|
Old Palace School
The Old Palace of John Whitgift School is a selective independent school for girls in Croydon, London. The Old Palace is protected as a Grade I listed building. It consists of a pre-school for the ages of 3-4, a preparatory department for the ages of 4-11 and a senior school for pupils aged 11–18. The school is operated by the Whitgift Foundation, along with Whitgift School and Trinity School of John Whitgift, and is consistently ranked as one of the top performing independent girls' schools in London. History The school was founded in 1889 by the Sisters of the Church. The " Old Palace" itself was for 500 years the summer residence of the Archbishops of Canterbury. In the 19th century the Archbishops ended their residence at Croydon Palace and used Addington Palace, also in Croydon, instead. The Palace was sold and subsequently used as a bleaching factory, amongst other things. The building was rescued by the Duke of Newcastle in 1887 and given to the Sisters Of The Churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent School (United Kingdom)
In the United Kingdom, independent schools () are fee-charging schools, some endowed and governed by a board of governors and some in private ownership. They are independent of many of the regulations and conditions that apply to state-funded schools. For example, pupils do not have to follow the National Curriculum, although, some schools do. They are commonly described as 'private schools' although historically the term referred to a school in private ownership, in contrast to an endowed school subject to a trust or of charitable status. Many of the older independent schools catering for the 12–18 age range in England and Wales are known as public schools, seven of which were the subject of the Public Schools Act 1868. The term "public school" derived from the fact that they were then open to pupils regardless of where they lived or their religion (while in the United States and most other English-speaking countries "public school" refers to a publicly-funded state school). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Grant Grammar School
A direct grant grammar school was a type of selective secondary school in the United Kingdom that existed between 1945 and 1976. One quarter of the places in these schools were directly funded by central government, while the remainder attracted fees, some paid by a Local Education Authority and some by the pupils' parents or guardians. On average, the schools received just over half of their income from the state. The status was introduced in England and Wales by the Education Act 1944 as a modification of an existing direct grant scheme to some long standing endowed grammar schools. There were 179 direct grant grammar schools, which, together with over 1,200 grammar schools maintained by local authorities, formed the most academic tier of the Tripartite System. They varied greatly in size and composition, but, on average, achieved higher academic results than either maintained grammar schools or independent schools. State secondary education was reorganised on comprehensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
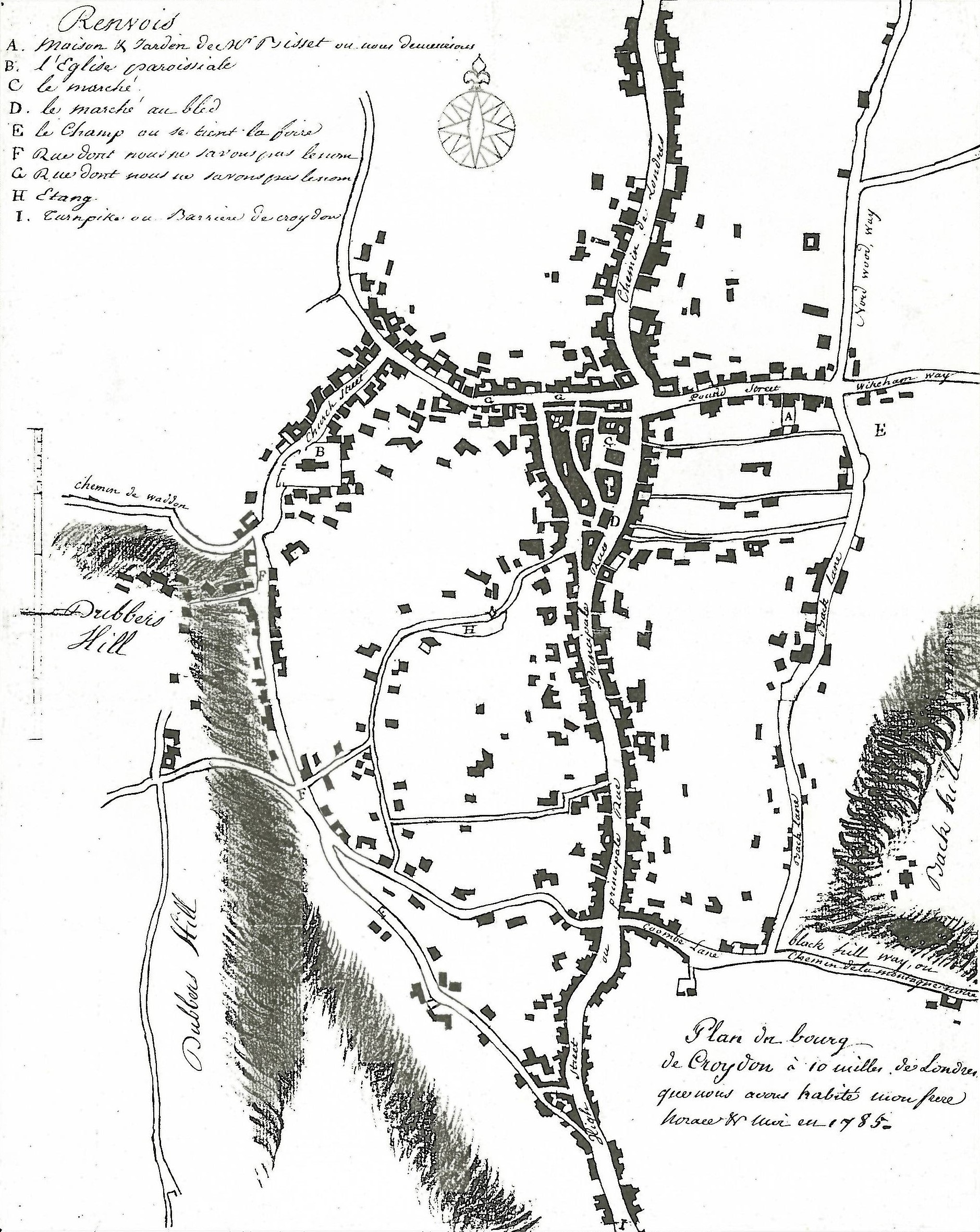
Croydon Central
Croydon is a large town in south London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensive shopping district and night-time economy. The entire town had a population of 192,064 as of 2011, whilst the wider borough had a population of 384,837. Historically an ancient parish in the Wallington hundred of Surrey, at the time of the Norman conquest of England Croydon had a church, a mill, and around 365 inhabitants, as recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086. Croydon expanded in the Middle Ages as a market town and a centre for charcoal production, leather tanning and brewing. The Surrey Iron Railway from Croydon to Wandsworth opened in 1803 and was an early public railway. Later 19th century railway building facilitated Croydon's growth as a commuter town for London. By the early 20th century, Croydon was an important industrial ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Jones (politician)
Sarah Ann Jones (born 20 December 1972) is a British Labour Party politician. She has been the Member of Parliament (MP) for Croydon Central since the 2017 general election. She was appointed as Shadow Minister for Housing in May 2018, and made Shadow Minister of State for Police and the Fire Service in 2020. Life and career Jones was born in Croydon and is a lifelong resident. She was educated at the private Old Palace School in Croydon and at Durham University, where she read History. She was a member of Trevelyan College. Jones joined the Labour Party aged 19 in 1992 after watching Conservative Party MP Peter Lilley, then the Secretary of State at the Department of Social Security, make a speech to his party's annual conference where he attacked benefit claimants and women who allegedly become pregnant to gain council housing. Jones, who was pregnant at the time, joined the Labour Party as a direct reaction to the speech. Before becoming an MP, Jones served as a senior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane Featherstone
Jane Featherstone (born 1969) is an English television producer and founder of Sister Pictures, a television production company. Prior to that, she was the chief executive of Kudos and co-chairman of Shine UK, now part of Endemol Shine Group. Biography Featherstone was educated at Old Palace School and the University of Leeds. Prior to joining Kudos, Featherstone produced the first two series of ''Touching Evil'' and the BBC2 film ''Sex ‘n’ Death''. She worked at Hat Trick Productions where she worked on ''Whose Line Is It Anyway?'', '' Have I Got News For You'', and ''Drop The Dead Donkey''. Featherstone joined Kudos in 2000 as Head of Drama. She became Creative Director in 2008 and the company's Chief Executive in 2011. Whilst at Kudos, she executive produced '' Spooks'', ''Life on Mars'', '' Ashes to Ashes'', ''Utopia'', '' The Tunnel'', and '' The Smoke''. Most recently she has executive produced ''River'' by Abi Morgan for BBC1/Netflix, ''Humans'' written bJon Brackle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Dorrit
''Little Dorrit'' is a novel by Charles Dickens, originally published in serial form between 1855 and 1857. The story features Amy Dorrit, youngest child of her family, born and raised in the Marshalsea prison for debtors in London. Arthur Clennam encounters her after returning home from a 20-year absence, ready to begin his life anew. The novel satirises some shortcomings of both government and society, including the institution of debtors' prisons, where debtors were imprisoned, unable to work and yet incarcerated until they had repaid their debts. The prison in this case is the Marshalsea, where Dickens's own father had been imprisoned. Dickens is also critical of the impotent bureaucracy of the British government, in this novel in the form of the fictional "Circumlocution Office". Dickens also satirises the stratification of society that results from the British class system. Plot summary Poverty The novel begins in Marseilles "thirty years ago" (c. 1826), with the noto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian era.. His works enjoyed unprecedented popularity during his lifetime and, by the 20th century, critics and scholars had recognised him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are widely read today. Born in Portsmouth, Dickens left school at the age of 12 to work in a boot-blacking factory when his father was incarcerated in a debtors' prison. After three years he returned to school, before he began his literary career as a journalist. Dickens edited a weekly journal for 20 years, wrote 15 novels, five novellas, hundreds of short stories and non-fiction articles, lectured and performed readings extensively, was an indefatigable letter writer, and campaigned vigorously for children's rights, for education, and for other social re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St George The Martyr Southwark
St George the Martyr is a church in the historic Borough district of south London. It lies within the modern-day London Borough of Southwark, on Borough High Street at the junction with Long Lane, Marshalsea Road, and Tabard Street. St George the Martyr is named after Saint George. The church is a Grade II* listed building. The church has strong associations with Charles Dickens, whose father was imprisoned for debt in the Marshalsea prison. The surviving wall of the prison adjoins the north side of the churchyard. Dickens himself lived nearby, in Lant Street, lodging in a house that belonged to the Vestry Clerk of St George's. This was during the darkest period of his life when, as a teenager, with his father in prison, he had to work in the 'blacking factory', and his literary career must have seemed an impossible dream. Later, he was to set several scenes of the novel ''Little Dorrit'' in and around St George's Church. There is a small representation of Little Dorrit in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Architecture
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used for English Romanesque architecture. The Normans introduced large numbers of castles and fortifications including Norman keeps, and at the same time monastery, monasteries, abbeys, Church (building), churches and cathedrals, in a style characterised by the usual Romanesque rounded arches (particularly over windows and doorways) and especially massive proportions compared to other regional variations of the style. Origins These Romanesque architecture, Romanesque styles originated in Normandy and became widespread in northwestern Europe, particularly in England, which contributed considerable development and where the largest number of examples survived. At about the same time, Hauteville family, a Norman dynasty that ruled in Sicily produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Laud
William Laud (; 7 October 1573 – 10 January 1645) was a bishop in the Church of England. Appointed Archbishop of Canterbury by Charles I in 1633, Laud was a key advocate of Charles I's religious reforms, he was arrested by Parliament in 1640 and executed towards the end of the First English Civil War in January 1645. A firm believer in episcopalianism, or rule by bishops, "Laudianism" refers to liturgical practices designed to enforce uniformity within the Church of England, as outlined by Charles. Often highly ritualistic, these were precursors to what are now known as high church views. In theology, Laud was accused of Arminianism, favouring doctrines of the historic church prior to the Reformation and defending the continuity of the English Church with the primitive and medieval church, and opposing Calvinism. On all three grounds, he was regarded by Puritan clerics and laymen as a formidable and dangerous opponent. His use of the Star Chamber to persecute opponents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VI Of England
Henry VI (6 December 1421 – 21 May 1471) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1422 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471, and disputed King of France from 1422 to 1453. The only child of Henry V, he succeeded to the English throne at the age of nine months upon his father's death, and succeeded to the French throne on the death of his maternal grandfather, Charles VI, shortly afterwards. Henry inherited the long-running Hundred Years' War (1337–1453), in which his uncle Charles VII contested his claim to the French throne. He is the only English monarch to have been also crowned King of France, in 1431. His early reign, when several people were ruling for him, saw the pinnacle of English power in France, but subsequent military, diplomatic, and economic problems had seriously endangered the English cause by the time Henry was declared fit to rule in 1437. He found his realm in a difficult position, faced with setbacks in France and divisions among the nobilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stafford (bishop)
John Stafford (died 25 May 1452) was a medieval English prelate and statesman who served as Lord Chancellor (1432–1450) and as Archbishop of Canterbury (1443–1452). Early life and education Stafford was the illegitimate son of Sir Humphrey Stafford of Southwick, a Wiltshire squire, and required papal permission before he became the rector of Farmborough, vicar of Bathampton and prebendary of Wells. He was educated at the University of Oxford. Career Stafford was appointed Dean of Arches in 1419 and served as Archdeacon of Salisbury from 1419 to 1421. From 1423 to 1424 he was Dean of Wells. He came to note under Henry VI, becoming Lord Privy Seal in 1421Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 95 and Lord High Treasurer the following year.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 106 He was Lord Chancellor from 1432 to 1450.Fryde, et al. ''Handbook of British Chronology'' p. 87 On 18 December 1424 Pope Martin V Pope Martin V ( la, Martinus V; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |