|
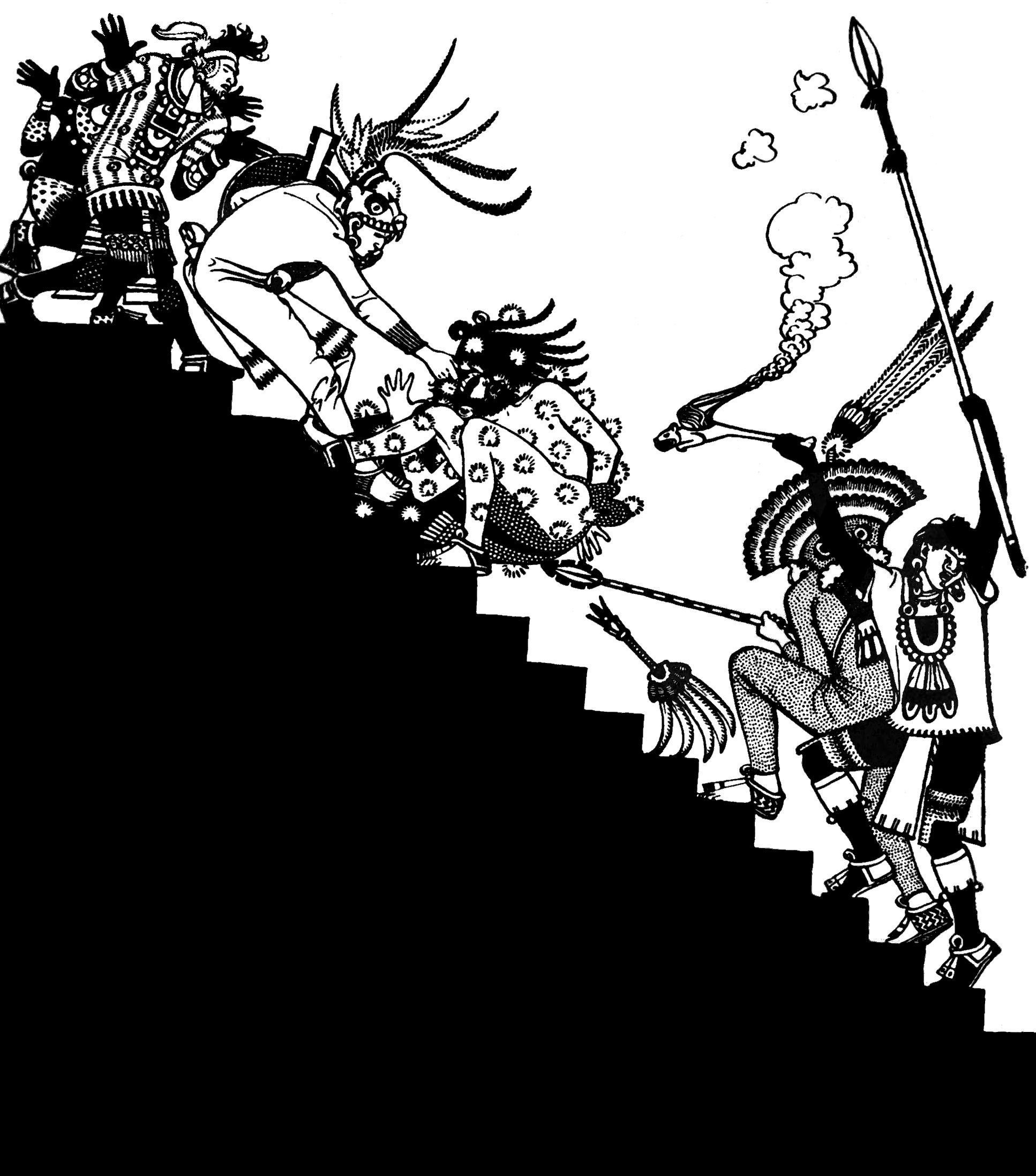
Ochpaniztli
Ochpaniztli is the Eleventh Month of the Aztec calendar. It is also a festival in the Aztec religion dedicated to Toci and Tlazolteotl and is also the month of cleaning or sweeping away. Meaning Ochpaniztli was largely concerned with sweeping, which was a reference to the rush of winds that occurred in the valley of Mexico before the winter rains came, the end of the growing season and the start of the harvesting season, the season of war when the Mexica went to war for captives to sacrifice to the gods, who could never have enough human flesh to eat. Rituals For the first five days of Ochpaniztli, the emphasis was on silence and quiet in Tenochtitlan. On the sixth day and continuing for eight more, warriors would march through the streets of Tenochtitlan carrying flowering branches until dusk. The warriors maintained tight discipline as they circled in elaborate maneuvers carrying marigolds and in complete silence except for the beating of the drums. After eight days, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Religion
The Aztec religion is a monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of was construed as the supreme god , as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion tended to embrace the mythological and polytheistic aspects, and the Aztec Empire's state religion sponsored both the monism of the upper classes and the popular heterodoxies. The Aztec Empire officially recognized the most popular cults such that the deity was represented in the central temple precinct of the capital . The imperial cult was specifically that of the distinctive warlike patron god of the Mexica . Subjugated peoples were allowed to retain their own religious traditions in conquered provinces so long as they added the imperial god to their local pantheons, while the Empire would often incorporate practices from its new territories into the mainstream religion. In common with many other indigenous Mesoamerican civilizations, the Aztecs put great ritual emphasis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toci
Toci (; nci, tocih, , “our grandmother”) is a deity figuring prominently in the religion and mythology of the pre-Columbian Aztec civilization of Mesoamerica. In Aztec mythology, she is seen as an aspect of the mother goddess Coatlicue or Xochitlicue and is thus labeled “mother of the gods” ( nci, tēteoh īnnān). She is also called Tlalli Iyollo ( nci, tlālli īyōlloh, , “heart of the earth”). Characteristics and associations Although considered to be an aged deity, Toci is not always shown with specific markers of great age. Toci is frequently depicted with black markings around the mouth and nose, wearing a headdress with cotton spools (Miller and Taube 1993, p. 170). These are also characteristic motifs for Tlazolteotl, a central Mesoamerican goddess of both purification and filth (''tlazolli'' in Nahuatl) and the two deities are closely identified with one another. Toci was also associated with healing and venerated by curers of ailments and midwives. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sacrifice In Aztec Culture
Human sacrifice was common in many parts of Mesoamerica, so the rite was nothing new to the Aztecs when they arrived at the Valley of Mexico, nor was it something unique to pre-Columbian Mexico. Other Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Purépechas and Toltecs, and the Maya performed sacrifices as well and from archaeological evidence, it probably existed since the time of the Olmecs (1200–400 BC), and perhaps even throughout the early farming cultures of the region. However, the extent of human sacrifice is unknown among several Mesoamerican civilizations. What distinguished Aztec practice from Maya human sacrifice was the way in which it was embedded in everyday life. These cultures also notably sacrificed elements of their own population to the gods. In 1519, explorers such as Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan and made observations of and wrote reports about the practice of human sacrifice. Bernal Díaz del Castillo, who participated in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inga Clendinnen
Inga Clendinnen, (; 17 August 1934 – 8 September 2016) was an Australian author, historian, anthropologist, and academic. Her work focused on social history, and the history of cultural encounters. She was an authority on Aztec civilisation and pre-Columbian ritual human sacrifice. She also wrote about the Holocaust, and on first contacts between Indigenous Australians and white explorers. At her death, she was an Emeritus Scholar at La Trobe University, Melbourne. Early life and education Clendinnen was born in Geelong, Victoria, in 1934. She was the youngest of four children. Her father owned a cabinet-making business and later became a Geelong City Councillor; her mother was a homemaker. Clendinnen graduated from the University of Melbourne in 1955 with a Bachelor of Arts with Honours, followed by a Master of Arts in 1975. Career Clendinnen's work focused on social history, and the history of cultural encounters. She was considered an authority on Aztec civilisation and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicomecōātl
In Aztec mythology, Chicomecōātl "Seven Serpent", was the Aztec goddess of agriculture during the Middle Culture period. She is sometimes called "goddess of nourishment", a goddess of plenty and the female aspect of maize. More generally, Chicomecōātl can be described as a deity of food, drink, and human livelihood. She is regarded as the female counterpart of the maize god ''Centeōtl'', their symbol being an ear of corn. She is occasionally called ''Xilonen'', (meaning doll made of corn), who was married also to ''Tezcatlipoca''. Significance of Name Chicomecōātl's name, "Seven Serpent", is thought to be a reference to the duality of the deity. While she symbolizes the gathering of maize and agricultural prosperity, she also is thought to be harmful to the Aztecs, as she was thought to be of blame during years of poor harvest. Appearance & Depiction Her appearance is mostly represented with red ochre on the face, paper headdress on top, water-flowers patterned shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Texcoco
Lake Texcoco ( es, Lago de Texcoco) was a natural lake within the "Anahuac" or Valley of Mexico. Lake Texcoco is best known as where the Aztecs built the city of Tenochtitlan, which was located on an island within the lake. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, efforts to control flooding by the Spanish led to most of the lake being drained. The entire lake basin is now almost completely occupied by Mexico City, the capital of the present-day nation of Mexico. Drainage of the lake has led to serious ecological and human consequences: the local climate and water availability have changed considerably, contributing to water scarcity in the area; subsequent groundwater extraction leads to land subsidence under much of the city; and native species endemic to the lake region have become severely endangered or extinct due to ecosystem change, such as the axolotl. After the cancellation of the Mexico City Texcoco Airport, the government initiated a major restoration project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |