|
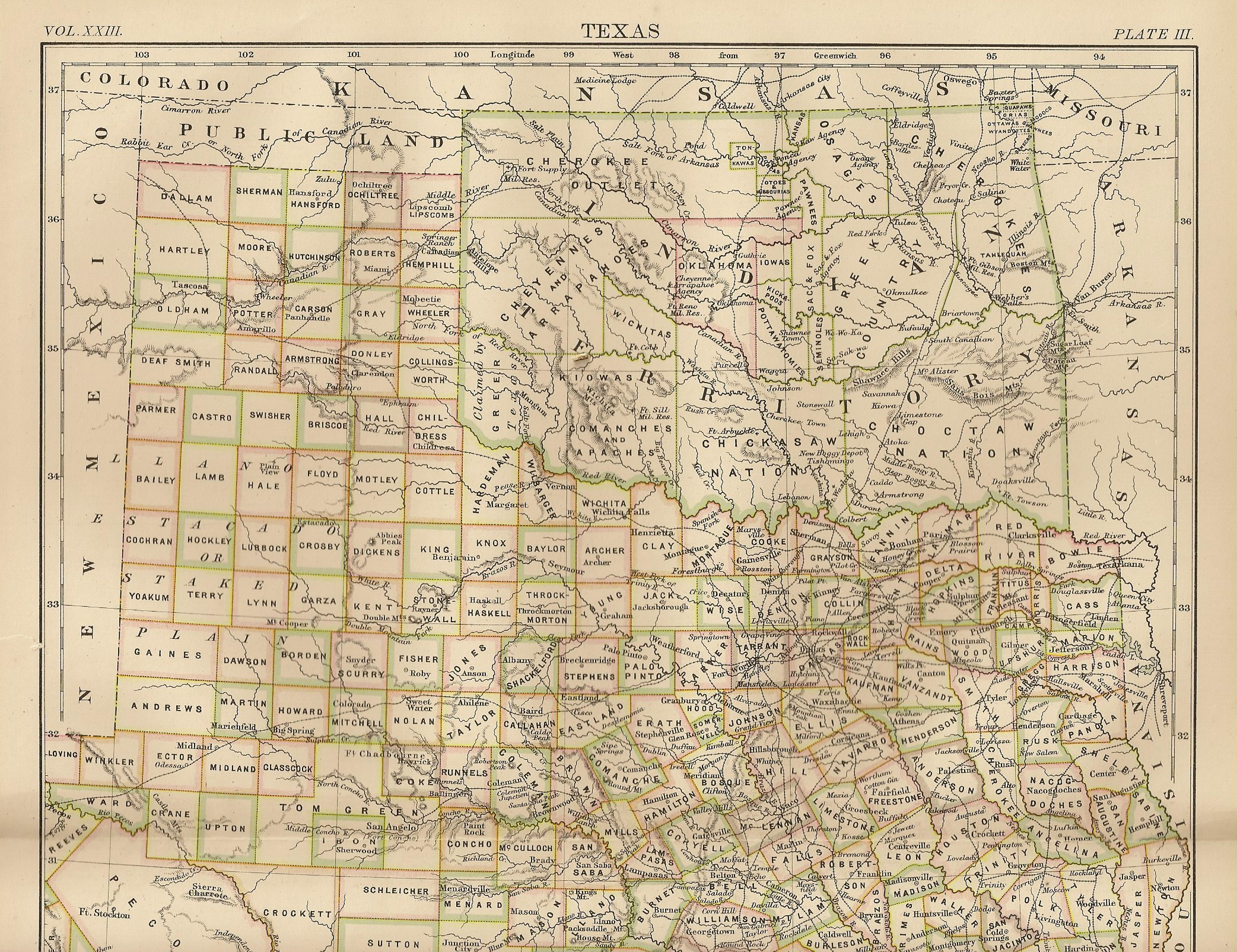
Oklahoma City Oil Field
The Oklahoma City Oil Field is one of the world's giant petroleum fields and is located in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma in the United States of America. The field was opened just south of the city limits on December 4, 1928, and first entered Oklahoma City limits on May 27, 1930.Weaver, Bobby D"Oklahoma City Field" a(accessed April 5, 2010) The field includes drill sites around the Oklahoma State Capitol and other nearby state government buildings. History The field was the first within an urban area in Oklahoma and caused immediate friction. The Oklahoma Corporation Commission passed an order stopping all drilling for 30 days on September 11, 1929. The Oklahoma City Council passed an ordinance in 1930 to limit drilling to one well per city block. Subsequent legal challenges and flagrant violations of the law led to Governor William H. Murray's declarations of martial law around the wells on May 5 and June 6 of 1932 and March 4, 1933. It also led to House Bill 481, passed April 10, 1933. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Mary Sudik
The Wild Mary Sudik gusher was an oil well blowout that took place on March 26, 1930 in what is now Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, USA. The gusher from Mary Sudik No. 1 well received extensive media coverage and was the subject of daily radio reports by NBC's Floyd Gibbons and newsreels that were shown in movie theaters. The gusher flowed for eleven days before it was capped on the third try. Mary Sudik No. 1 well was developed by the Indian Territory Illuminating Oil Company on the property of Vincent and Mary Sudik. The well, located about to the southeast of the present intersection of Interstate 240 and Bryant Avenue, to the south of the Oklahoma City center, blew out when the drilling crew underestimated well pressures in the newly developed Wilcox formation, producing 20,000 barrels of oil and of gas per day from the well. According to the well completion report, it produced 15,441 barrels of oil in a test run for 13 hours and 15 minutes. The crew had neglected to keep suffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat of Oklahoma County, it ranks 20th among United States cities in population, and is the 8th largest city in the Southern United States. The population grew following the 2010 census and reached 687,725 in the 2020 census. The Oklahoma City metropolitan area had a population of 1,396,445, and the Oklahoma City–Shawnee Combined Statistical Area had a population of 1,469,124, making it Oklahoma's largest municipality and metropolitan area by population. Oklahoma City's city limits extend somewhat into Canadian, Cleveland, and Pottawatomie counties, though much of those areas outside the core Oklahoma County area are suburban tracts or protected rural zones ( watershed). The city is the eighth-largest in the United States by area including consolidated city-counties; it is the second-largest, after Houston, not inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Fields In Oklahoma
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated lipids that are liquid at room temperature. The general definition of oil includes classes of chemical compounds that may be otherwise unrelated in structure, properties, and uses. Oils may be animal, vegetable, or petrochemical in origin, and may be volatile or non-volatile. They are used for food (e.g., olive oil), fuel (e.g., heating oil), medical purposes (e.g., mineral oil), lubrication (e.g. motor oil), and the manufacture of many types of paints, plastics, and other materials. Specially prepared oils are used in some religious ceremonies and rituals as purifying agents. Etymology First attested in English 1176, the word ''oil'' comes from Old French ''oile'', from Latin ''oleum'', which in turn comes from the Greek (''elaion'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Oklahoma City
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (rock)
Dolomite (also known as dolomite rock, dolostone or dolomitic rock) is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2. It occurs widely, often in association with limestone and evaporites, though it is less abundant than limestone and rare in Cenozoic rock beds (beds less than about 66 million years in age). The first geologist to distinguish dolomite rock from limestone was Belsazar Hacquet in 1778. Most dolomite was formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or of lime mud before lithification. The geological process of conversion of calcite to dolomite is known as dolomitization and any intermediate product is known as dolomitic limestone. The "dolomite problem" refers to the vast worldwide depositions of dolomite in the past geologic record in contrast to the limited amounts of dolomite formed in modern times. Recent research has revealed sulfate-reducing bacteria living in anoxic conditions precipitate dolomite which ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Trap
In petroleum geology, a trap is a geological structure affecting the reservoir rock and caprock of a petroleum system allowing the accumulation of hydrocarbons in a reservoir. Traps can be of two types: stratigraphic or structural. Structural traps are the most important type of trap as they represent the majority of the world's discovered petroleum resources. Structural traps A structural trap is a type of geological trap that forms as a result of changes in the structure of the subsurface, due to tectonic, diapiric, gravitational and compactional processes. Anticlinal trap An anticline is an area of the subsurface where the strata have been pushed into forming a domed shape. If there is a layer of impermeable rock present in this dome shape, then hydrocarbons can accumulate at the crest until the anticline is filled to the ''spill point'' - the highest point where hydrocarbons can escape the anticline. This type of trap is by far the most significant to the hydrocarbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geologic map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold causes compression of strata that preferentially erodes to a deeper st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anadarko Basin
The Anadarko Basin is a geologic depositional and structural basin centered in the western part of the state of Oklahoma and the Texas Panhandle, and extending into southwestern Kansas and southeastern Colorado. The basin covers an area of . By the end of the 20th Century, the Anadarko Basin was producing the largest amount of natural gas in the United States. Notable oil and gas fields within the basin include the Hugoton-Panhandle Gas Field, West Edmond Field, Union City Field and the Elk City Field.Bobby D. Weaver, "Anadarko Basin." ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. Accessed September 13, 2014. The basin is also the only commercial source of iodine in the United States and a major producer of helium. ...
|
Nemaha Ridge
The Nemaha Ridge (also called the Nemaha Uplift and the Nemaha Anticline) is located in the Central United States. It is a buried structural zone associated with a granite high in the Pre-Cambrian basement that extends from approximately Omaha, Nebraska to Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. The ridge is associated with the seismically active Humboldt Fault zone. It is also associated with the Proterozoic Midcontinent Rift System, which extends into northern Kansas about fifty miles west of the Nemaha.Kansas Geological Survey, Current Research in Earth Sciences, Bulletin 250, part 1 "Review of the Nemaha Ridge: A New Look at an Old Structure" Along the Nemaha Ridge is a series of faults referred to as the "Nemaha Fault Zone". The long term uplift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)

