|
Odom's Indicator
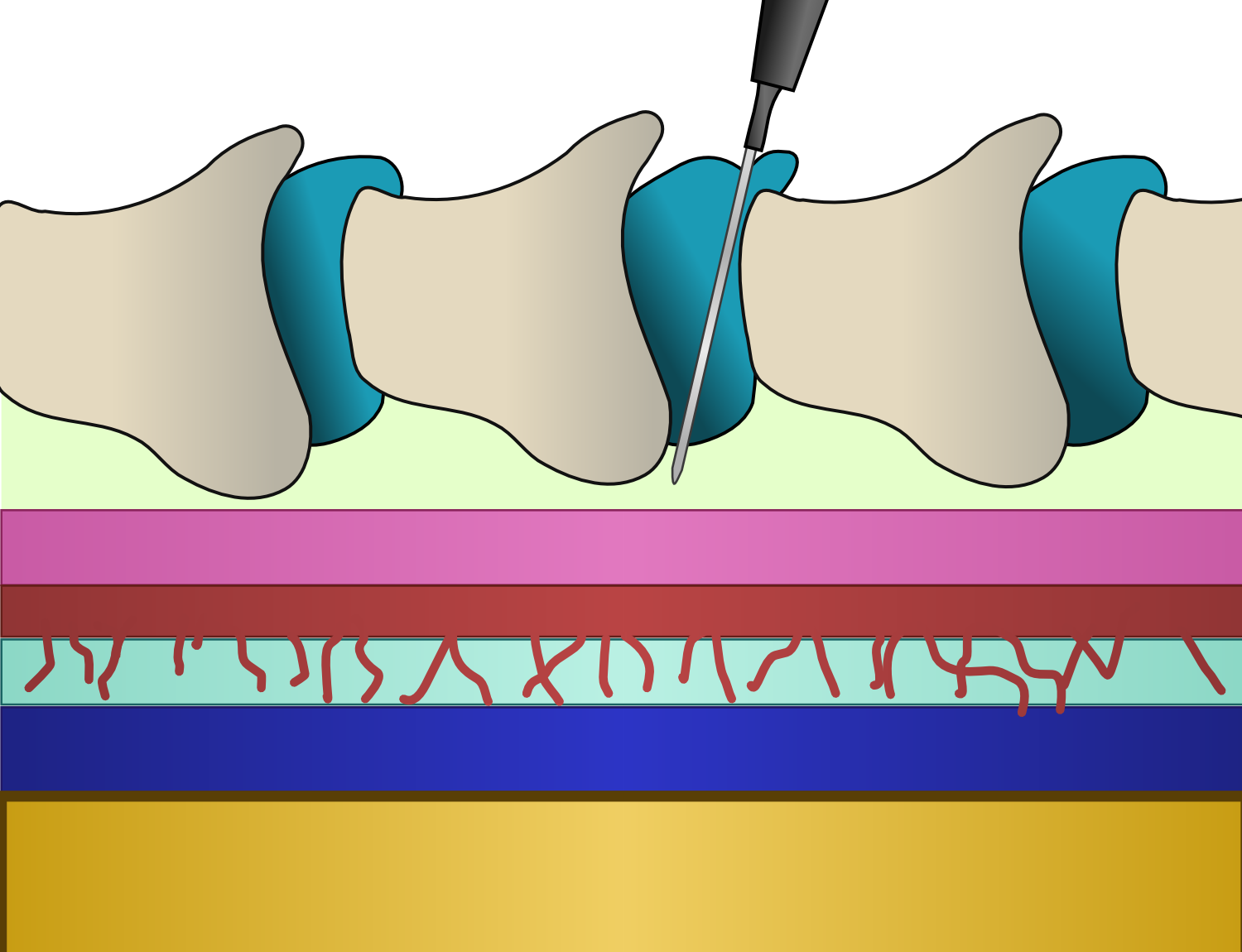
Odom's indicator is a device used for locating the epidural space In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae (spine). The anatomy term "epidural space" has its origin in the Ancient Greek language; , "on, upon" + dura mater also known as "epidural cavity", "e ... in regional anaesthesia. The device works on Dogliotti's principle by finding an area of decreased resistance to injection. It was originally designed on the assumption that the pressure in the epidural space was negative. This device is no-longer popular and alternative methods (e.g. loss of resistance to saline, loss of resistance to air) are now used. See also * Epidural procedure, which contains additional information on identification of the epidural space References Anesthetic equipment {{medical-equipment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidural Space
In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae ( spine). The anatomy term "epidural space" has its origin in the Ancient Greek language; , "on, upon" + dura mater also known as "epidural cavity", "extradural space" or "peridural space". In humans the epidural space contains lymphatics, spinal nerve roots, loose connective tissue, adipose tissue, small arteries, dural venous sinuses and a network of internal vertebral venous plexuses. Cranial epidural space In the skull, the periosteal layer of the dura mater adheres to the inner surface of the skull bones while the meningeal layer lays over the arachnoid mater. Between them is the epidural space. The two layers of the dura mater separate at several places, with the meningeal layer projecting deeper into the brain parenchyma forming fibrous septa that compartmentalize the brain tissue. At these sites, the epidural space is wide enough to house the epidural venous sinuses. There are fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthesia (journal)
{{med-journal-stub ...
''Anaesthesia'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering research in anaesthesia, including intensive care, peri-operative medicine, critical care medicine and pain therapy. It is the official journal of thAssociation of Anaesthetists According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal's 2020 impact factor is 6.955, ranking it fifth out of 33 journals in the category "Anesthesiology". References External links * Publications established in 1946 Wiley-Blackwell academic journals Monthly journals English-language journals Anaesthesia Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogliotti's Principle
Dogliotti's principle is a principle in epidural anaesthesia first described by Professor Achille Mario Dogliotti in 1933. It is a method for the identification of the epidural space, a potential space. As a needle is advanced through the ligamentum flavum, to the epidural space, with constant pressure applied to the piston of a syringe, loss of resistance occurs once the needle enters the epidural space due to the change in pressure. The identification of this space, allows subsequent administration of epidural anaesthesia, a technique used primarily for analgesia during childbirth. This technique remains in use at , and is commonly referred to the loss of resistance to saline technique (LORS) or its variation, the loss of resistance to air technique (LORA). These use, respectively, saline or air to identify the epidural space. The LORS technique is generally favoured due to the increased complication risk with the LORA technique such as pneumocephalus or air embolism. See a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Journal Of Anaesthesia
The ''British Journal of Anaesthesia'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier on behalf of the Royal College of Anaesthetists (and its Faculty of Pain Medicine), the College of Anaesthesiologists of Ireland, and the Hong Kong College of Anaesthesiologists, for all of which it serves as their official journal. The journal covers all aspects of anaesthesia, perioperative medicine, intensive care medicine, and pain management. The editor-in-chief is Hugh C. Hemmings (Weill Cornell Medical College). The journal was established in 1923, one year after the first anaesthetic journal (''Anesthesia & Analgesia'') was published by the International Anaesthesia Research Society. The first editor-in-chief was H.M. Cohen, who edited the journal from 1923 to 1928. Recent editors-in-chief include Ravi Mahajan (University of Nottingham), Charles Reilly (University of Sheffield), and Jennifer Hunter (University of Liverpool). ''BJA Education'' ''BJA Education'' is a sist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Manometric u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidural
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, , upon" + ''dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians and nurse anesthetists to administer local anesthetic agents, analgesics, diagnostic medicines such as radiocontrast agents, and other medicines such as glucocorticoids. Epidural administration involves the placement of a catheter into the epidural space, which may remain in place for the duration of the treatment. The technique of intentional epidural administration of medication was first described in 1921 by Spanish military surgeon Fidel Pagés. In the United States, over 50% of childbirths involve the use of epidural anesthesia. Epidural anaesthesia causes a loss of sensation, including pain, by blocking the transmission of signals through nerve fibres in or near the spinal cord. For this reason, epidurals are commonly used for pain cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |