|
Oncolytic Herpes Virus
Many variants of herpes simplex virus have been considered for viral therapy of cancer; the early development of these was thoroughly reviewed in the journal ''Cancer Gene Therapy'' in 2002. This page describes (in the order of development) the most notable variants—those tested in clinical trials: G207, HSV1716, NV1020 and Talimogene laherparepvec (previously Oncovex-GMCSF). These attenuated versions are constructed by deleting viral genes required for infecting or replicating inside normal cells but not cancer cells, such as ICP34.5, ICP6/UL39, and ICP47. HSV1716 HSV1716 is a first generation oncolytic virus developed by The Institute of Virology, Glasgow, UK, and subsequently by Virttu Biologics (formerly Crusade Laboratories, a spin-out from The Institute of Virology), to selectively destroy cancer cells. The virus has the trade name SEPREHVIR. It is based on the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). The HSV1716 strain has a deletion of the gene ICP34.5. ICP34.5 is a neurovir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
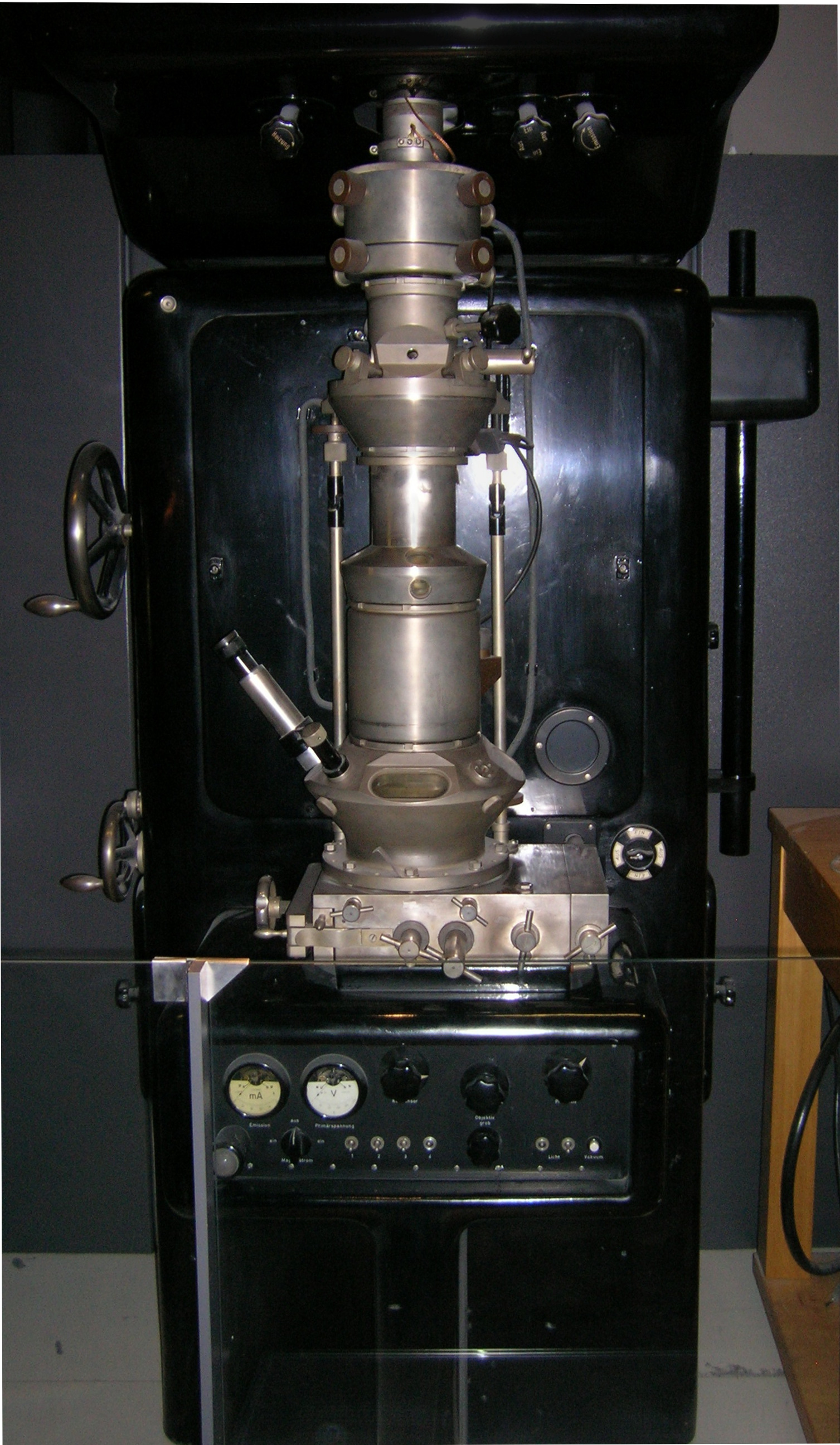
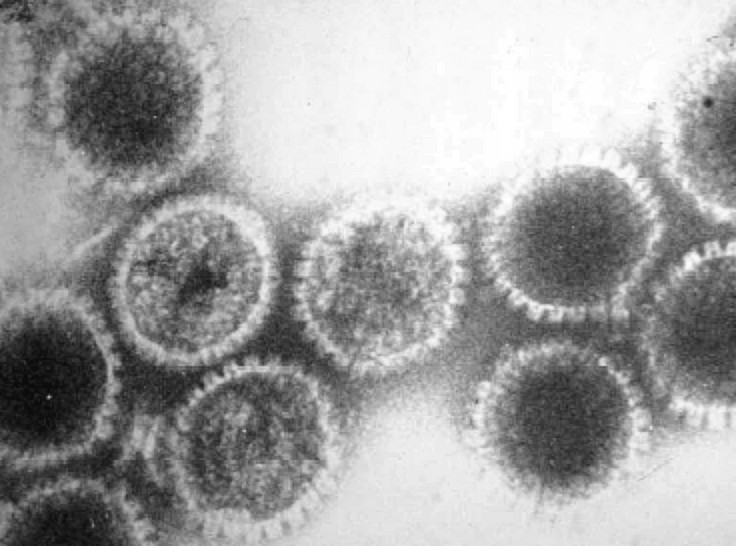
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a sensor such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy is a major analytical method i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noradrenaline Transporter
The norepinephrine transporter (NET), also known as noradrenaline transporter (NAT), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the solute carrier family 6 member 2 (SLC6A2) gene. NET is a monoamine transporter and is responsible for the sodium-chloride (Na+/Cl−)-dependent reuptake of extracellular norepinephrine (NE), which is also known as noradrenaline. NET can also reuptake extracellular dopamine (DA). The reuptake of these two neurotransmitters is essential in regulating concentrations in the synaptic cleft. NETs, along with the other monoamine transporters, are the targets of many antidepressants and recreational drugs. In addition, an overabundance of NET is associated with ADHD. There is evidence that single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the NET gene (''SLC6A2'') may be an underlying factor in some of these disorders. Gene The norepinephrine transporter gene, SLC6A2 is located on human chromosome 16 locus 16q12.2. This gene is encoded by 14 exons. Based on the nucleotide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FDG-PET
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron collides with an ordinary electron, the two particles annihilate and gamma rays are emitted. These gamma rays are detected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
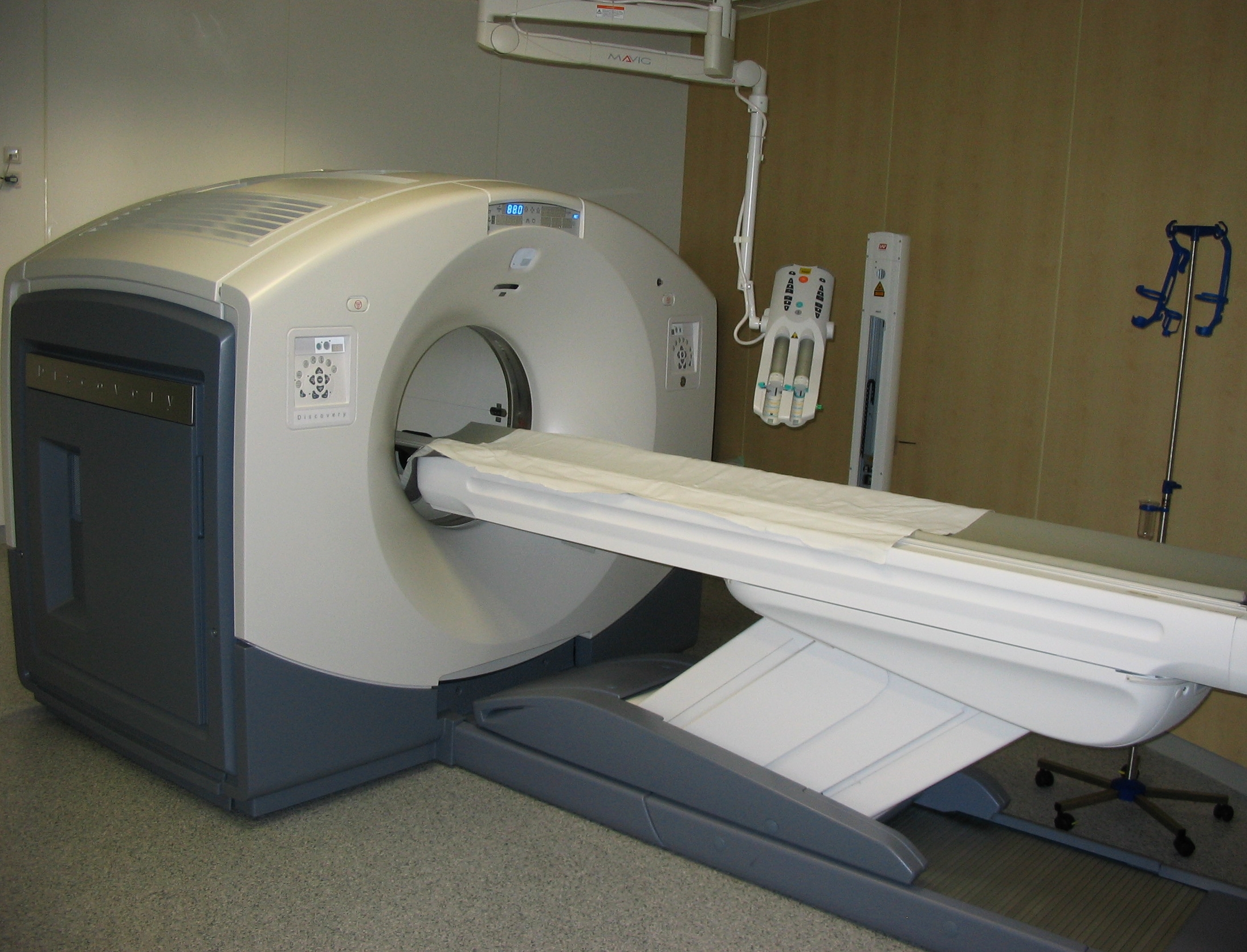
X-ray Computed Tomography
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to old age and lifestyle factors, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneal Cancer
Primary peritoneal cancer or carcinoma is also known as serous surface papillary carcinoma, primary peritoneal carcinoma, extra-ovarian serous carcinoma, primary serous papillary carcinoma, and psammomacarcinoma. It was historically classified under "carcinoma of unknown primary" (CUP). Primary peritoneal cancer (PPC, or PPCa) is a cancer of the cells lining the peritoneum, or abdominal cavity. Histomorphological and molecular biological characteristics suggest that serous carcinomas, which include ovarian serous carcinoma, uterine serous carcinoma, Fallopian tube serous carcinoma, cervical serous carcinoma, and primary peritoneal serous carcinoma really represent one entity. Genetic causes Although the precise causes are not known, a link with certain variants of BRCA1/2 has been described. Furthermore, women with BRCA1/2 mutation have a 5% risk of developing primary peritoneal cancer even after prophylactic oophorectomy. Primary peritoneal carcinoma shows similar rates of tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouse Model
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LacZ
The ''lactose'' operon (''lac'' operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in ''E. coli'' and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the ''lac'' operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of beta-galactosidase. Gene regulation of the ''lac'' operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes for this reason. This lactose metabolism system was used by François Jacob and Jacques Monod to determine how a biological cell knows which enzyme to synthesize. Their work on the ''lac'' operon won them the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 1965. Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
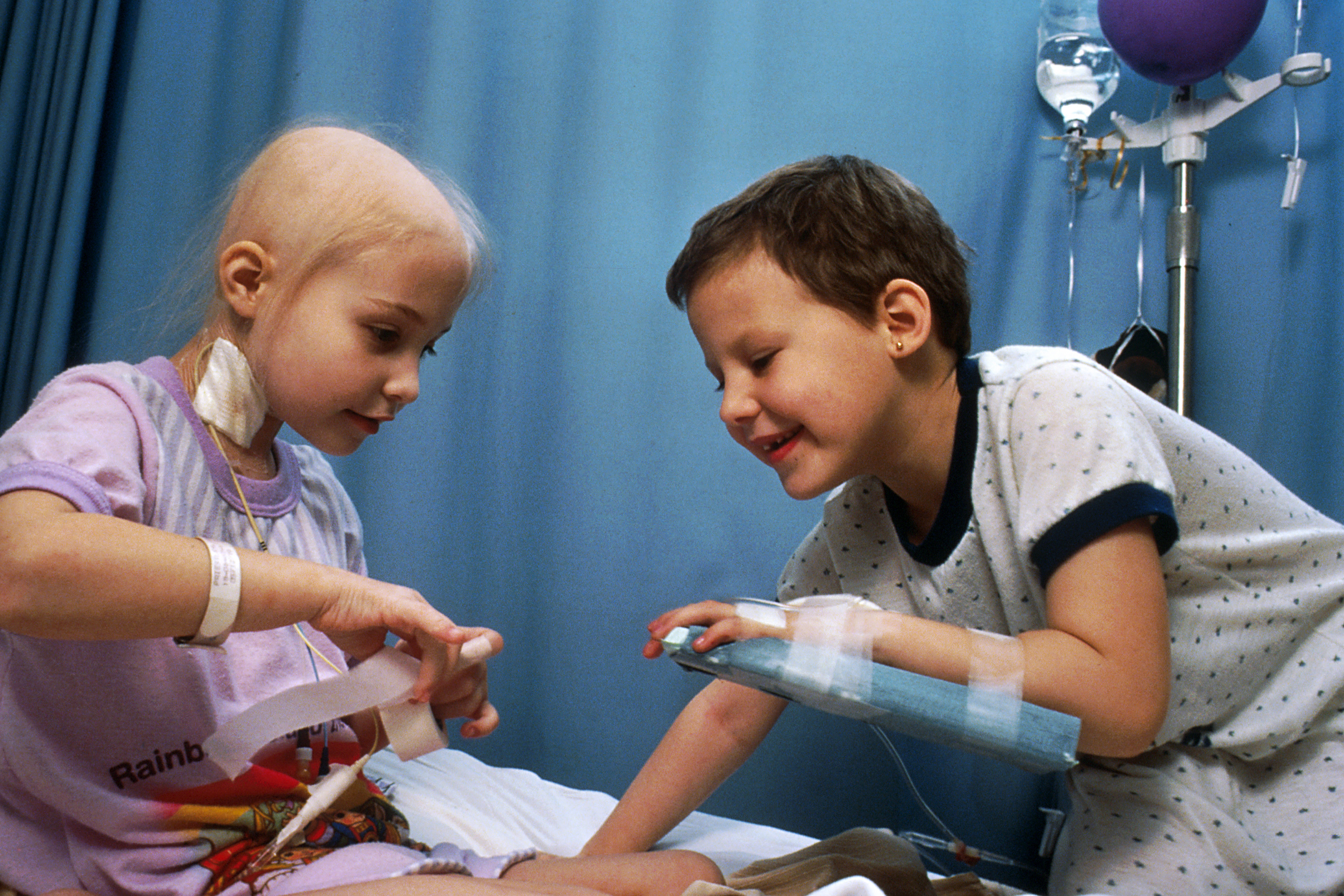
Pediatric Cancer
Childhood cancer is cancer in a child. About 80% of childhood cancer cases can be successfully treated thanks to modern medical treatments and optimal patient care. However, only about 10% of children diagnosed with cancer reside in high-income countries where the necessary treatments and care is available. Childhood cancer represents only about 1% of all types of cancers diagnosed in children and adults. For this reason, childhood cancer is often ignored in control planning, contributing to the burden of missed opportunities for its diagnoses and management in countries that are low- and mid-income. In the United States, an arbitrarily adopted standard of the ages used are 0–14 years inclusive, that is, up to 14 years 11.9 months of age. However, the definition of childhood cancer sometimes includes adolescents between 15 and 19 years old. Pediatric oncology is the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer in children. Signs and symptoms Leu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that develops from the thin layer of tissue that covers many of the internal organs (known as the mesothelium). The most common area affected is the lining of the lungs and chest wall. Less commonly the lining of the abdomen and rarely the sac surrounding the heart, or the sac surrounding the testis may be affected. Signs and symptoms of mesothelioma may include shortness of breath due to fluid around the lung, a swollen abdomen, chest wall pain, cough, feeling tired, and weight loss. These symptoms typically come on slowly. More than 80% of mesothelioma cases are caused by exposure to asbestos. The greater the exposure the greater the risk. As of 2013, about 125 million people worldwide have been exposed to asbestos at work. High rates of disease occur in people who mine asbestos, produce products from asbestos, work with asbestos products, live with asbestos workers, or work in buildings containing asbestos. Asbestos exposure and the onse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. It occurs in the setting of chronic liver inflammation, and is most closely linked to chronic viral hepatitis infection (hepatitis B or C) or exposure to toxins such as alcohol, aflatoxin, or pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Certain diseases, such as hemochromatosis and alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency, markedly increase the risk of developing HCC. Metabolic syndrome and NASH are also increasingly recognized as risk factors for HCC. As with any cancer, the treatment and prognosis of HCC vary depending on the specifics of tumor histology, size, how far the cancer has spread, and overall health. The vast majority of HCC cases and the lowest survival rates after treatment occur in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, in countries where hepatitis B infection is endem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the Biological pigment, pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In women, they most commonly occur on the legs, while in men, they most commonly occur on the back. About 25% of melanomas develop from nevus, moles. Changes in a mole that can indicate melanoma include an increase in size, irregular edges, change in color, itchiness, or ulcer (dermatology), skin breakdown. The primary cause of melanoma is ultraviolet light (UV) exposure in those with low levels of the human skin color, skin pigment melanin. The UV light may be from the sun or other sources, such as tanning lamp, tanning devices. Those with many moles, a history of affected family members, and immunosuppression, poor immune function are at greater risk. A number of rare genetic conditions, such as xerod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |