|
On Nature (Zoroaster)
''On Nature'' (Περὶ Φύσεως, ''Peri Physeos'') is the name of several works of ancient philosophy: * ''On Nature'' (Anaximander) * ''On Nature'' (Empedocles) * ''On Nature'' (Epicurus) * ''On Nature'' (Heraclitus) * ''On Nature'' (Melissus) * ''On Nature'' (Parmenides) * ''On Nature'' (Philolaus) * ''On Nature'' (Zeno) See also * Physis, a Greek philosophical, theological, and scientific term, usually translated into English as 'nature' *Pseudo-Zeno Pseudo-Zeno is the conventional name for the anonymous sixth- or seventh-century Christian author of a Greek philosophical treatise known only in an Armenian translation of the Hellenizing School. It survives in at least four late manuscripts, one ... {{disambig Ancient Greek philosophical literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Nature (Anaximander)
Anaximander (; grc-gre, Ἀναξίμανδρος ''Anaximandros''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 403. a city of Ionia (in modern-day Turkey). He belonged to the Milesian school and learned the teachings of his master Thales. He succeeded Thales and became the second master of that school where he counted Anaximenes and, arguably, Pythagoras amongst his pupils. Little of his life and work is known today. According to available historical documents, he is the first philosopher known to have written down his studies, although only one fragment of his work remains. Fragmentary testimonies found in documents after his death provide a portrait of the man. Anaximander was an early proponent of science and tried to observe and explain different aspects of the universe, with a particular interest in its origins, claiming that nature is ruled by laws, just like human soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
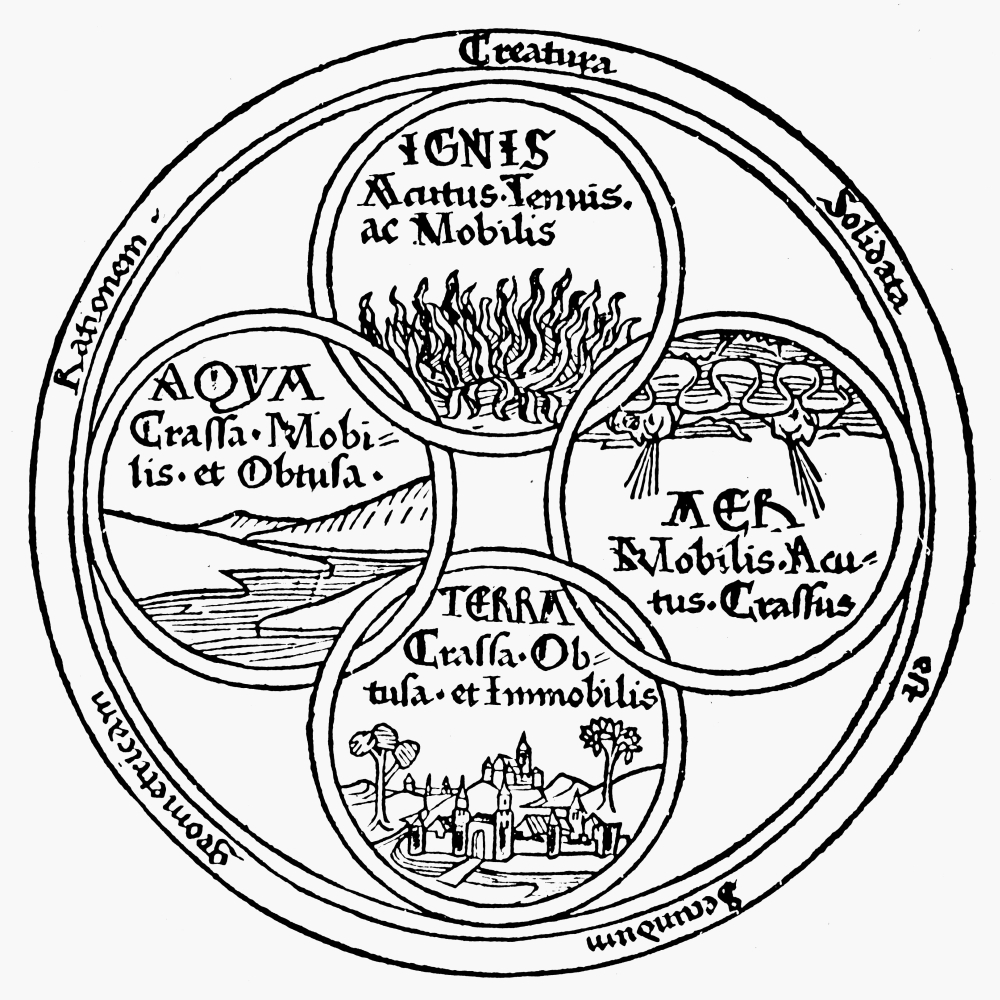
On Nature (Empedocles)
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the four classical elements. He also proposed forces he called Love and Strife which would mix and separate the elements, respectively. Empedocles challenged the practice of animal sacrifice and killing animals for food. He developed a distinctive doctrine of reincarnation. He is generally considered the last Greek philosopher to have recorded his ideas in verse. Some of his work survives, more than is the case for any other pre-Socratic philosopher. Empedocles' death was mythologized by ancient writers, and has been the subject of a number of literary treatments. Life Although the exact dates of Empedocles birth and death are unknown and ancient accounts of his life conflict on the exact details, they agree that he was born in the early 5th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Nature (Epicurus)
Epicureanism is a system of philosophy founded around 307 BC based upon the teachings of the ancient Greek philosopher Epicurus. Epicureanism was originally a challenge to Platonism. Later its main opponent became Stoicism. Few writings by Epicurus have survived. However, there are independent attestations of his ideas from his later disciples. Some scholars consider the epic poem ''De rerum natura'' (Latin for ''On the Nature of Things'') by Lucretius to present in one unified work the core arguments and theories of Epicureanism. Many of the scrolls unearthed at the Villa of the Papyri at Herculaneum are Epicurean texts. At least some are thought to have belonged to the Epicurean philosopher Philodemus. Epicurus also had a wealthy 2nd-century AD disciple, Diogenes of Oenoanda, who had a portico wall inscribed with tenets of the philosophy erected in Oenoanda, Lycia (present day Turkey). Epicurus was an atomic materialist, following in the steps of Democritus. His materialism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Nature (Heraclitus)
Heraclitus of Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἡράκλειτος , "Glory of Hera"; ) was an ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Persian Empire. Little is known of Heraclitus's life. He wrote a single work, only fragments of which have survived. Most of the ancient stories about him are later said to be fabrications based on interpretations of the preserved fragments. His paradoxical philosophy and appreciation for wordplay and cryptic utterances has earned him the epithet "the obscure" since antiquity. He was considered a misanthrope who was subject to melancholia. Consequently, he became known as "the weeping philosopher" in contrast to the ancient philosopher Democritus, who was known as "the laughing philosopher". The central idea of Heraclitus' philosophy is the unity of opposites. One of his most notable applications of this idea was to the concept of impermanence; he saw the world as constantly in flux, changing as it rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Nature (Melissus)
Melissus of Samos (; grc, Μέλισσος ὁ Σάμιος; ) was the third and last member of the ancient school of Eleatic philosophy, whose other members included Zeno and Parmenides. Little is known about his life, except that he was the commander of the Samian fleet in the Samian War. Melissus’ contribution to philosophy was a treatise of systematic arguments supporting Eleatic philosophy. Like Parmenides, he argued that reality is ungenerated, indestructible, indivisible, changeless, and motionless. In addition, he sought to show that reality is wholly unlimited, and infinitely extended in all directions; and since existence is unlimited, it must also be one. Life Not much information remains regarding the life of Melissus. He may have been born around 500 BC; the date of his death is unknown. The little which is known about him is mostly gleaned from a small passage in Plutarch’s ''Life of Pericles''. He was the commander of the Samian fleet in the Samian War, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Nature (Parmenides)
Parmenides of Elea (; grc-gre, Παρμενίδης ὁ Ἐλεάτης; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Elea in Magna Graecia. Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Elea, from a wealthy and illustrious family. His dates are uncertain; according to doxographer Diogenes Laërtius, he flourished just before 500 BC, which would put his year of birth near 540 BC, but in the dialogue ''Parmenides'' Plato has him visiting Athens at the age of 65, when Socrates was a young man, c. 450 BC, which, if true, suggests a year of birth of c. 515 BC. He is thought to have been in his prime (or "floruit") around 475 BC. The single known work by Parmenides is a poem whose original title is unknown but which is often referred to as ''On Nature.'' Only fragments of it survive. In his poem, Parmenides prescribes two views of reality. The first, the Way of "Alethia" or truth, describes how all reality is one, change is impossible, and existence is timeless and uniform. The second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
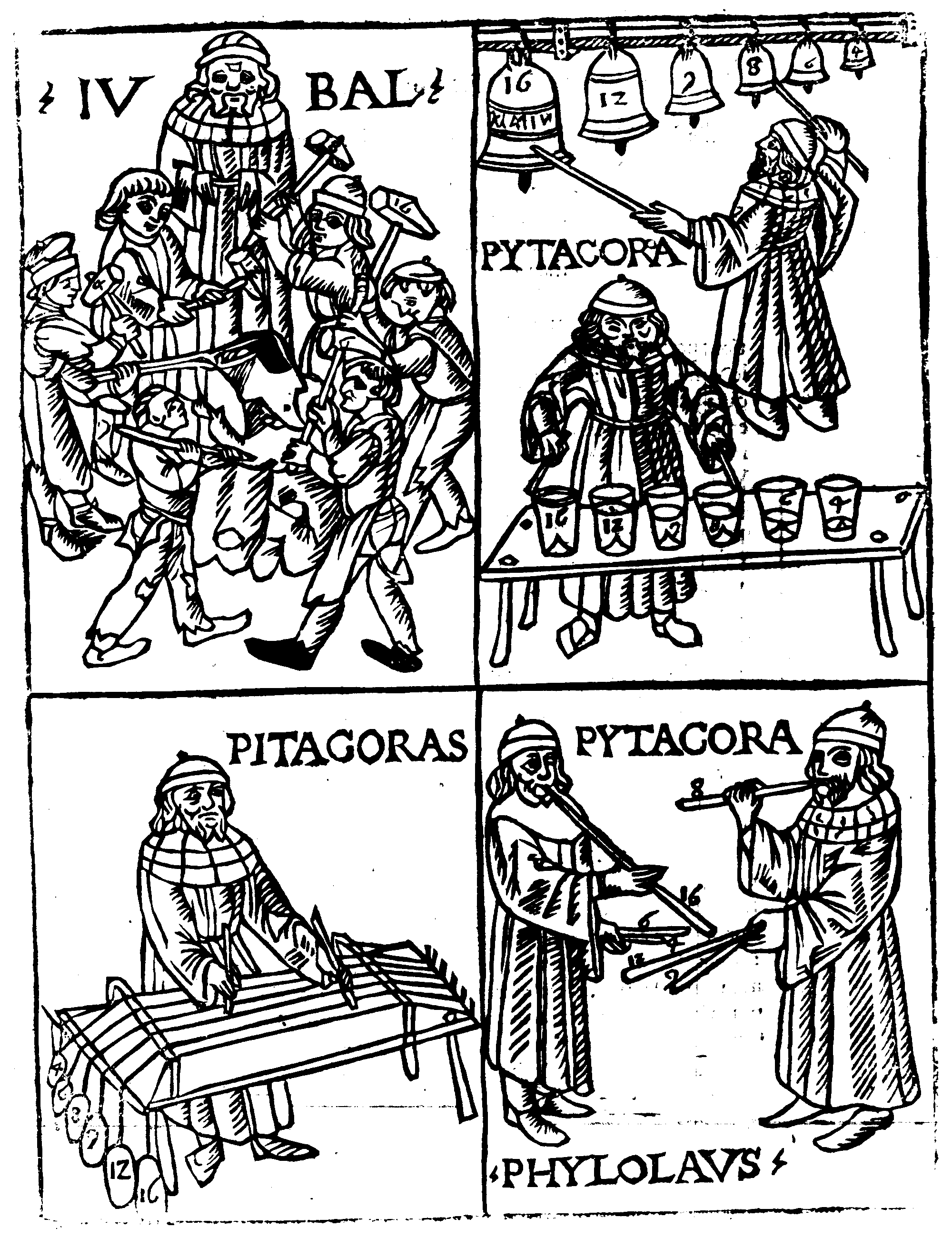
On Nature (Philolaus)
Philolaus (; grc, Φιλόλαος, ''Philólaos''; ) was a Greek Pythagorean and pre-Socratic philosopher. He was born in a Greek colony in Italy and migrated to Greece. Philolaus has been called one of three most prominent figures in the Pythagorean tradition and the most outstanding figure in the Pythagorean school. Pythagoras developed a school of philosophy that was dominated by both mathematics and mysticism. Most of what is known today about the Pythagorean astronomical system is derived from Philolaus's views. He may have been the first to write about Pythagorean doctrine. According to August Böckh (1819), who cites Nicomachus, Philolaus was the successor of Pythagoras. He argued that at the foundation of everything is the part played by the limiting and limitless, which combine in a harmony. With his assertions that the Earth was not the center of the universe (geocentrism), he is credited with the earliest known discussion of concepts in the development of heliocentr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On Nature (Zeno)
Zeno of Elea (; grc, Ζήνων ὁ Ἐλεᾱ́της; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher of Magna Graecia and a member of the Eleatic School founded by Parmenides. Aristotle called him the inventor of the dialectic. He is best known for his paradoxes, which Bertrand Russell described as "immeasurably subtle and profound". Life Little is known for certain about Zeno's life. Although written nearly a century after Zeno's death, the primary source of biographical information about Zeno is Plato's ''Parmenides'' and he is also mentioned in Aristotle's ''Physics''. In the dialogue of ''Parmenides'', Plato describes a visit to Athens by Zeno and Parmenides, at a time when Parmenides is "about 65", Zeno is "nearly 40", and Socrates is "a very young man".Plato, ''Parmenides'127b–e (at footnote n. 2) Assuming an age for Socrates of around 20 and taking the date of Socrates' birth as 469 BC gives an approximate date of birth for Zeno of 490 BC. Plato says that Zeno was "tall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physis
Fusis, Phusis or Physis (; grc, φύσις ) is a Greek philosophical, theological, and scientific term, usually translated into English—according to its Latin translation "natura"—as "nature". The term originated in ancient Greek philosophy, and was later used in Christian theology and Western philosophy. In pre-Socratic usage, ''physis'' was contrasted with , , "law, human convention". Another opposition, particularly well-known from the works of Aristotle, is that of ''physis'' and ''techne'' – in this case, what is produced and what is artificial are distinguished from beings that arise spontaneously from their own essence, as do agents such as humans. Further, since Aristotle the ''physical'' (the subject matter of ''physics'', properly "natural things") has been juxtaposed to the ''metaphysical''. Linguistics The Greek word ''physis'' can be considered the equivalent of the Latin ''natura''. The abstract term physis is derived from the verb ''phyesthai/phynai'', w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-Zeno
Pseudo-Zeno is the conventional name for the anonymous sixth- or seventh-century Christian author of a Greek philosophical treatise known only in an Armenian translation of the Hellenizing School. It survives in at least four late manuscripts, one of which attributes it to Zeno of Citium, the founder of Stoicism. This attribution was sometimes accepted and the work identified with Zeno's lost treatise ''On Nature''. In fact, the work is untitled, anonymous and belongs mainly to the Aristotelian tradition. The style, however, is extremely obscure. Work Title The treatise is untitled in the manuscripts. Levon Khachikyan assigned it the provisional title ''On Nature'' (or ''Concerning Nature''). One manuscript describes it as "of Zeno the Philosopher". Another introduces it with the words "another discourse". Both facilitated Khachikyan's naming. The latter manuscript also contains a work entitled ''On Nature'' by an unnamed rhetorician, suggesting that the work of Pseudo-Zeno may hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |