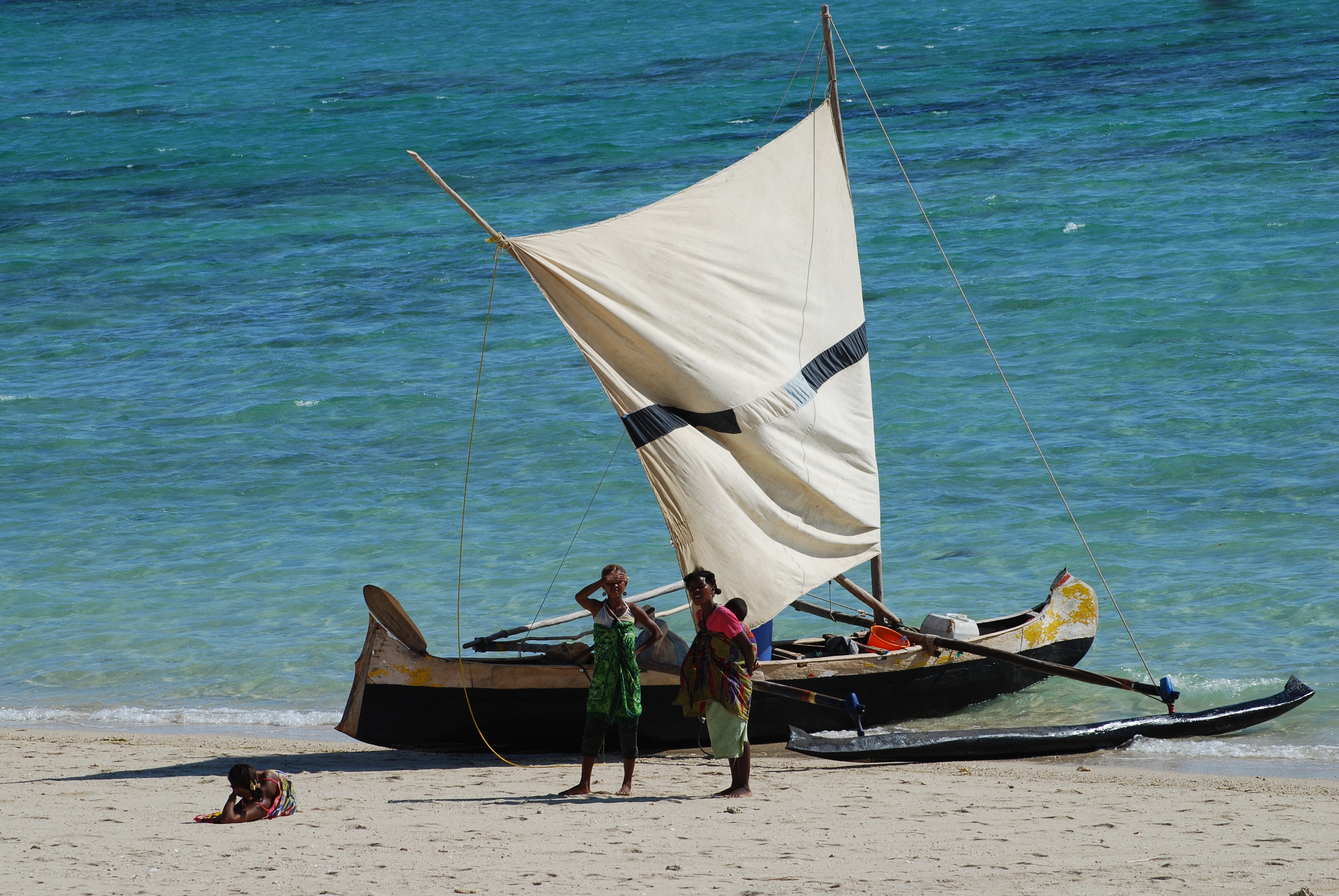|
Okandﺣ۸
The Okandﺣ۸ are a people of north-eastern Gabon who belong to the Mﺣ۷mbﺣ۷ language group (Okandﺣ۷, Apindzi, Simba, Vovﺣ۸, Tsogho, Evia and Kotakota). Their language overlaps that of the Apindzi and the Simba about 80/86% according to professor Van Der Veen. Their estimated population of 2,000 persons (in 2003) live in the Lopﺣ۸ region in Ogoouﺣ۸-Ivindo. The Mwiri, a male initiation institution, still plays an important role in the traditional social and religious life of the Okandﺣ۸. While their history is little known today, the archives do speak of them. The Okandﺣ۷, fierce conservators of their environment, through their initiation rites, (Douwa, Diyandzi, Ghﺣ۸tolﺣ۷, Bwﺣ۸tﺣ۸, Mwiri) were formerly dubbed the "kings of the Ogoouﺣ۸, the vainquishers of the rapids", better known than the Adouma and the Sisiwu, have taught their traditions, such as navigation of the Ogoouﺣ۸, okouyi dancing, Mvudi, Bodi, Mboudi, Mouiri, Ndjﺣ۷mbﺣ۷ and others) to the Galois, Enﺣ۷nga, Aduma, Mbangwﺣ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adouma
The Adouma (or Duma) are an ethnic group of Gabon, in central Africa. They primarily live on the South bank of the upper Ogoouﺣ۸ River, in the vicinity of Lastoursville (originally an Adouma village), and are known as expert canoeists or the boatmen. They speak Duma, a Nzebi language of the Bantu family. Their traditions hold that they arrived from the East or Southeast, coming down the Sebe River to the Ogowe, and thence to the Doumﺣ۸ rapids. They made canoes of Aucoumea wood, and sold slaves to the Okandﺣ۸, receiving European products such as guns and cloth in exchange. The Sociﺣ۸tﺣ۸ du Haut-Ogoouﺣ۸ (SHO) established a post at Lastoursville and engaged the Adouma in trade for rubber, ivory, and ebony . During the 1970s and 1980s, many Adouma moved down the Ogowe, towards Port-Gentil Port-Gentil () or Mandji is the second-largest city of Gabon, and it is a leading seaport. It is the center of Gabon's petroleum and timber industries. The city is located on a delta islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: Rﺣ۸publique gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of nearly and its population is estimated at million people. There are coastal plains, mountains (the Cristal Mountains and the Chaillu Massif in the centre), and a savanna in the east. Since its independence from France in 1960, the sovereign state of Gabon has had three presidents. In the 1990s, it introduced a multi-party system and a democratic constitution that aimed for a more transparent electoral process and reformed some governmental institutions. With petroleum and foreign private investment, it has the fourth highest HDI in the region (after Mauritius, Seychelles and South Africa) and the fifth highest GDP per capita (PPP) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lope Department
Lope is an old given name of Basque, Gascon and Spanish origin, derived from Latin ''lupus'', meaning "wolf". Lope may refer to: *Lope de Isﺣ۰saga (1493ﻗ1515), Basque Spanish ''conquistador'' *Lope de Aguirre (1510s ﻗ 1561), Basque Spanish ''conquistador'' *Lope de Vega (1562ﻗ1635), Spanish poet *Lope Martﺣn, Spanish sailor * Lope Recio Loynaz (1860-1927), Cuban general *Lupo II of Gascony (died 778) * ''Lope'' (film), a 2010 film *Lope de Vega (horse), an Irish bred Thoroughbred racehorse *Lope language, a Loloish language of China * Lopﺣ۸ Department, Gabon * Lope, a type of canter and gallop in horseback riding See also * Lop (other) * Lﺣﭖpe (other) * Lﺣﺏpez * Loping Airfield, a World War II United States Army Air Forces airfield China * Luoping County, China * Lupe (other) * Ochoa Ochoa ( eu, Otxoa or ''Otsoa'') is a Spanishhttps://www.ancestry.com/name-origin?surname=ochoa surname of Basque origin common throughout Spain, France, the America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogoouﺣ۸-Ivindo Province
Ogoouﺣ۸-Ivindo Province is the northeasternmost of Gabon's nine provinces, though its Lopﺣ۸ Department is in the very center of the country. It gets its name from two rivers, the Ogoouﺣ۸ and the Ivindo. This province, containing thousands of square kilometres of rainforest, is the largest and most sparsely populated and much less developed than the rest of the country. As of 2013 it had a population of 63,293 people. The principal town is Makokou. History In 1873ﻗ4, Antoine-Alfred Marche and Victor de Compiﺣ۷gne (the Marquis de Compiegnﺣ۸) explored the Ogoouﺣ۸ River region. They arrived in Lopﺣ۸ in 1874 but encountered hostility from the Fang-Meke people at the mouth of the Ivindo. Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza similarly made excursion to the region in November 1875 and between 1879 and 1882. In January 1995, a bout of the Ebola virus broke out in the forests of Ogoouﺣ۸-Ivindo. Nine out of 19 people died in the cases registered out of a population of 350 people. In 2010 it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okuyi
The Okuyi (plural: Mekuyo, also known as Ukuyi, Ocuya, Mokoi, Mukudj, Ikwara, Okukwe and Mbwanda, in Equatorial Guinea (Spanish): ''Mamarracho'') is a rite of passage practised by several Bantu peoples, Bantu Ethnic groups in Africa, ethnic groups in different countries mainly across the west coast of Central Africa. Some of the countries where the rite is exercised include Cameroon in West Central Africa, Gabon and Equatorial Guinea. Traditionally, the rite is performed at numerous special occasions including funerals and weddings. Usually when an infant reaches four months of age or when a child becomes an adolescent, an Okuyi ritual is applied as well. Today, the Mekuyo rite is exercised by a range of ethnic peoples within the Bantu cluster. The coastal community known as Ndowe, also known as ''playeros'', is a primary example, as peoples across Equatorial Guinea frequently perform the ritual in public. Gabon has two chief ethnic groups that exercise the Okuyi rite including the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Savorgnan De Brazza
Pietro Paolo Savorgnan di Brazzﺣ , later known as Pierre Paul Franﺣ۶ois Camille Savorgnan de Brazza; 26 January 1852 ﻗ 14 September 1905), was an Italian-born, naturalized French explorer. With his family's financial help, he explored the Ogoouﺣ۸ region of Central Africa, and later with the backing of the Sociﺣ۸tﺣ۸ de Gﺣ۸ographie de Paris, he reached far into the interior along the right bank of the Congo. He has often been depicted as a man of friendly manner, great charm and peaceful approach towards the Africans he met and worked with on his journeys, but recent research has revealed that he in fact alternated this kind of approach with more calculated deceit and at times relentless armed violence towards local populations. Under French colonial rule, the capital of the Republic of the Congo was named Brazzaville after him and the name was retained by the post-colonial rulers, one of the few African nations to do so. (Other exceptions are Pretoria, South Africa; Port Louis, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirogues
A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small boats, particularly dugouts and native canoes. The word is French and is derived from Spanish , which comes from the Carib '. Description The term 'pirogue' does not refer to a specific kind of boat, but is a generic term for small native boats in regions once colonized by France and Spain, particularly dugouts made from a single log. In French West Africa, the term refers to handcrafted banana-shaped boats used by traditional fishermen. In Madagascar, it also includes the more elaborate Austronesian ''lakana'' outrigger canoe. Pirogues are usually propelled by paddles that have one blade (as opposed to a kayak paddle, which has two). It can also be punted with a push pole in shallow water. Small sails are built by local fishermen, and they can also be employed. There are two types of sails with differences in their shapes: the square one is used mainly for fishing near the coast and is only usef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸
Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸ is a town and the capital of Moyen-Ogoouﺣ۸ in Gabon. It has a population of 38,775 as of 2013, and is located 75 kilometres south of the equator. Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸ is based in the Central African Rainforest at the river Ogoouﺣ۸. This river divides the city into 3 districts: Rive Gauche, Ile Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸ and Rive Droite. The Albert Schweitzer Hospital and the districts Adouma and Abongo are located on Rive Droite. The districts Atongowanga, Sahoty, Dakar, Grand Village, Chﺣ۱teau, Lalala and Bordamur build the Ile Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸. The majority of the people in Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸ live in the district Isaac located on Rive Gauche. This district hosts the Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸ Airport. Today Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸ is inhabited mainly by Bantu ethnic groups such as the Fang, Bapounou, Eshira, and Myﺣ۸nﺣ۸; these displaced the Pygmies to the east and north of Gabon. The main economic activity in the town is the fishery and a new port is under construction. Schweitzer The Franco-German Nobel Peace Prize winn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ndjolﺣ۸
Ndjolﺣ۸ is the capital town in the Abanga-Bigne Department in Gabon, lying northeast of Lambarﺣ۸nﺣ۸ on the Ogoouﺣ۸ River, the N2 road (Gabon), N2 road and the Trans-Gabon Railway. It is known as a base for logging and as a transport hub. Ndjolﺣ۸ is the last city that can be reached by barge, barge traffic traveling up the Ogoouﺣ۸ River. Above Ndjolﺣ۸ there are rapids on the river. History In 1883, Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza founded the military post of Ndjolﺣ۸, a strategic point located on the Ogoouﺣ۸ River, Ogoouﺣ۸ River. The river being difficult to navigate upstream, it is here that foresters loaded their wood to bring it down to Port-Gentil. The N'djolﺣ۸ prison, built in 1898 on an island on the Ogoouﺣ۸, opposite Ndjolﺣ۸, was part of a French policy to build detention centres in the French overseas departments and territories then in the French colonial empire, colonies. It was here that Samori Ture, Samory Tourﺣ۸,ﺡ founder and leader of the short-lived Wassoulou Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boouﺣ۸
Boouﺣ۸ is a small town in central Gabon. It is situated in Lopﺣ۸ Department, southwest side of the Ogoouﺣ۸-Ivindo Province. The town lies just 6.6 miles to the south of the Equator and is the province's only Department capital in the Southern Hemisphere. History Boouﺣ۸ is a bad transcription and a francization effort of the word "Mbue" or "Mboue" from the Shiwe language erroneously attributed to a town located in Ogoouﺣ۸-Ivindo province, Gabon by Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza in 1878. Boouﺣ۸ is still referred to as "Mboue" by the Shiwe people who were the first settlers of this town and who named it Nangashiki, but was changed to Mboue and subsequently to Boouﺣ۸. From all historical accounts, this change resulted from a miscommunication between De Brazza and Mpami Nani Shui, a Shiwe Chief, during some negotiation talks between the two men. Many accounts from the Shiwe people indicate that while negotiating his passage to the upper Ogoouﺣ۸ River, De Brazza asked Mpami Nani Shui t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus (''Choeropsis liberiensis'' or ''Hexaprotodon liberiensis''). Its name comes from the ancient Greek for "river horse" (). Aside from elephants and rhinos, the hippopotamus is the largest land mammal. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl. Despite their physical resemblance to pigs and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar-like legs, and large size: adults average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |