|
Okuyoshino Dialect
The Okuyoshino dialect (Japanese: 奥吉野方言 ''okuyoshino hogen'') is a Kansai dialect of Japanese spoken in several villages in the Okuyoshino region of southern Nara Prefecture. It is well-known as a language island, with various rare and unique characteristics. The dialect is currently spoken in the villages of Totsukawa, Kamikitayama, Shimokitayama, Tenkawa and Oto (now part of Gojo), and although it is classified as part of the neighbouring Nara dialect, the village of Nosegawa is also sometimes included in definitions. Overview Despite the relatively small size of Nara Prefecture, there is a major difference between the dialects of the north-central and southern parts of the prefecture. The mountain ridges of Tentsuji, Kominami and Obamine form a natural boundary, north of which the Nara dialect is spoken and south of which the Okuyoshino dialect is spoken. The many atypical traits of the Okuyoshino dialect, such as its having a Tokyo-style pitch accent despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
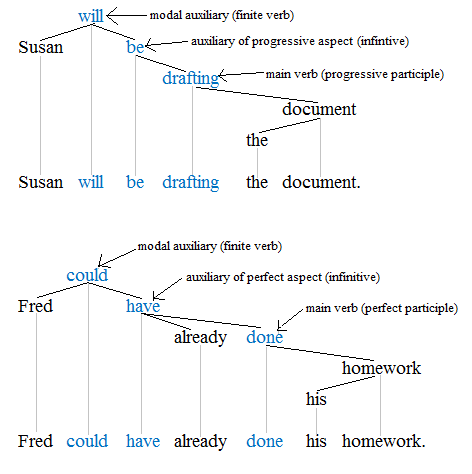
Modal Verb
A modal verb is a type of verb that contextually indicates a modality such as a ''likelihood'', ''ability'', ''permission'', ''request'', ''capacity'', ''suggestion'', ''order'', ''obligation'', or ''advice''. Modal verbs generally accompany the base (infinitive) form of another verb having semantic content. In English, the modal verbs commonly used are ''can'', ''could'', ''may'', ''might'', ''shall'', ''should'', ''will'', ''would'', ''ought to'', ''used to'', ''dare'' and ''must.'' Function A modal auxiliary verb gives information about the function of the main verb that it governs. Modals have a wide variety of communicative functions, but these functions can generally be related to a scale ranging from possibility ("may") to necessity ("must"), in terms of one of the following types of modality: *epistemic modality, concerned with the theoretical ''possibility of propositions being true or not true'' (including likelihood and certainty) *deontic modality, concerned with ''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Particles
Japanese particles, or , are suffixes or short words in Japanese grammar that immediately follow the modified noun, verb, adjective, or sentence. Their grammatical range can indicate various meanings and functions, such as speaker affect and assertiveness. Orthography and diction Japanese particles are written in hiragana in modern Japanese, though some of them also have kanji forms ( or for ''te'' ; for ''ni'' ; or for ''o'' ; and for ''wa'' ). Particles follow the same rules of phonetic transcription as all Japanese words, with the exception of (written ''ha'', pronounced ''wa'' as a particle), (written ''he'', pronounced ''e'') and (written using a hiragana character with no other use in modern Japanese, originally assigned as ''wo'', now usually pronounced ''o'', though some speakers render it as ''wo''). These exceptions are a relic of historical kana usage. Types of particles There are eight types of particles, depending on what function they serve. : : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfective Aspect
The perfective aspect (abbreviated ), sometimes called the aoristic aspect, is a grammatical aspect that describes an action viewed as a simple whole; i.e., a unit without interior composition. The perfective aspect is distinguished from the imperfective aspect, which presents an event as having internal structure (such as ongoing, continuous, or habitual actions). The term ''perfective'' should be distinguished from ''perfect'' (see below). The distinction between perfective and imperfective is more important in some languages than others. In Slavic languages, it is central to the verb system. In other languages such as German, the same form such as ''ich ging'' ("I went", "I was going") can be used perfectively or imperfectively without grammatical distinction. In other languages such as Latin, the distinction between perfective and imperfective is made only in the past tense (e.g., Latin ''veni'' "I came" vs. ''veniebam'' "I was coming", "I used to come"). However, perfective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Aspect
The continuous and progressive aspects (abbreviated and ) are grammatical aspects that express incomplete action ("to do") or state ("to be") in progress at a specific time: they are non-habitual, imperfective aspects. In the grammars of many languages the two terms are used interchangeably. This is also the case with English: a construction such as ''"He is washing"'' may be described either as ''present continuous'' or as ''present progressive''. However, there are certain languages for which two different aspects are distinguished. In Chinese, for example, ''progressive'' aspect denotes a current action, as in "he is getting dressed", while ''continuous'' aspect denotes a current state, as in "he is wearing fine clothes". As with other grammatical categories, the precise semantics of the aspects vary from language to language, and from grammarian to grammarian. For example, some grammars of Turkish count the -iyor form as a present tense; some as a progressive tense; and som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godan Verb
The Japanese language has two main types of verbs which are referred to as and . Verb groups Categories are important when conjugating Japanese verbs, since conjugation patterns vary according to the verb's category. For example, and belong to different verb categories (godan and ichidan, respectively) and therefore follow different conjugation patterns. Most Japanese verbs are allocated into two categories: # # Statistically, there are far more godan verbs than ichidan verbs. Sometimes categorization is expanded to include a third category of irregular verbs—which most notably include the verbs and . Classical Japanese had more verb groups, such as and , which are archaic in Modern Japanese. Terminology Within the terms and , the numbers and correspond with the number of rows that a verb stem (or inflectional suffix) can span in the gojūon kana table. This is best visualized by comparing various verb conjugations to an extracted column of the gojūon table: In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōwa (1926–1989)
Shōwa may refer to: * Hirohito (1901–1989), the 124th Emperor of Japan, known posthumously as Emperor Shōwa * Showa Corporation, a Japanese suspension and shock manufacturer, affiliated with the Honda keiretsu Japanese eras * Jōwa (Heian period) (承和), alternatively read as Shōwa, from 834 to 848 * Shōwa (Kamakura period) (正和), from 1312 to 1317 * Shōwa (1926–1989) (昭和), from 1926 to 1989 Japanese places * Shōwa, Akita, a former town in Akita Prefecture * Shōwa, Yamanashi, a town in Yamanashi Prefecture * Shōwa, a former town in Tokyo, now part of Akishima, Tokyo * Shōwa-ku, a ward of Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture * Shōwa, Fukushima, a village in Fukushima Prefecture * Shōwa, Gunma, a village in Gunma Prefecture * Shōwa, Saitama, a dissolved town in Saitama Prefecture * Showa Station (Antarctica), a Japanese research station located in Antarctica Japanese educational institutions * Showa University, in Tokyo * Showa Women's University, in Tokyo * Showa Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichidan
The Japanese language has two main types of verbs which are referred to as and . Verb groups Categories are important when conjugating Japanese verbs, since conjugation patterns vary according to the verb's category. For example, and belong to different verb categories (godan and ichidan, respectively) and therefore follow different conjugation patterns. Most Japanese verbs are allocated into two categories: # # Statistically, there are far more godan verbs than ichidan verbs. Sometimes categorization is expanded to include a third category of irregular verbs—which most notably include the verbs and . Classical Japanese had more verb groups, such as and , which are archaic in Modern Japanese. Terminology Within the terms and , the numbers and correspond with the number of rows that a verb stem (or inflectional suffix) can span in the gojūon kana table. This is best visualized by comparing various verb conjugations to an extracted column of the gojūon table: In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb
A verb () is a word (part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. Verbs have tenses: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; future, to indicate that an action will be done. For some examples: * I ''washed'' the car yesterday. * The dog ''ate'' my homework. * John ''studies'' English and French. * Lucy ''enjoys'' listening to music. *Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence)'' * Mike Trout ''is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasalization
In phonetics, nasalization (or nasalisation) is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. An archetypal nasal sound is . In the International Phonetic Alphabet, nasalization is indicated by printing a tilde diacritic above the symbol for the sound to be nasalized: is the nasalized equivalent of , and is the nasalized equivalent of . A subscript diacritic , called an ogonek or ''nosinė'', is sometimes seen, especially when the vowel bears tone marks that would interfere with the superscript tilde. For example, are more legible in most fonts than . Nasal vowels Many languages have nasal vowels to different degrees, but only a minority of world languages around the world have nasal vowels as contrasting phonemes. That is the case, among others, of French, Portuguese, Hindustani, Nepali, Breton, Gheg Albanian, Hmong, Hokkien, Yoruba, and Cherokee. Those nasal vowels con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatalisation (phonetics)
In phonetics, palatalization (, also ) or palatization is a way of pronouncing a consonant in which part of the tongue is moved close to the hard palate. Consonants pronounced this way are said to be palatalized and are transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet by affixing the letter ⟨ʲ⟩ to the base consonant. Palatalization cannot minimally distinguish words in most dialects of English, but it may do so in languages such as Russian, Mandarin, and Irish. Types In technical terms, palatalization refers to the secondary articulation of consonants by which the body of the tongue is raised toward the hard palate and the alveolar ridge during the articulation of the consonant. Such consonants are phonetically palatalized. "Pure" palatalization is a modification to the articulation of a consonant, where the middle of the tongue is raised, and nothing else. It may produce a laminal articulation of otherwise apical consonants such as and . Phonetically palatalized consona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yotsugana
are a set of four specific kana, じ, ぢ, ず, づ (in the Nihon-shiki romanization system: ''zi'', ''di'', ''zu'', ''du''), used in the Japanese writing system. They historically represented four distinct voiced morae (syllables) in the Japanese language. However, most dialects, such as Standard Japanese-speakers, have undergone mergers and now pronounce two sounds. Modern sound usage in various dialects Most of the far northern dialects (Tōhoku dialects and Hokkaidō) and far southern dialects (notably Okinawan Japanese) and the Ryukyuan languages (the other Japonic languages) have also mostly merged the four sounds to one sound. However, a few dialects, mainly around Shikoku and Kyushu in the southwest, still distinguish three or even all four sounds. In the current Tokyo dialect, the base of the modern standard language, as well as in the widely spoken Kansai dialect, only two sounds are distinguished, as is represented in the Hepburn (''ji'', ''ji'', ''zu'', ''zu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |