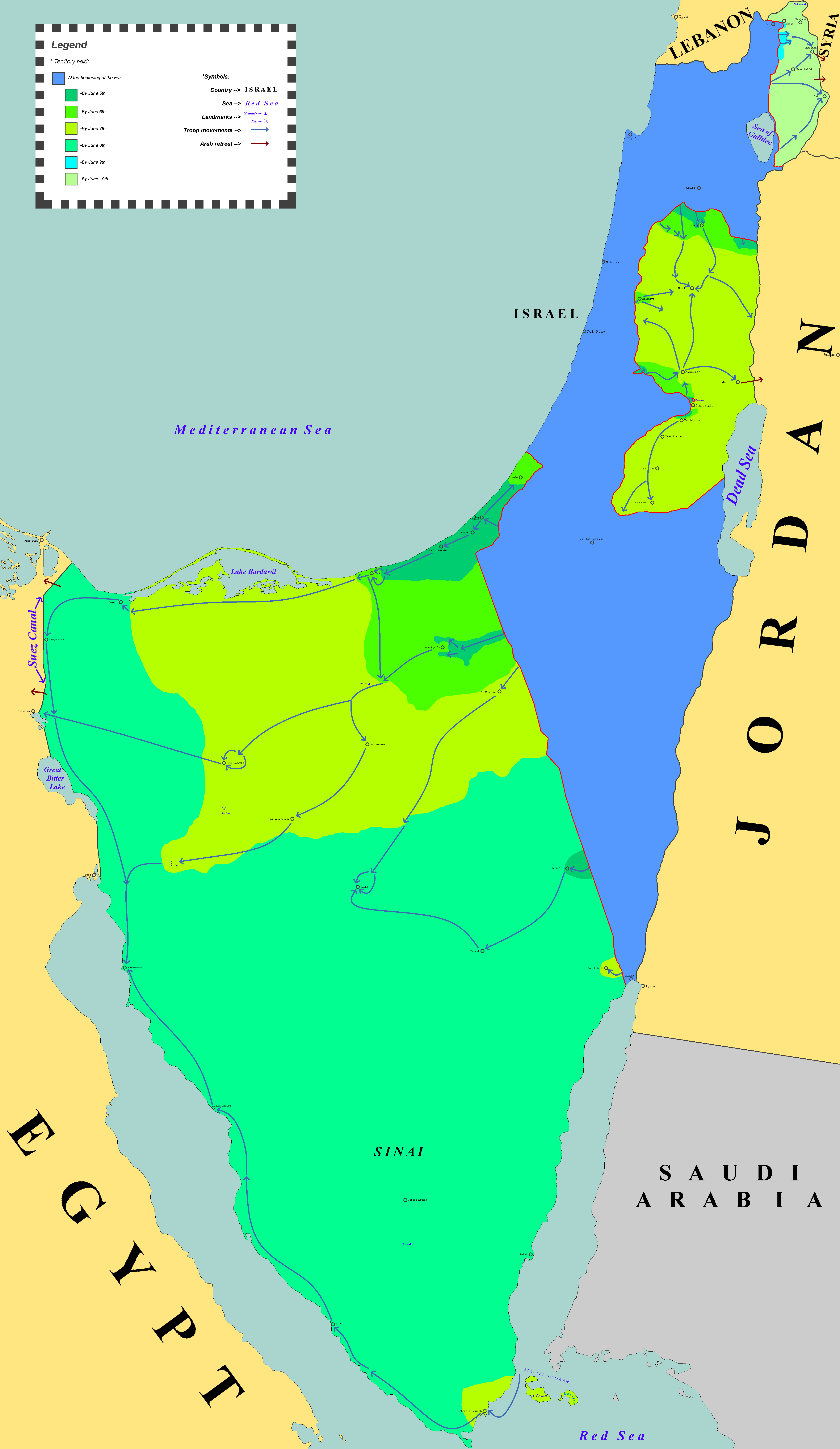
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-runway Penetration Bomb
Anti-runway penetration bombs are systems involving bombs or bomblets designed to disrupt the surface of an airfield runway and make it unusable for flight operations. Perhaps the most strategically decisive, best known, and first wartime use of specialized cratering anti-runway weapons was by Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. The dibber bombs played a major part in the near complete destruction of the large Egyptian Air Force, mostly on the ground, in a preemptive strike on the first morning of the war by the commitment of the whole of the far smaller Israeli Air Force to the strike. The surprising elimination of the Egyptian air force and resulting Israeli air supremacy contributed significantly to the outcome of the war on all fronts. The IMI 'Runway Piercing Bomb' was a prototype Israeli-French anti-runway weapon. It used rocket braking over the target and a second rocket burst to plunge through the runway surface and explode. One system available from 1977 diverging from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Superiority
Aerial supremacy (also air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of command of the sea. Air power has increasingly become a powerful element of military campaigns; military planners view having an environment of at least air superiority as a necessity. Air supremacy allows increased bombing efforts, tactical air support for ground forces, paratroop assaults, airdrops and simple cargo plane transfers, which can move ground forces and supplies. Air power is a function of the degree of air superiority and numbers or types of aircraft, but it represents a situation that defies black-and-white characterization. The degree of a force's air control is a zero-sum game with its opponent's; increasing control by one corresponds to decreasing control by the other. Air forces unable to contest for air superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast, Saudi Arabia to the south, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraq is home to diverse ethnic groups including Iraqi Arabs, Kurds, Iraqi Turkmen, Turkmens, Assyrian people, Assyrians, Armenians in Iraq, Armenians, Yazidis, Mandaeans, Iranians in Iraq, Persians and Shabaks, Shabakis with similarly diverse Geography of Iraq, geography and Wildlife of Iraq, wildlife. The vast majority of the country's 44 million residents are Muslims – the notable other faiths are Christianity in Iraq, Christianity, Yazidism, Mandaeism, Yarsanism and Zoroastrianism. The official langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SA-2
The S-75 (Russian: С-75; NATO reporting name SA-2 Guideline) is a Soviet-designed, high-altitude air defence system, built around a surface-to-air missile with command guidance. Following its first deployment in 1957 it became one of the most widely deployed air defence systems in history. It scored the first destruction of an enemy aircraft by a surface-to-air missile, with the shooting down of a Taiwanese Martin RB-57D Canberra over China on 7 October 1959 that was hit by a salvo of three V-750 (1D) missiles at an altitude of 20 km (65,600 ft). This success was credited to Chinese fighter aircraft at the time to keep the S-75 program secret. This system first gained international fame when an S-75 battery, using the newer, longer-range, higher-altitude V-750VN (13D) missile was deployed in the 1960 U-2 incident, when it shot down the Lockheed U-2, U-2 of Francis Gary Powers overflying the Soviet Union on May 1, 1960. The system was also deployed in Cuba during the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almaza Air Base
Almaza Air Force Base Airport is a regional airport in north-eastern Cairo, the capital of Egypt. It was established as a civilian aerodrome, but was partly taken over by the British military, designated RAF Heliopolis and later RAF Almaza. Today it is a military aerodrome of the Egyptian Air Force as well as regional civil airport. History The aerodrome was established in the Cairo suburb of Heliopolis in February 1910, when Baron Empain organised the first air meeting in Africa. The event was supervised by the ''Aéro-Club de France'', and attracted several leading French aviators, including Hubert Latham, Henri Rougier, Jacques Balsan, Hubert Le Blon, Arthur Duray, and Mme. Raymonde de Laroche. Other entrants included Hans Grade from Germany, Frederick van Riemsdijk from the Netherlands, and Hayden Sands from the USA (although apparently not an official entrant). The only British flier A. Mortimer Singer crashed during a practice flight, breaking his leg, and was forced to wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohamed Sedky Mahmoud
Mohamed Sedky Mahmoud ( ar, محمد صدقي محمود, December 12, 1914 – 1984) was an Egyptian military leader. He served as Air Force Chief of Staff from June 23, 1953 to September 19, 1959, and Air Force and Defense Commander from September 20, 1959 to June 11, 1967. Sedky Mahmoud was born in Sendalia village, Daqahliah. He graduated from the Egyptian Military Academy in 1936, and studied at the Abu Swair Aviation School No. 4. He became the first Egyptian instructor in 1936, later became the lead aviation instructor and headed the High Aviation School in 1944. Sedky Mahmoud achieved the rank of Wing Commander and became head of the Dekhila Air Base in August 1949, and then Almaza Air Base in August 1951. He was promoted as the 1st Lt. Gen. in 1952. Air Marshal M Sedky Mahmoud was involved in the development of the Helwan HA-300. During his tenure, he carried out official visits to the United States, India, Algeria, Iraq, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia. He took part in World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdel Hakim Amer
Mohamed Abdel Hakim Amer ( arz, محمد عبد الحكيم عامر, ; 11 December 1919 – 13 September 1967) was an Egyptian military officer and politician. Amer served in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and played a leading role in the military coup that overthrew King Farouk in 1952. After leading Egyptian forces in the 1956 Suez war, he was appointed Minister for Defense by President Gamal Abdel Nasser and was Egyptian Vice President between 1958 to 1965. Early life and education Amer was born in Samalut, in the El Minya on 11 December 1919. He was from an affluent family, and his father was a land owner and village mayor. His uncle served as the minister of war during the reign of King Farouk. After finishing school, Amer attended the Egyptian Military Academy and graduated in 1938. He was commissioned into the Egyptian Army in 1939. Military career Amer served in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, took part in the 1952 Revolution and commanded the Egyptian Army in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-aircraft Warfare
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes Surface-to-air missile, surface based, subsurface (Submarine#Armament, submarine launched), and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures (e.g. barrage balloons). It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries, the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defense, Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight. In some countries, such as Britain and Germany during the World War II, Second World War, the Soviet Union, and modern NATO a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardened Aircraft Shelter
A hardened aircraft shelter (HAS) or protective aircraft shelter (PAS) is a reinforced hangar to house and protect military aircraft from enemy attack. Cost considerations and building practicalities limit their use to fighter size aircraft. Background HASs are a passive defence measure (i.e., they limit the effect of an attack, as opposed to active defences, such as surface-to-air missiles) which aim to prevent or at least degrade enemy attacks. The widespread adoption of hardened aircraft shelters can be traced back to lessons learned from Operation Focus in the 1967 Arab-Israeli Six-Day War, when the Israeli Air Force destroyed the unprotected Egyptian Air Force, at the time the largest and most advanced air force in the Arab world, at its airfields’ airbases. As with many military items, whether structures, tanks or aircraft, its most prolific use was during the Cold War. NATO and Warsaw Pact countries built hundreds of HASs across Europe. In this context, hardened airc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |