|
Oglala Aquifer
The Ogallala Aquifer () is a shallow water table aquifer surrounded by sand, silt, clay, and gravel located beneath the Great Plains in the United States. One of the world's largest aquifers, it underlies an area of approximately in portions of eight states (South Dakota, Nebraska, Wyoming, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and Texas). It was named in 1898 by geologist N. H. Darton from its type locality near the town of Ogallala, Nebraska. The aquifer is part of the High Plains Aquifer System, and resides in the Ogallala Formation, which is the principal geologic unit underlying 80% of the High Plains. Large-scale extraction for agricultural purposes started after World War II due partially to center pivot irrigation and to the adaptation of automotive engines for groundwater wells. Today about 27% of the irrigated land in the entire United States lies over the aquifer, which yields about 30% of the ground water used for irrigation in the United States. The aqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogallala Saturated Thickness 1997-sattk97-v2
Ogallala may refer to: *Ogallala, Nebraska *Ogallala Aquifer * Ogallala Commons *Ogallala Formation *Oglala Lakota The Oglala (pronounced , meaning "to scatter one's own" in Lakota language) are one of the seven subtribes of the Lakota people who, along with the Dakota people, Dakota, make up the Sioux, Očhéthi Šakówiŋ (Seven Council Fires). A majority ... (Sioux) {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogallala, Nebraska
Ogallala is a city in and the county seat of Keith County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 4,737 at the 2010 census. In the days of the Nebraska Territory, the city was a stop on the Pony Express and later along the transcontinental railroad. The Ogallala Aquifer was named after the city. History Ogallala first gained fame as a terminus for cattle drives that traveled from Texas to the Union Pacific railhead located there. These trails are known as the Western or Great Western trails. The Union Pacific Railroad reached Ogallala on May 24, 1867. The city itself was not laid out until 1875 and not incorporated until 1884 The town's name comes from the Oglala Sioux tribe. Geography Ogallala is located at (41.128806, -101.719460). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which is land and is water. Ogallala is in the US Mountain Time Zone (UTC−7/-6). Ogallala is close to Lake McConaughy, a large man-made lake and a state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
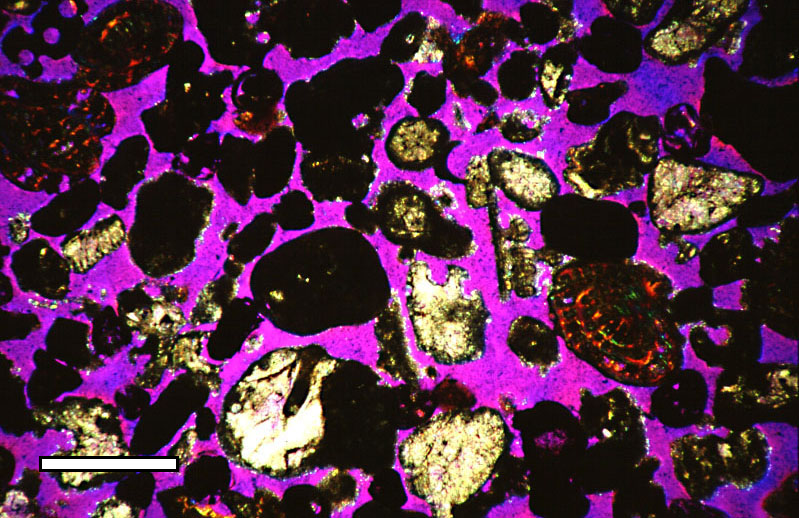
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansas River
The Kansas River, also known as the Kaw, is a river in northeastern Kansas in the United States. It is the southwesternmost part of the Missouri River drainage, which is in turn the northwesternmost portion of the extensive Mississippi River drainage. Its two names both come from the Kanza (Kaw) people who once inhabited the area; ''Kansas'' was one of the anglicizations of the French transcription ''Cansez'' () of the original '' kką:ze''. The city of Kansas City, Missouri, was named for the river, as was later the state of Kansas. The river valley averages in width, with the widest points being between Wamego and Rossville, where it is up to wide, then narrowing to or less in places below Eudora and De Soto. Much of the river's watershed is dammed for flood control, but the Kansas River is generally free-flowing and has only minor obstructions, including diversion weirs and one low-impact hydroelectric dam. Course Beginning at the confluence of the Republican and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolian Processes
Aeolian processes, also spelled eolian, pertain to wind activity in the study of geology and weather and specifically to the wind's ability to shape the surface of the Earth (or other planets). Winds may erode, transport, and deposit materials and are effective agents in regions with sparse vegetation, a lack of soil moisture and a large supply of unconsolidated sediments. Although water is a much more powerful eroding force than wind, aeolian processes are important in arid environments such as deserts. The term is derived from the name of the Greek god Aeolus, the keeper of the winds. Definition and setting ''Aeolian processes'' are those processes of erosion, transport, and deposition of sediments that are caused by wind at or near the surface of the earth. Sediment deposits produced by the action of wind and the sedimentary structures characteristic of these deposits are also described as ''aeolian''. Aeolian processes are most important in areas where there is little or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in the southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the U.S., its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/ British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande rift and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the tectonically younger Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada, which both lie farther to its west. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large national audience. Daily broadsheet editions are printed for D.C., Maryland, and Virginia. The ''Post'' was founded in 1877. In its early years, it went through several owners and struggled both financially and editorially. Financier Eugene Meyer purchased it out of bankruptcy in 1933 and revived its health and reputation, work continued by his successors Katharine and Phil Graham (Meyer's daughter and son-in-law), who bought out several rival publications. The ''Post'' 1971 printing of the Pentagon Papers helped spur opposition to the Vietnam War. Subsequently, in the best-known episode in the newspaper's history, reporters Bob Woodward and Carl Bernstein led the American press's investigation into what became known as the Watergate scandal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Pivot Irrigation
Center-pivot irrigation (sometimes called central pivot irrigation), also called water-wheel and circle irrigation, is a method of crop irrigation in which equipment rotates around a pivot and crops are watered with sprinklers. A circular area centered on the pivot is irrigated, often creating a circular pattern in crops when viewed from above (sometimes referred to as ''crop circles'', not to be confused with those formed by circular flattening of a section of a crop in a field). Most center pivots were initially water-powered, however today most are propelled by electric motors. Center-pivot irrigation systems are beneficial due to their ability to efficiently use water and optimize a farm's yield. The systems are highly effective on large land fields. History Center-pivot irrigation was invented in 1940 by the farmer Frank Zybach, who lived in Strasburg, Colorado. It is recognized as an effective method to improve water distribution to fields. In 1952, Zybach went into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |