|
Ontario (mine)
The Ontario silver mine is a mine that was active starting in 1872, and is located near Park City, Utah, United States. History The lode was discovered by accident on 19 January 1872 by Herman Budden, Rector Steen (Pike), John Kain, and Gus McDowell. The mine was purchased by George Hearst through R. C. Chambers from the prospectors for $27,000 on 24 August 1872. Hearst and his business partners James Ben Ali Haggin and Lloyd Tevis owned this mine and constructed the necessary infrastructure to make it productive, including hoists and stamp mill. The mine was not profitable for its first three years. According to legend, expenses of development substantially drained Hearst's financial resources. As a result of his straitened circumstances, Hearst sold his home and horses, and even dismissed his servants and enrolled his son William Randolph Hearst in public school. Chambers, who had been retained as manager, brought the bonanza ore body into production by the late 1870s. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic viability of investing in the equipment, labor, and energy required to extract, refine and transport the materials found at the mine to manufacturers who can use the material. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
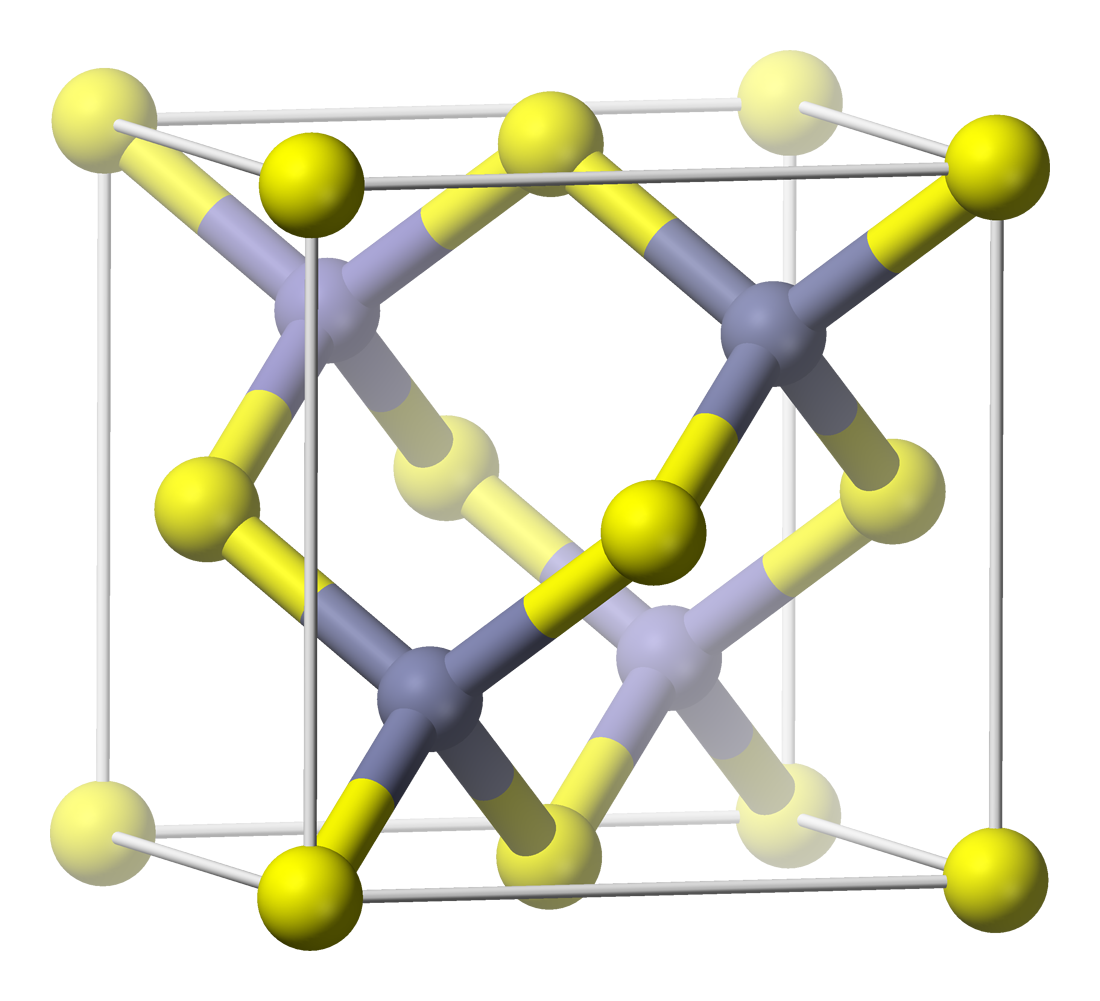
Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landmarks In Utah
A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and is often visible from long distances. In modern use, the term can also be applied to smaller structures or features, that have become local or national symbols. Etymology In old English the word ''landmearc'' (from ''land'' + ''mearc'' (mark)) was used to describe a boundary marker, an "object set up to mark the boundaries of a kingdom, estate, etc.". Starting from approx. 1560, this understanding of landmark was replaced by a more general one. A landmark became a "conspicuous object in a landscape". A ''landmark'' literally meant a geographic feature used by explorers and others to find their way back or through an area. For example, the Table Mountain near Cape Town, South Africa is used as the landmark to help sailors to navigate around southern tip of Africa during the Age of Exploration. Artificial structures are also sometimes built to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1872 In Utah Territory
Year 187 ( CLXXXVII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Quintius and Aelianus (or, less frequently, year 940 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 187 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Septimius Severus marries Julia Domna (age 17), a Syrian princess, at Lugdunum (modern-day Lyon). She is the youngest daughter of high-priest Julius Bassianus – a descendant of the Royal House of Emesa. Her elder sister is Julia Maesa. * Clodius Albinus defeats the Chatti, a highly organized German tribe that controlled the area that includes the Black Forest. By topic Religion * Olympianus succeeds Pertinax as bishop of Byzantium (until 198). Births * Cao Pi, Chinese emperor of the Cao Wei state (d. 226) * Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearst Family
Hearst may refer to: Places * Hearst, former name of Hacienda, California, United States * Hearst, Ontario, town in Northern Ontario, Canada * Hearst, California, an unincorporated community in Mendocino County, United States * Hearst Island, an island in Antarctica * Hearst Castle, a mansion built by William Randolph Hearst in San Simeon, California, United States * Hearst Block, a provincial government building in Toronto, Ontario, Canada People * Hearst (surname) * William Randolph Hearst (1863–1951), newspaper magnate * Hunter Hearst Helmsley (b. 1969), WWE professional wrestler Arts, entertainment, and media * Hearst College, a fictional College in the CW series ''Veronica Mars'' * Hearst Communications, a privately held media conglomerate * Hearst Television, Hearst Communications' broadcast television division (formerly Hearst-Argyle Television) Other uses * Université de Hearst, a French-language university federated with Laurentian University, based in Hearst, Ontario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mines In Utah
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging *Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging *Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine Grammar *Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun Military * Anti-tank mine, a land mine made for use against armored vehicles * Antipersonnel mine, a land mine targeting people walking around, either with explosives or poison gas * Bangalore mine, colloquial name for the Bangalore torpedo, a man-portable explosive device for clearing a path through wire obstacles and land mines * Cluster bomb, an aerial bomb which releases many small submunitions, which often act as mines * Land mine, explosive mines placed under or on the ground * Mining (military), digging under a fortified military position to penetrate its defenses * Naval mine, or sea mine, a mine at sea, either floating or on the sea bed, often dropped via parachute from aircraft, or otherwise lain by surface ships or submarines * Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Summit County, Utah
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangue
In mining, gangue () is the commercially worthless material that surrounds, or is closely mixed with, a wanted mineral in an ore deposit. It is thus distinct from overburden, which is the waste rock or materials overlying an ore or mineral body that are displaced during mining without being processed, and from tailings, which is rock already stripped of valuable minerals. The separation of valuable mineral from gangue minerals is known as mineral processing, mineral dressing, or ore dressing. It is a necessary, and often significant, aspect of mining. It can be a complicated process, depending on the nature of the minerals involved. For example, galena, an ore of lead, is usually found in large pieces within its gangue, so it does not normally need extensive processing to remove it; but cassiterite, the chief ore mineral of tin, is usually disseminated as very small crystals throughout its gangue, so when it is mined from hard rock, the ore-bearing rock first needs to be crushed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the pyrite group, sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennantite
Tennantite is a copper arsenic sulfosalt mineral with an ideal formula . Due to variable substitution of the copper by iron and zinc the formula is . It is gray-black, steel-gray, iron-gray or black in color. A closely related mineral, tetrahedrite ) has antimony substituting for arsenic and the two form a solid solution series. The two have very similar properties and is often difficult to distinguish between tennantite and tetrahedrite. Iron, zinc, and silver substitute up to about 15% for the copper site. The mineral was first described for an occurrence in Cornwall, England in 1819, where it occurs as small crystals of cubic or dodecahedral form, and was named after the English chemist Smithson Tennant (1761–1815). It is found in hydrothermal veins and contact metamorphic deposits in association with other Cu–Pb–Zn–Ag sulfides and sulfosalts, pyrite, calcite, dolomite, siderite, barite, fluorite and quartz. The arsenic component of tennantite causes the metal smelte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedrite
Tetrahedrite is a copper antimony sulfosalt mineral with formula: . It is the antimony endmember of the continuous solid solution series with arsenic-bearing tennantite. Pure endmembers of the series are seldom if ever seen in nature. Of the two, the antimony rich phase is more common. Other elements also substitute in the structure, most notably iron and zinc, along with less common silver, mercury and lead. Bismuth also substitutes for the antimony site and ''bismuthian tetrahedrite'' or ''annivite'' is a recognized variety. The related, silver dominant, mineral species freibergite, although rare, is notable in that it can contain up to 18% silver. Mineralogy Tetrahedrite gets its name from the distinctive tetrahedron shaped cubic crystals. The mineral usually occurs in massive form, it is a steel gray to black metallic mineral with Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4 and specific gravity of 4.6 to 5.2. Tetrahedrite occurs in low to moderate temperature hydrothermal veins and in some co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |