|
Operation Bolo
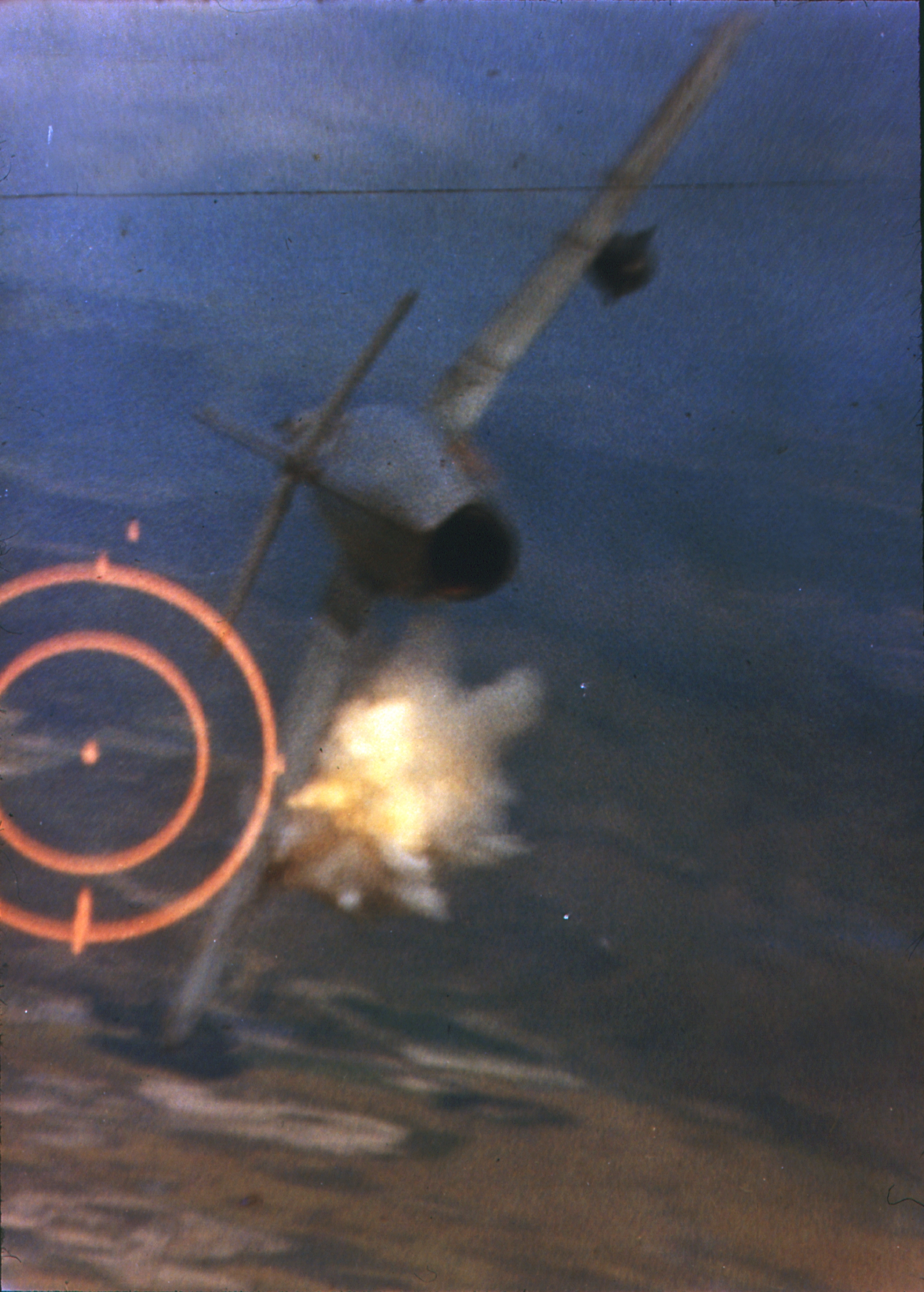
Operation Bolo was a United States Air Force mission during the Vietnam War, considered to be a successful combat ruse. The mission was a response to the heavy losses sustained during the Operation Rolling Thunder aerial-bombardment campaign of 1966, during which Vietnam People's Air Force fighter jets had evaded U.S. escort fighters and attacked U.S. bombers flying predictable routes. On January 2, 1967, U.S. Air Force F-4 Phantom II multirole fighters flew a mission along flight paths typically used by the bombers during Rolling Thunder. The ruse drew an attack by Vietnamese Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 interceptors, whose pilots expected to find heavily loaded fighter-bombers. Instead, they were met by the far more agile F-4s, which shot down seven of the MiGs. The battle prompted VPAF pilots and strategists, as well as Soviet tacticians, to re-evaluate the tactics and deployment of the MiG-21. Background Opposing aircraft The F-4 Phantom II had been in operational service with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rules Of Engagement
Rules of engagement (ROE) are the internal rules or directives afforded military forces (including individuals) that define the circumstances, conditions, degree, and manner in which the use of force, or actions which might be construed as provocative, may be applied. They provide authorization for and/or limits on, among other things, the use of force and the employment of certain specific capabilities. In some nations, articulated ROE have the status of guidance to military forces, while in other nations, ROE constitute lawful command. Rules of engagement do not normally dictate how a result is to be achieved, but will indicate what measures may be unacceptable. While ROE is used in both domestic and international operations by some militaries, ROE is not used for domestic operations in the United States. Instead, the use of force by the U.S. military in such situations is governed by Rules for the Use of Force (RUF). An abbreviated description of the rules of engagement ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogfight
A dogfight, or dog fight, is an aerial battle between fighter aircraft conducted at close range. Dogfighting first occurred in Mexico in 1913, shortly after the invention of the airplane. Until at least 1992, it was a component in every major war, though with steadily declining frequency. Since then, longer-range weapons have made dogfighting largely obsolete. Modern terminology for air-to-air combat is air combat maneuvering (ACM), which refers to tactical situations requiring the use of individual basic fighter maneuvers (BFM) to attack or evade one or more opponents. This differs from aerial warfare, which deals with the strategy involved in planning and executing various missions. Etymology The term ''dogfight'' has been used for centuries to describe a melee: a fierce, fast-paced close quarters battle between two or more opponents. The term gained popularity during World War II, although its origin in air combat can be traced to the latter years of World War I. One of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Ace
A flying ace, fighter ace or air ace is a military aviator credited with shooting down five or more enemy aircraft during aerial combat. The exact number of aerial victories required to officially qualify as an ace is varied, but is usually considered to be five or more. The concept of the "ace" emerged in 1915 during World War I, at the same time as aerial dogfighting. It was a propaganda term intended to provide the home front with a cult of the hero in what was otherwise a war of attrition. The individual actions of aces were widely reported and the image was disseminated of the ace as a chivalrous knight reminiscent of a bygone era. For a brief early period when air-to-air combat was just being invented, the exceptionally skilled pilot could shape the battle in the skies. For most of the war, however, the image of the ace had little to do with the reality of air warfare, in which fighters fought in formation and air superiority depended heavily on the relative availability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Tactical Fighter Wing
The United States Air Force 8th Fighter Wing is the host unit at Kunsan Air Base, Republic of Korea and is assigned to Seventh Air Force. Seventh Air Force falls under Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). The Wing's 8th Operations Group is the successor of the 8th Pursuit Group, one of the 15 original combat air groups formed by the Army before World War II. Established in Japan after World War II in 1948, the wing flew combat missions throughout the Korean War. Redesignated the 8th Tactical Fighter Wing in 1958, it remained in Japan until 1964. After a year in California, it moved to Southeast Asia, where its F-4 Phantom II crews earned the nicknames "MiG killers" and "bridge busters". In 1974 the wing relocated to Kunsan Air Base, South Korea, where it was redesignated the 8th Fighter Wing in 1992. History : ''For additional history and lineage, see 8th Operations Group'' Established in August 1948 in Japan, the wing provided air defense to the islands. On 20 January 1951, the wing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Air Patrol
Combat air patrol (CAP) is a type of flying mission for fighter aircraft. A combat air patrol is an aircraft patrol provided over an objective area, over the force protected, over the critical area of a combat zone, or over an air defense area, for the purpose of intercepting and destroying hostile aircraft before they reach their target. Combat air patrols apply to both overland and overwater operations, protecting other aircraft, fixed and mobile sites on land, or ships at sea. Known by the acronym CAP, it typically entails fighters flying a tactical pattern around or screening a defended target, while looking for incoming attackers. Effective CAP patterns may include aircraft positioned at both high and low altitudes, in order to shorten response times when an attack is detected. Modern CAPs are either GCI or AWACS-controlled to provide maximum early warning for defensive reaction. The first CAPs were characteristic of aircraft carrier operations, where CAPs were flown to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-air Missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft system; in modern armed forces, missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first attempt at SAM development took place during World War II, but no operational systems were introduced. Further development in the 1940s and 1950s led to operational systems being introduced by most major forces during the second half of the 1950s. Smaller systems, suitable for close-range work, evolved through the 1960s and 1970s, to modern systems that are man-portable. Shipborne systems followed the evolution of land-based models, starting with long-range weapons and steadily evolving toward smaller designs to provide a layered defence. This evolution of design increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Countermeasure
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting information to an enemy. The system may make many separate targets appear to the enemy, or make the real target appear to disappear or move about randomly. It is used effectively to protect aircraft from guided missiles. Most air forces use ECM to protect their aircraft from attack. It has also been deployed by military ships and recently on some advanced tanks to fool laser/IR guided missiles. It is frequently coupled with stealth advances so that the ECM systems have an easier job. Offensive ECM often takes the form of jamming. Self-protecting (defensive) ECM includes using blip enhancement Blip enhancement is an electronic warfare technique used to fool radar. When the radar transmits a burst of energy some of that energy is reflected off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rules Of Engagement
Rules of engagement (ROE) are the internal rules or directives afforded military forces (including individuals) that define the circumstances, conditions, degree, and manner in which the use of force, or actions which might be construed as provocative, may be applied. They provide authorization for and/or limits on, among other things, the use of force and the employment of certain specific capabilities. In some nations, articulated ROE have the status of guidance to military forces, while in other nations, ROE constitute lawful command. Rules of engagement do not normally dictate how a result is to be achieved, but will indicate what measures may be unacceptable. While ROE is used in both domestic and international operations by some militaries, ROE is not used for domestic operations in the United States. Instead, the use of force by the U.S. military in such situations is governed by Rules for the Use of Force (RUF). An abbreviated description of the rules of engagement ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leland T
Leland may refer to: Places United States * Leland, Illinois, a village * Leland, Iowa, a city * Leland, Michigan, an unincorporated community and census-designated place * Leland, Mississippi, a city * Leland, North Carolina, a town * Leland, Oregon, an unincorporated community * Leland, Utah, an unincorporated community * Leland, Washington, an unincorporated community * Leland, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * Leland Township, Michigan * Leland River, Michigan * Leland Pond, New York Elsewhere * Leland, Norway, a village * Mount Leland, Victoria Land, Antarctica People Given name * Leland Austin (born 1986), American rapper under the stage name Yung L.A. * Leland Bardwell (1922–2016), Irish poet, novelist and playwright * Leland Chapman (born 1976), American bounty hunter on the reality television series ''Dog the Bounty Hunter'' * Leland Christensen (1959–2022), American politician * Leland D. Melvin (born 1964), American engineer and retired astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-controlled Interception
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic was pioneered during World War I by the London Air Defence Area organization, which became the Royal Air Force's Dowding system in World War II, the first national-scale system. The ''Luftwaffe'' introduced similar systems during the war, but most other combatants did not suffer the same threat of air attack and did not develop complex systems like these until the Cold War era. Today the term GCI refers to the style of battle direction, but during WWII it also referred to the radars themselves. Specifically, the term was used to describe a new generation of radars that spun on their vertical axis in order to provide a complete 360 degree view of the sky around the station. Previous systems, notably Chain Home (CH), could only be directed along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-105 Thunderchief
The Republic F-105 Thunderchief is an American supersonic fighter-bomber that served with the United States Air Force from 1958 to 1984. Capable of Mach 2, it conducted the majority of strike bombing missions during the early years of the Vietnam War; it was the only American aircraft to have been removed from combat due to high loss rates. It was originally designed as a single-seat, nuclear-attack aircraft; a two-seat Wild Weasel version was later developed for the specialized Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD) role against surface-to-air missile sites. The F-105 was commonly known as the "Thud" by its crews. As a follow-on to the Mach 1 capable North American F-100 Super Sabre, the F-105 was also armed with missiles and a rotary cannon; however, its design was tailored to high-speed low-altitude penetration carrying a single nuclear weapon internally. First flown in 1955, the Thunderchief entered service in 1958. The single-engine F-105 could deliver a bomb load great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |