|
OpenSolaris Network Virtualization And Resource Control
Solaris network virtualization and resource control is a set of features originally developed by Sun Microsystems as the OpenSolaris Crossbow umbrella project, providing an internal network virtualization and quality of service framework within the Solaris Operating System. Major features of the Crossbow project include: * Virtual NIC ( VNIC) pseudo-network interface technology * Exclusive IP zones * Bandwidth management and flow control on a per interface and per VNIC basis Description The Crossbow project software, combined with next generation network interfaces like xge and bge, enable network virtualization and resource control for a single system. By combining VNICs with features such aexclusive IP zonesor the Sun xVM hypervisor, system administrators can run applications on separate virtual machines to improve performance and provide security. Resource management and flow control features provide bandwidth management and quality of service for packet flows on separate virt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. (Sun for short) was an American technology company that sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services and created the Java programming language, the Solaris operating system, ZFS, the Network File System (NFS), and SPARC microprocessors. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualized computing. Notable Sun acquisitions include Cray Business Systems Division, Storagetek, and ''Innotek GmbH'', creators of VirtualBox. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California (part of Silicon Valley), on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center. Sun products included computer servers and workstations built on its own RISC-based SPARC processor architecture, as well as on x86-based AMD Opteron and Intel Xeon processors. Sun also developed its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAC Address
A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in communications within a network segment. This use is common in most IEEE 802 networking technologies, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Within the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) network model, MAC addresses are used in the medium access control protocol sublayer of the data link layer. As typically represented, MAC addresses are recognizable as six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by hyphens, colons, or without a separator. MAC addresses are primarily assigned by device manufacturers, and are therefore often referred to as the burned-in address, or as an Ethernet hardware address, hardware address, or physical address. Each address can be stored in hardware, such as the card's read-only memory, or by a firmware mechanism. Many network interfaces, however, support changing their MAC address. The address typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Virtualization
In computing, network virtualization is the process of combining hardware and software network resources and network functionality into a single, software-based administrative entity, a virtual network. Network virtualization involves platform virtualization, often combined with resource virtualization. Network virtualization is categorized as either external virtualization, combining many networks or parts of networks into a virtual unit, or internal virtualization, providing network-like functionality to software containers on a single network server. In software testing, software developers use network virtualization to test software which are under development in a simulation of the network environments in which the software is intended to operate. As a component of application performance engineering, network virtualization enables developers to emulate connections between applications, services, dependencies, and end users in a test environment without having to physically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solaris Containers
Solaris Containers (including Solaris Zones) is an implementation of operating system-level virtualization technology for x86 and SPARC systems, first released publicly in February 2004 in build 51 beta of Solaris 10, and subsequently in the first full release of Solaris 10, 2005. It is present in illumos (formerly OpenSolaris) distributions, such as OpenIndiana, SmartOS, Tribblix and OmniOS, as well as in the official Oracle Solaris 11 release. A Solaris Container is the combination of system resource controls and the boundary separation provided by ''zones''. Zones act as completely isolated virtual servers within a single operating system instance. By consolidating multiple sets of application services onto one system and by placing each into isolated virtual server containers, system administrators can reduce cost and provide most of the same protections of separate machines on a single machine. Terminology The name of this technology changed during development and the pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illumos
Illumos (stylized as illumos) is a partly free and open-source Unix operating system. It is based on OpenSolaris, which was based on System V Release 4 (SVR4) and the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Illumos comprises a kernel, device drivers, system libraries, and utility software for system administration. This core is now the base for many different open-sourced illumos distributions, in a similar way in which the Linux kernel is used in different Linux distributions. The maintainers write ''illumos'' in lowercase since some computer fonts do not clearly distinguish a lowercase ''L'' from an uppercase ''i'': ''Il'' (see homoglyph). The project name is a combination of words ''illuminare'' from Latin for ''to light'' and ''OS'' for ''Operating System''. Overview Illumos was announced via webinar on Thursday, 3 August 2010, as a community effort of some core Solaris engineers to create a truly open source Solaris by swapping closed source bits of OpenSolaris wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Acquisition Of Sun
The acquisition of Sun Microsystems by Oracle Corporation was completed on January 27, 2010. After the acquisition was completed, Oracle, only a software vendor prior to the merger, owned Sun's hardware product lines, such as SPARC Enterprise, as well as Sun's software product lines, including the Java programming language. Concerns about Sun's position as a competitor to Oracle were raised by antitrust regulators, open source advocates, customers, and employees over the acquisition. The EU Commission delayed the acquisition for several months over questions about Oracle's plans for MySQL, Sun's competitor to Oracle Database. The commission finally approved the takeover, apparently pressured by the United States to do so, according to a WikiLeaks cable released in September 2011. History In late 2008, Sun was approached by IBM to discuss a possible merger. At about the same time, Sun also began discussions with another company, widely rumored but not confirmed to be Hewlett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solaris (operating System)
Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. After the Sun acquisition by Oracle in 2010, it was renamed Oracle Solaris. Solaris superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993, and became known for its scalability, especially on SPARC systems, and for originating many innovative features such as DTrace, ZFS and Time Slider. Solaris supports SPARC and x86-64 workstations and servers from Oracle and other vendors. Solaris was registered as compliant with the Single UNIX Specification until 29 April 2019. Historically, Solaris was developed as proprietary software. In June 2005, Sun Microsystems released most of the codebase under the CDDL license, and founded the OpenSolaris open-source project. With OpenSolaris, Sun wanted to build a developer and user community around the software. After the acquisition of Sun Microsystems in January 2010, Oracle decided to discontinue the OpenSolaris distribution and the development model. In Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snoop (software)
Snoop software is a command line packet analyzer included in the Solaris Operating System created by Sun Microsystems. Its source code was available via the OpenSolaris project. See also *Comparison of packet analyzers *Network tap A network tap is a system that monitors events on a local network. A tap is typically a dedicated hardware device, which provides a way to access the data flowing across a computer network. The network tap has (at least) three ports: an ''A port ... References External linksTCP/IP and Data Communications Administration Guide [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
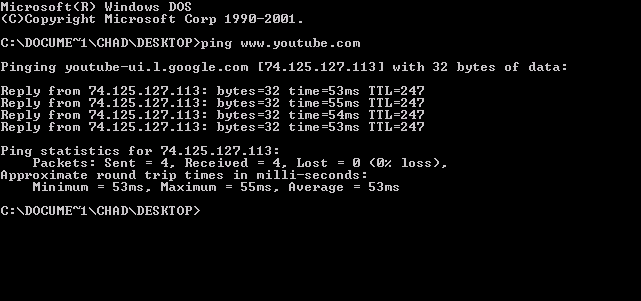
Ping (networking Utility)
ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It is available for virtually all operating systems that have networking capability, including most embedded network administration software. Ping measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. The name comes from active sonar terminology that sends a pulse of sound and listens for the echo to detect objects under water. Ping operates by means of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets. ''Pinging'' involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The program reports errors, packet loss, and a statistical summary of the results, typically including the minimum, maximum, the mean round-trip times, and standard deviation of the mean. The command-line options of the ping utility and its output vary between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Link Layer
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer. The data link layer is concerned with local delivery of frames between nodes on the same level of the network. Data-link frames, as these protocol data units are called, do not cross the boundaries of a local area network. Inter-network routing and global addressing are higher-layer functions, allowing data-link protocols to focus on local delivery, addressing, and media arbitration. In this way, the data link layer is analogous to a neighborhood traffic cop; it endeavors to arbitrate between parties contending for access to a medium, without con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Interface Controller
A network interface controller (NIC, also known as a network interface card, network adapter, LAN adapter or physical network interface, and by similar terms) is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network. Early network interface controllers were commonly implemented on expansion cards that plugged into a computer bus. The low cost and ubiquity of the Ethernet standard means that most newer computers have a network interface built into the motherboard, or is contained into a USB-connected dongle. Modern network interface controllers offer advanced features such as interrupt and DMA interfaces to the host processors, support for multiple receive and transmit queues, partitioning into multiple logical interfaces, and on-controller network traffic processing such as the TCP offload engine. Purpose The network controller implements the electronic circuitry required to communicate using a specific physical layer and data link layer standard such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris () is a discontinued open-source computer operating system based on Solaris and created by Sun Microsystems. It was also, perhaps confusingly, the name of a project initiated by Sun to build a developer and user community around the eponymous operating system software. OpenSolaris is a descendant of the UNIX System V Release 4 (SVR4) code base developed by Sun and AT&T in the late 1980s and is the only version of the System V variant of UNIX available as open source. OpenSolaris was developed as a combination of several software ''consolidations'' that were open sourced starting with Solaris 10. It includes a variety of free software, including popular desktop and server software. After Oracle’s acquisition of Sun Microsystems in 2010, Oracle discontinued development of OpenSolaris in house, pivoting to focus exclusively on the development of the proprietary Solaris Express (now Oracle Solaris). Prior to Oracle's close-sourcing Solaris, a group of former O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |