|
Old Somerby
Old Somerby (pronounced ''Summerby'') is a village and civil parish in the South Kesteven district of Lincolnshire, England, south-east of Grantham. It lies on the B1176 road, with the village centre about east of its junction with the A52 and B6403, and adjacent to the East Coast Main Line. Structure The civil parish population at the 2011 census was 224. Adjacent villages are Ropsley and Boothby Pagnell. The village divides into Old Somerby, High Somerby and Low Somerby. Amenities The church parish is part of The North Beltisloe Group of Beltisloe Deanery in the Diocese of Lincoln. Its church in High Somerby is dedicated to St Mary Magdalene, the same dedication as at nearby Bitchfield. There is bed-and-breakfast accommodation in School Lane. The village public house is the ''Fox and Hounds'' in Grantham Road (B1176). Schools, shops and other amenities are available in Grantham (, to which there are occasional daytime, weekday buses. Heritage Somerby was a colony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary Magdalene
Mary Magdalene (sometimes called Mary of Magdala, or simply the Magdalene or the Madeleine) was a woman who, according to the four canonical gospels, traveled with Jesus as one of his followers and was a witness to his crucifixion and resurrection. She is mentioned by name twelve times in the canonical gospels, more than most of the apostles and more than any other woman in the gospels, other than Jesus' family. Mary's epithet ''Magdalene'' may mean that she came from the town of Magdala, a fishing town on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee in Roman Judea. The Gospel of Luke chapter 8 lists Mary Magdalene as one of the women who traveled with Jesus and helped support his ministry "out of their resources", indicating that she was probably wealthy. The same passage also states that seven demons had been driven out of her, a statement which is repeated in Mark 16. In all the four canonical gospels, Mary Magdalene was a witness to the crucifixion of Jesus and, in the Syno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Lincolnshire
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
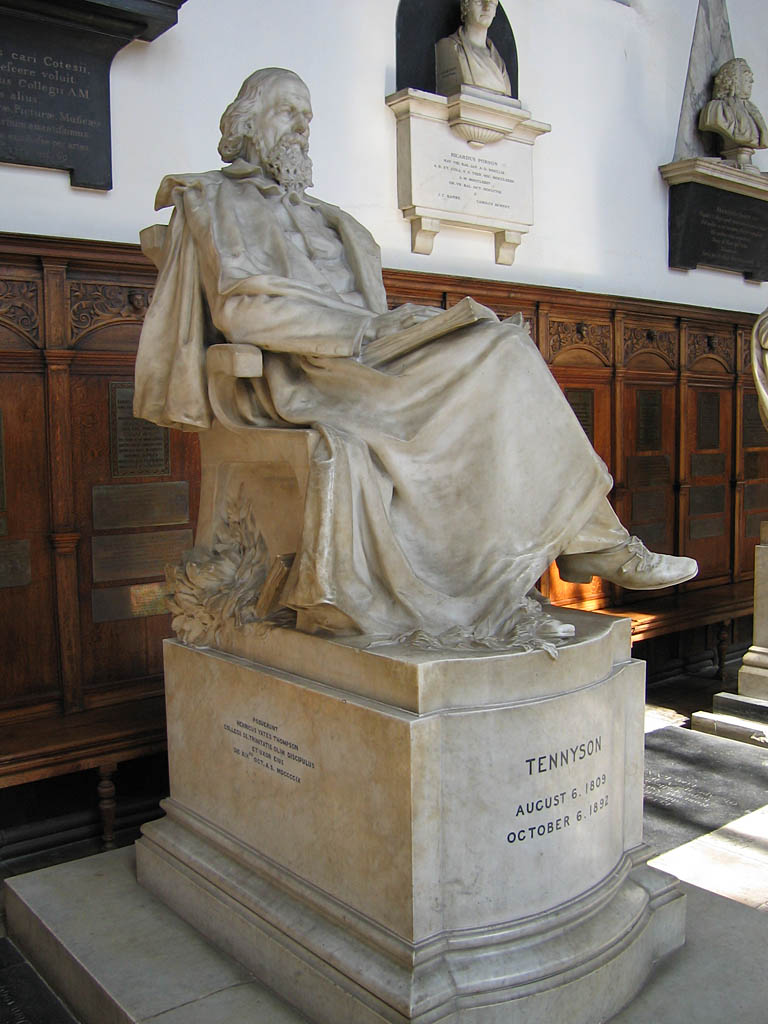
Alfred, Lord Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his first pieces, "Timbuktu". He published his first solo collection of poems, ''Poems, Chiefly Lyrical'', in 1830. "Claribel" and "Mariana", which remain some of Tennyson's most celebrated poems, were included in this volume. Although described by some critics as overly sentimental, his verse soon proved popular and brought Tennyson to the attention of well-known writers of the day, including Samuel Taylor Coleridge. Tennyson's early poetry, with its medievalism and powerful visual imagery, was a major influence on the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. Tennyson also excelled at short lyrics, such as "Break, Break, Break", "The Charge of the Light Brigade", "Tears, Idle Tears", and "Crossing the Bar". Much of his verse was based on classical mytho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Brookfield
William Henry Brookfield (31 August 1809 – 12 July 1874) was an Anglican priest, Inspector of Schools, and chaplain-in-ordinary to Queen Victoria.. His son was the playwright Charles Brookfield. Biography William Henry Brookfield was the second son of Charles Brookfield, a solicitor at Sheffield, where he was born on 31 August 1809. He attended Leeds Grammar School, and in 1827 he was articled to a solicitor at Leeds, but left this position to enter Trinity College, Cambridge, in October 1829 (B.A. 1833, and M.A. 1836). In 1834 he became tutor to George William Lyttelton. In December 1834 he was ordained to the curacy of Maltby in Lincolnshire. He was afterwards curate at Southampton, in 1840 of St. James's, Piccadilly, and in 1841 of St. Luke's, Berwick Street. In 1841 he married Jane Octavia, the eight and youngest daughter of Sir Charles Elton of Clevedon Court, Somerset. Julia Maria, wife of Henry Hallam the historian was Sir Charles's sister. In 1848 Brookfield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Weston (politician)
Edward Weston (1703–1770) was an English didactic writer and politician. Early life and education He was the second son of Stephen Weston, bishop of Exeter. He was born at Eton in 1703 and was educated at Eton College and at King's College, Cambridge, where he was admitted in 1719, graduating B.A. in 1723 and M.A. in 1727. Horace Walpole states that he went in 1725 to Bexley in Kent with his cousins, "the four younger sons of Lord Townshend, and with a tutor, Edward Weston ... and continued there some months." (The first date is considered a misprint for 1723, since Walpole was under Weston's charge in July 1724. Career Weston was secretary to Lord Townshend during the king's residence at Hanover in 1729, and, on his retirement from office, lost "a very generous friend and patron". In May 1730 he offered his services to Lord Harrington, and when that peer was made secretary of state for the northern department, Weston became under-secretary, remaining in the position un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Subdivision)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Southern Schleswig, Sweden, Finland, Norway, the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek, Curonia, the Ukrainian state of the Cossack Hetmanate and in Cumberland County, New South Wales, Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''#wapentake, wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål, Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' (Nynorsk, Nynorsk Norwegian), ''hérað'' (Icelandic), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' (North Frisian language, North Frisian), ''satakunta'' or ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), ''kihelkond'' (Estonian), ''kiligunda'' (Livonian), ''cantref'' (Welsh) and ''sotnia'' (Slavic). In Ireland, a similar subdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter D'Aincourt
Walter D'Aincourt (or Walter Deincourt or d'Eyncourt) was a landholder in Derby under King Edward the Confessor in 1065/1066. Later in 1066, he fought for William the Conqueror against Harold Godwinson and was rewarded with a large number of manors in a number of counties but particularly Nottinghamshire after the Norman conquest. Biography D'Aincourt's mark on history is recorded principally in the Domesday Book which records him as tenant-in-chief of thirteen manors in Derbyshire, one manor in Northamptonshire, four in Yorkshire, nineteen in Lincolnshire and thirty-seven in Nottinghamshire. He made his home in Blankney in Lincolnshire.The Conqueror and His Companions by J.R. Planché, Somerset Herald. London: Tinsley Brothers, 1874 accessed 13 December 2007. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by the Latin name ''Liber de Wintonia'', meaning "Book of Winchester", where it was originally kept in the royal treasury. The '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and dues owed to him. Written in Medieval Latin, it was highly abbreviated and included some vernacular native terms without Latin equivalents. The survey's main purpose was to record the annual value of every piece of landed property to its lord, and the resources in land, manpower, and livestock from which the value derived. The name "Domesday Book" came into use in the 12th century. Richard FitzNeal wrote in the ''Dialogus de Scaccario'' ( 1179) that the book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred The Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfred was young. Three of Alfred's brothers, Æthelbald, Æthelberht and Æthelred, reigned in turn before him. Under Alfred's rule, considerable administrative and military reforms were introduced, prompting lasting change in England. After ascending the throne, Alfred spent several years fighting Viking invasions. He won a decisive victory in the Battle of Edington in 878 and made an agreement with the Vikings, dividing England between Anglo-Saxon territory and the Viking-ruled Danelaw, composed of northern England, the north-east Midlands and East Anglia. Alfred also oversaw the conversion of Viking leader Guthrum to Christianity. He defended his kingdom against the Viking attempt at conquest, becoming the dominant ruler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danes (Germanic Tribe)
The Danes were a North Germanic tribe inhabiting southern Scandinavia, including the area now comprising Denmark proper, and the Scanian provinces of modern-day southern Sweden, during the Nordic Iron Age and the Viking Age. They founded what became the Kingdom of Denmark. The name of their realm is believed to mean " Danish March", viz. "the march of the Danes", in Old Norse, referring to their southern border zone between the Eider and Schlei rivers, known as the Danevirke. Origins The origin of the Danes remains undetermined, but several ancient historical documents and texts refer to them and archaeology has revealed and continues to reveal insights into their culture, beliefs, organization and way of life. The Danes first appear in written history in the 6th century with references in Jordanes' ''Getica'' (551 AD), by Procopius, and by Gregory of Tours. They spoke Old Norse (''dǫnsk tunga''), which the Danes shared with the people in Norway and Sweden and later in Icelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)