|
Oh (surname)
O or Oh is a family name in Korea. It is written using the hanja characters, 吳, 五, 伍, 吾, and 晤. According to the 2015 census in South Korea, there were 763,281 people carrying the O surname. History O also spelled Oh (Hangul: ) is the Korean form of the Chinese surname Wu (Hanja: ). The character 吳 is phonetically pronounced "Oh" in Korean, but "Wu" in Mandarin Chinese, however the historic origin of the surname is the same. The name originates from the ancient state of Wu in present-day province of Jiangsu. Wu (, , "Oh" or "O" romanization) is the sixth name listed in the Song Dynasty classic ''Hundred Family Surnames''. In the 13th century BC, the state of Zhou (which will later become the Zhou Dynasty) was ruled by Tai Wang (King Tai of Zhou). His surname was originally Ji (). He had three sons: Taibo, Zhongyong, and Jili. King Tai of Zhou favored the youngest son, Jili to inherit the reins of power, therefore Taibo and his brother Zhongyong volunta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Name
A Korean name (Hangul: ; Hanja: ) consists of a family name followed by a given name, as used by the Korean people in both South Korea and North Korea. In the Korean language, ''ireum'' or ''seongmyeong'' usually refers to the family name (''seong'') and given name (''ireum'' in a narrow sense) together. Korean names are descended from Chinese names as part of Sino-Korean vocabulary. Traditional Korean family names typically consist of only one syllable. There is no middle name in the English language sense. Many Koreans have their given names made of a generational name syllable and an individually distinct syllable, though this practice is rarely seen nowadays. The generational name syllable is shared by siblings in North Korea, and by all members of the same generation of an extended family in South Korea. Married men and women keep their full personal names, and children inherit the father's family name unless otherwise settled when registering the marriage. The family nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Ji Of Zhou
Jili was a leader of the Predynastic Zhou during the Shang dynasty of ancient China. His son King Wen and grandson King Wu would defeat the Shang to establish the Zhou dynasty. He was posthumously granted the title of king, and often referred to as Ji, King of Zhou. Jili's ancestral name was Ji. He was the youngest son of King Tai. Sima Qian recorded that Jili and his son were both renowned for their wisdom and this reputation caused his elder brothers Taibo and Zhongyong to renounce voluntarily their claims to the throne and to leave in exile to Wu.Sima Qian. ''Records of the Grand Historian'"Annals of Zhou"/ref> Surviving historical records portray him travelling to the Shang capital to submit to Wu Yi and being rewarded with land, jade, and horses in 1118 BC.Bamboo Annals. In 1117, he captured 20 "kings" of the Guirong tribes. During the reign of the Shang king Wen Ding, he was defeated by the Yanjing Rong but managed to subdue the Yuwu (), Hu (), and Xitu () Rong. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the '' Book of Documents'', '' Bamboo Annals'' and '' Records of the Grand Historian''. According to the traditional chronology based on calculations made approximately 2,000 years ago by Liu Xin, the Shang ruled from 1766 to 1122 BC, but according to the chronology based upon the "current text" of ''Bamboo Annals'', they ruled from 1556 to 1046 BC. Comparing the same text with dates of five-planet conjunctions, David Pankenier, supported by David Nivison, proposed dates of the establishment of the dynasty to 1554 BC. The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project dated the establishment to c. 1600 BC based on the carbon-14 dates of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wu Of Zhou
King Wu of Zhou () was the first king of the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. The chronology of his reign is disputed but is generally thought to have begun around 1046 BC and ended three years later in 1043 BC. King Wu's ancestral name was Ji () and given name Fa (). He was the second son of King Wen of Zhou and Queen Taisi. In most accounts, his older brother Bo Yikao was said to have predeceased his father, typically at the hands of King Zhou, the last king of the Shang dynasty; in the ''Book of Rites'', however, it is assumed that his inheritance represented an older tradition among the Zhou of passing over the eldest son.''Book of Rites''Tan Gong I, 1 Accessed 4 Nov 2012. (Fa's grandfather Jili had likewise inherited Zhou despite two older brothers.) Upon his succession, Fa worked with his father-in-law Jiang Ziya to accomplish an unfinished task: overthrowing the Shang dynasty. In 1048 BC, Fa marched down the Yellow River to the Mengjin ford and met with more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
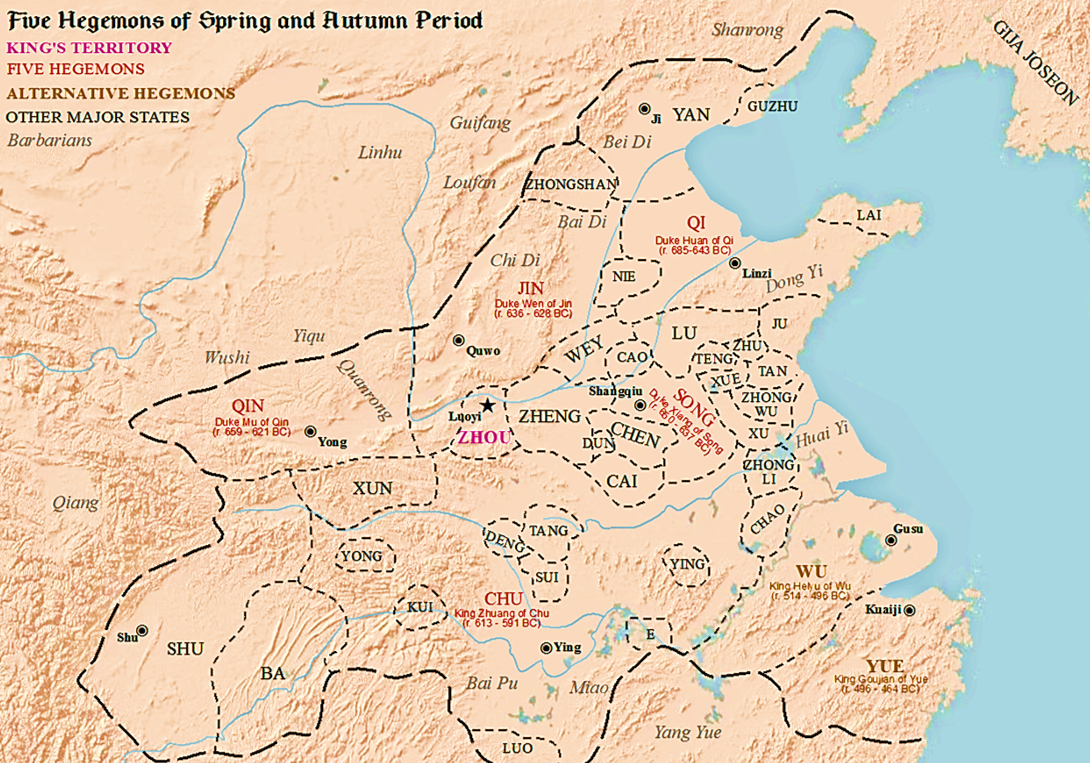
Five Hegemons
The Five Hegemons () refers to several especially powerful rulers of Chinese states of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history (770 to 476 BCE), sometimes alternatively referred to as the "Age of Hegemons". There are various lists of five rulers of those certain states which rose to power over the other states of this time period, states which were also formed during the period of dissolution of a once real and strong central state, namely the empire of the Zhou dynasty. The Hegemons mobilized the remnants of the Zhou empire, according to shared mutual political and martial interests. An especially prominent Hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi. Pronunciation and meaning In ancient Chinese, (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ) '' has a similar meaning and pronunciation to (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ), which means 'the eldest son in a family', or 'senator'. Both and can be translated as the 'Five Hegemons'. () literally means 'five', but in the context of ancient Chinese also has a more ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, screening, and skirmishing in many armies, or as heavy cavalry for decisive shock attacks in other armies. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as cavalryman, horseman, trooper, cataphract, knight, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any military forces that used other animals for mounts, such as camels or elephants. Infantry who moved on horseback, but dismounted to fight on foot, were known in the early 17th to the early 18th century as '' dragoons'', a class of mounted infantry which in most armies later evolved into standard cavalry while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege engine, constructed to protect assailants and ladders while approaching the defensive walls of a fortification. The tower was often rectangular with four wheels with its height roughly equal to that of the wall or sometimes higher to allow archers to stand on top of the tower and shoot arrows into the fortification. Because the towers were wooden and thus flammable, they had to have some non-flammable covering of iron or fresh animal skins. Used since the 11th century BC by the Babylonians and Assyrians in the ancient Near East, the 4th century BC in Europe and also in antiquity in the Far East, siege towers were of unwieldy dimensions and, like trebuchets, were therefore mostly constructed on site of the siege. Taking considerable time t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battering Ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient history, ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried by several people and propelled with force against an obstacle; the ram would be sufficient to damage the target if the log were massive enough and/or it were moved quickly enough (that is, if it had enough momentum). Later rams encased the log in an arrow-proof, fire-resistant canopy mounted on wheels. Inside the canopy, the log was swung from suspensory chains or ropes. Rams proved effective weapons of war because at the time wall-building materials such as stone and brick were weak in Tension (physics), tension, and therefore prone to cracking when impacted with force. With repeated blows, the cracks would grow steadily until a hole was created. Eventually, a breach would appear in the fabric of the wall, enabling armed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000 BCE. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more horses that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze and Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by light and heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and transport, in processions, for games, and in races. Etymology The word "chariot" comes from the Latin term ''carrus'', a loanword from Gaulish. In ancient Rome and some other ancient Mediterranean civilizations, a ''biga'' re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Zixu
:''Note: names are in simplified characters followed by traditional and Pinyin transliteration.'' Wu Yun (died 484 BC), better known by his courtesy name Zixu, was a Chinese military general and politician of the Wu kingdom in the Spring and Autumn period (722–481 BC). Since his death, he has evolved into a model of loyalty in Chinese culture. He is the best known historical figure with the Chinese family name " Wu" (). All branches of the Wu clan claim that he was their "first ancestor". Classical sources The historical records of Wu are found in the famous Chinese classics: ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (史記; Shǐjì) by Sima Qian, ''The Art of War'' by Sun Tzu and '' The Annals of Lü Buwei''. He is also mentioned in ''Guliang Zhuan'' and ''Gongyang Zhuan''. The accounts differ, showing the significant influence of folklore on his historical character. Life Early life Wu Zixu was the second son of Wu She, the Grand Tutor of the crown prince Jian of the state of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yue (state)
Yue (, Old Chinese: ''*''), also known as Yuyue (), was a state in ancient China which existed during the first millennium BC the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods of China's Zhou dynasty in the modern provinces of Zhejiang, Shanghai and Jiangsu. Its original capital was Kuaiji (modern Shaoxing); after its conquest of Wu, Yue relocated its court north to the city of Wu (modern-day Suzhou). Yue was conquered by Chu in 306 BC. History A specific kingdom, which had been known as the "Yue Guo" () in modern Zhejiang, was not mentioned until it began a series of wars against its northern neighbor Wu during the late 6th century BC. According to the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' and '' Discourses of the States'', the Yue are descended from Wuyu, the son of Shao Kang which as known as the sixth king of the Xia dynasty. With help from Wu's enemy Chu, Yue was able to be victorious after several decades of conflict. The famous Yue King Goujian destroyed and ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |