|
Onega Research And Development Technological Bureau
{{Disambiguation, geo, surn ...
Onega may refer to: Places Russia * Onega (river), in Arkhangelsk Oblast * Onega, Russia, a town in Arkhangelsk Oblast * Onega Bay (Onega Gulf) * Onega Peninsula * Lake Onega United States *Onega, Minnesota, United States *Onega, Texas (now called Aubrey), United States People *Ermindo Onega (1940–1979), Argentine footballer *Daniel Onega (born 1945), Argentine footballer Ships *, a Russian factory ship in service 1945-69 Other *''Onega stepanovi'', an Ediacaran fossil genus renamed ''Cephalonega'' in 2019 * ''Onega'' (leafhopper), a genus of leafhoppers *Onega rocket, a proposed further upgrade version of the Soyuz-2 launch vehicle See also *Onezhsky (other) *Omega (other) __NOTOC__ Omega (Ω or ω) is the twenty-fourth and last letter of the Greek alphabet. __NOTOC__ Omega may also refer to: Arts, entertainment and media Fictional entities * Omega (Doctor Who), Omega (''Doctor Who'') * Omega, List of Maximum Ride ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onega (river)
The Onega (russian: Оне́га; fi, Äänisjoki) is a river in Kargopolsky, Plesetsky, and Onezhsky Districts of Arkhangelsk Oblast in Russia. The Onega connects Lake Lacha with the Onega Bay in the White Sea southwest of Arkhangelsk, flowing in the northern direction. The discharge at the source is and at the mouth is . The river is long, and the area of its basin . Its main tributaries are the Voloshka (right), the Kena (left), the Mosha (right), the Kodina (right), and the Kozha (left). The major tributary of the Lake Lacha is the Svid. In terms of both area of the basin and the average discharge, the Onega is the third river basin of the White Sea (behind the Northern Dvina and the Mezen). The river basin of the Onega is spread over the west of Arkhangelsk Oblast, north-west of Vologda Oblast, and also includes minor areas in the east of Republic of Karelia. The Onega basin includes some of the biggest lakes of Arkhangelsk and Vologda Oblasts, such as Lake Vozhe, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onega, Russia
Onega (russian: Оне́га) is a town in the northwest of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, situated at the mouth of the Onega River, a few kilometers from the shore of the Onega Bay of the White Sea. Population: History The Pomor village of Ust-Onega () was first mentioned in Novgorodian documents in the 14th century. In 1699, it was designated as one of the 4 ports in Russia whose exports to Britain were subject to the monopoly enjoyed by the Russia Company. It was chartered on August 19, 1780, after Pyotr Shuvalov had sold his rights to fell timber to English industrialists who built several sawmills there. Since 1784, Onega was the administrative center of Onezhsky Uyezd. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, Onega serves as the administrative center of Onezhsky District, even though it is not a part of it. As an administrative division, it is, together with three rural localities, incorporated separately as the town of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
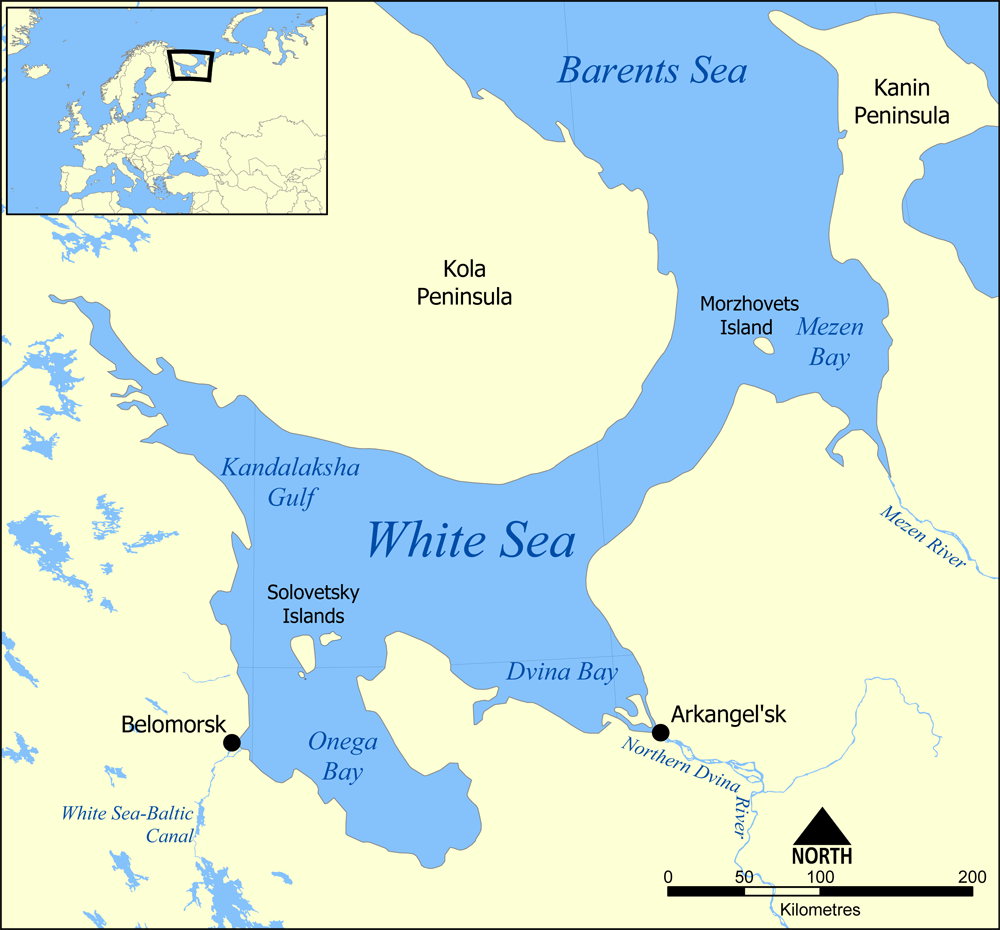
Onega Bay
The Onega Bay (russian: Онежская губа, Онежский залив) is located in the Republic of Karelia and Arkhangelsk Oblast in Northwestern Russia, west of the city of Arkhangelsk. It is the southernmost of four large bays and gulfs of the White Sea, the others being the Dvina Bay, the Mezen Bay, and the Kandalaksha Gulf. The area of the bay is . The Onega Bay is long and - wide. The average depth of the bay is , and the maximum depth is . The bay freezes in winter. Onega, Kem, and Vyg Rivers flow into the bay. The bay has numerous islands. Solovetsky Islands, which are the largest and the most famous, are located on the entrance to the bay and separate it from the main body of the White Sea. Along the west coast, there are hundreds of small islands (russian: луда, luda's). The biggest of these are Shuyostrov Island, Russky Kuzov Island, Myagostrov Island, Kondostrov Island, and Sumostrov Island. The group of islands around Kondostrov Island are coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onega Peninsula
The Onega Peninsula is located in Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It protrudes into the White Sea, with Onega Bay to the south-west, and Dvina Bay to the north-east. The length of the peninsula is about , and the width varies between and . Geography The coastal area of the peninsula is populated. The villages (counterclockwise) of Nyonoksa, Syuzma, Krasnaya Gora, Pertominsk, Unsky, Yarenga, Lopshenga, Letny Navolok, Letnyaya Zolotitsa, Pushlakhta, Lyamtsa, Purnema, and Nizhmozero are all located at or near the coast. The north-eastern coast of the peninsula is crossed by the Una Bay, a gulf in the Dvina Bay, which is about long. The villages of Una and Luda are located at the inner coast of the Una Bay. The interior of the peninsula (north-west of the line connecting Luda and Purnema) is a wilderness without any permanent population. There is some logging at Verkhneozersk, south-east of Luda. The interior of the peninsula is hilly, and there are many lakes, the biggest of which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego, rus, Оне́жское о́зеро, r=Onezhskoe ozero, p=ɐˈnʲɛʂskəɪ ˈozʲɪrə; fi, Ääninen, Äänisjärvi; vep, Änine, Änižjärv) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic Sea, and is the second-largest lake in Europe after Lake Ladoga, slightly smaller than Lebanon. The lake is fed by about 50 rivers and is drained by the Svir. There are about 1,650 islands on the lake. They include Kizhi, which hosts a historical complex of 89 Orthodox churches and other wooden structures of the 15th–20th centuries. The complex includes a UNESCO World Heritage site, Kizhi Pogost. The eastern shores of the lake contain about 1,200 petroglyphs (rock engravings) dated to the 4th–2nd millennia BC, which have also been inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage site. The major cities on the lake are Petrozavodsk, Kondopoga and Medvezhye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onega, Minnesota
Hibbing is a city in Saint Louis County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 16,214 at the 2020 census. The city was built on mining the rich iron ore of the Mesabi Iron Range and still relies on that industrial activity today. At the edge of town is the world's largest open-pit iron mine, the Hull–Rust–Mahoning Open Pit Iron Mine. It is the hometown of famous singer Bob Dylan and former Governor of Minnesota Rudy Perpich. The main routes in Hibbing are U.S. Highway 169, State Highway 37, State Highway 73, Howard Street, and 1st Avenue. It is about northwest of Duluth, Minnesota. History The town was founded in 1893 by Frank Hibbing, born in Walsrode, Germany on December 1, 1856, and christened Franz Dietrich von Ahlen. His mother died when he was still in infancy and it was her name, Hibbing, which he assumed when he set out to seek his fortune in the New World. He first settled in Beaver Dam, Wisconsin, where he worked on a farm and in a shingle mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onega, Texas
Aubrey is a city in Denton County, Texas, United States. The population was 5,006 at the 2020 census. History Aubrey, the town, was officially founded 1867, when Civil War veteran Lemuel Noah Edwards (1838–1910) built the second frame house there. Edwards eventually gave each of his 10 children a lot on which to build a home. The Edwards family was instrumental in several civil developments. Dancing was not allowed, but the townspeople often gathered in the Edwards home for singing and listening to music performed on an organ that Edwards had imported. In 1881, the Texas and Pacific Railway completed a track and station in Aubrey and commenced operations.''Former Teacher Remembers When Aubrey Was Founded,'' Denton Record-Chronicle, pg. 2, sec 4, July 28, 1963 In 1885, Edwards offered a lot to each congregation that would build a church within a year. In 1882 Edwards and Louis Caddel Sr. donated land for a one-room schoolhouse in town. Edwards, through one of his daughters� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ermindo Onega
Ermindo Ángel Onega (30 April 1940 – 21 December 1979) was an Argentine footballer, attacking midfielder and forward from River Plate. He played for River Plate from 1957 to 1968, scoring 98 goals in 222 matches. In 1972, he played for Club Atlético Vélez Sársfield, scoring 6 goals in 30 matches. Onega also had spells with Peñarol in Uruguay and La Serena in Chile. He was the older brother of Daniel Onega, also a River Plate footballer. Onega died in a road accident in 1979 on his way to the city of Rosario Rosario () is the largest city in the central provinces of Argentina, Argentine province of Santa Fe Province, Santa Fe. The city is located northwest of Buenos Aires, on the west bank of the Paraná River. Rosario is the third-most populous ci .... He was only 39 years old. External links * * * 1940 births 1979 deaths People from Belgrano Department, Santa Fe Road incident deaths in Argentina Club Atlético River Plate footballers Peñarol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Onega
Daniel Onega (born March 17, 1945) is a retired Argentine football player who played most of his career for River Plate. He also played for the Argentina national team between 1966 and 1972. He is the brother of the late midfielder Ermindo Onega. Onega started his career at River Plate. It was with River Plate that he became the topscorer in the 1966 Copa Libertadores with 17 goals, setting the record for the most goals ever scored in a single season in that tournament, a record that has never been surpassed. He is also the 4th in the all time Copa Libertadores topscorers list with 31 goals in 47 games. In 1972 Onega moved to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onega Stepanovi
''Cephalonega stepanovi'' is a fossil organism from Ediacaran deposits of the Arkhangelsk Region, Russia. It was described by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1976 Name Its original genus name ''Onega'' comes from the Onega Peninsula of the White Sea, where the first fossils were found. The species name was given to honour V.A. Stepanov, who discovered the Ediacaran fossil site on the Letniy Bereg ("Summer Coast") in 1972, on the Onega Peninsula, the first Proterozoic site found in the Arkhangelsk Oblast. The original generic name is previously occupied by the hemipteran genus ''Onega'' Distant (1908). Ivantsov ''et al.'' (2019) coined a replacement generic name ''Cephalonega''. Morphology The small fossils, which range up to long, have oval outlines and low bodies with an articulated central zone built of isomers encircled by an undivided zone. The surface of the undivided region of ''Cephalonega'' is covered with small tubercles. ''Cephalonega'' was originally described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onega (leafhopper)
''Onega'' is a genus of leafhoppers in the family Cicadellidae. Description All nine described species of the Genus ''Onega'' are comparably large leafhoppers with a size between 12.4 and 16.8 Millimeters. The pronotum of ''Onega'' is typically wider than the head and the Scutellum is swollen. Distribution ''Onega'' occurs in the Andean rainforests of Peru, Ecuador, Colombia and Bolivia. Old records of ''Onega'' from the Caribbean islands are now believed to have been mislabelled. Species Genus ''Onega'' Distant, 1908 * '''' Distant, 1908 * '' |
Onega Rocket
Soyuz (russian: Союз, meaning "union", GRAU index 11A511) is a family of expendable Russian and Soviet carrier rockets developed by OKB-1 and manufactured by Progress Rocket Space Centre in Samara, Russia. With over 1,900 flights since its debut in 1966, the Soyuz is the most frequently used launch vehicle in the world as of 2021. For nearly a decade, between the final flight of the Space Shuttle program in 2011 and the 2020 first crewed mission of SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket, Soyuz rockets were the only launch vehicles able and approved for transporting astronauts to the International Space Station. The Soyuz vehicles are used as the launcher for the crewed Soyuz spacecraft as part of the Soyuz programme, as well as to launch uncrewed Progress supply spacecraft to the International Space Station and for commercial launches marketed and operated by Starsem and Arianespace. All Soyuz rockets use RP-1 and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellant, with the exception of the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |