|
Ocepesuchus
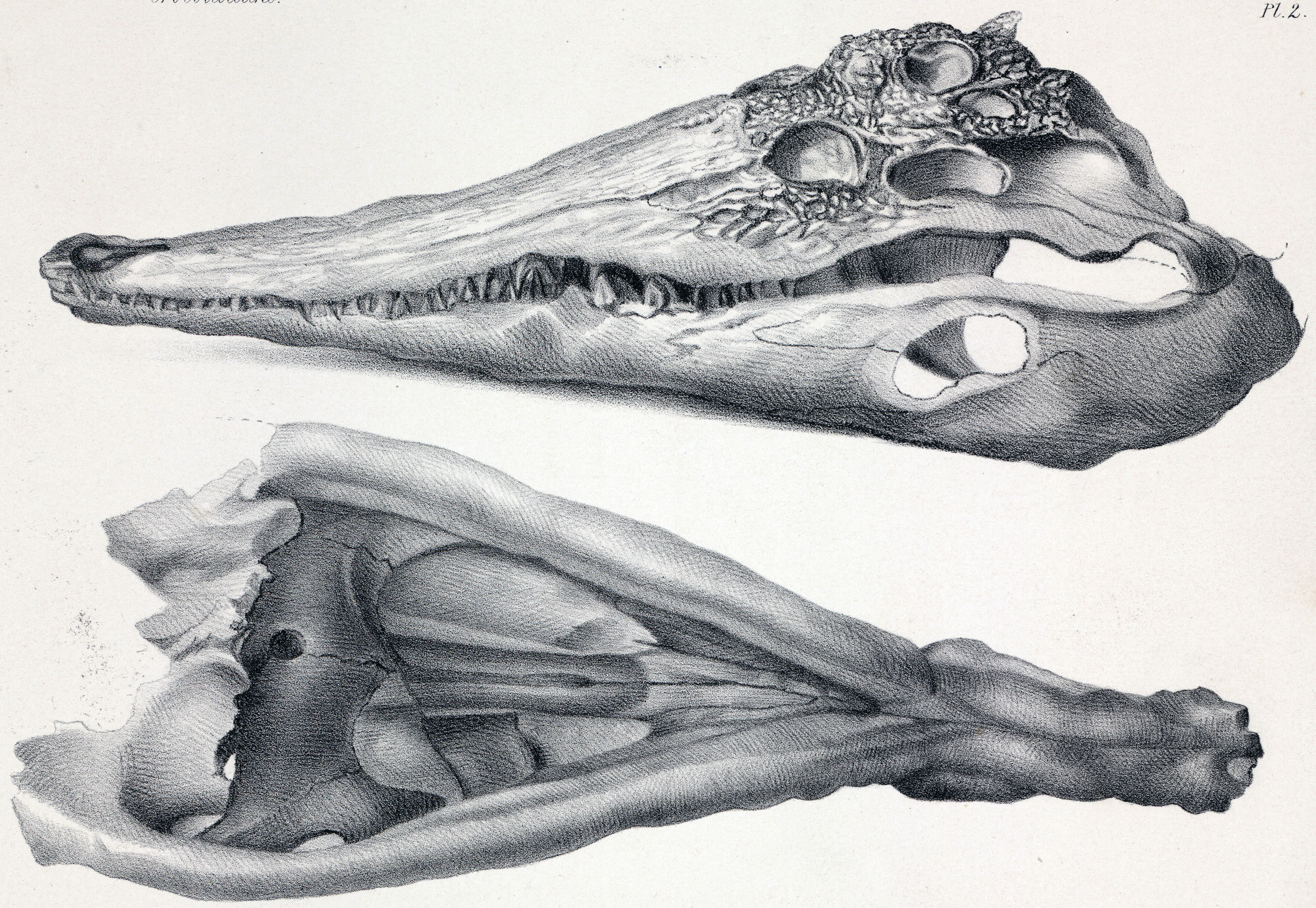
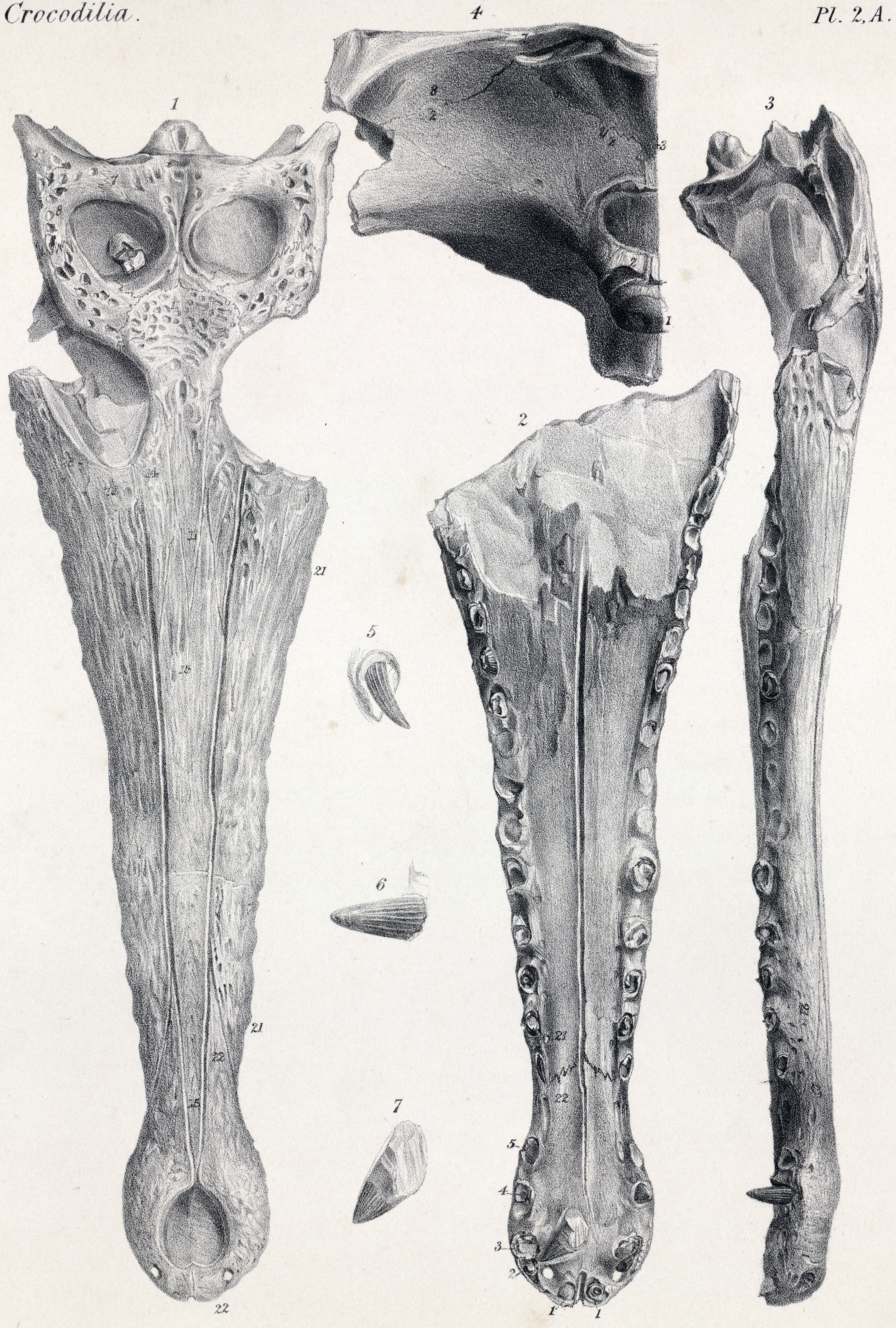
''Ocepesuchus'' (meaning "Ocepe crocodile", in reference to the OCP, or Office Chérifien des Phosphates, a phosphate-mining company that participated in the excavation of the specimen) is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodilian, related to modern gharials. It lived in the Late Cretaceous of Morocco. Described by Jouve and colleagues in 2008, the type species is ''O. eoafricanus'', with the specific name meaning "dawn African" in reference to its great age relative to other African crocodilians. ''Ocepesuchus'' had a long snout with a tubular shape, wider than high. It is the oldest known true crocodilian from Africa.Other crocodile-like animals from older strata in Africa, like ''Sarcosuchus'', are not true crocodilians, but related animals. ''Ocepesuchus'' is based on OCP DEK-GE 45, a crushed but mostly complete skull from late Maastrichtian (Late Cretaceous)-age rocks in the Oulad Abdoun Basin, in the vicinity of Khouribga, Morocco. The individual is interpreted as a small a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialidae
Gavialidae is a family (biology), family of large semiaquatic crocodilians with elongated, narrow snouts. Gavialidae consists of two extant taxon, living species, the gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), both occurring in Asia. Many extinct members are known from a broader range, including the recently extinct ''Hanyusuchus''. Gavialids are generally regarded as lacking the jaw strength to capture the large mammalian prey favoured by crocodiles and alligators of similar size so their thin snout is best used to catch fish, however the false gharial has been found to have a Generalist and specialist species, generalist diet with mature adults preying upon larger vertebrates, such as Ungulate, ungulates. Taxonomy The family Gavialidae was proposed by Arthur Adams (zoologist), Arthur Adams in 1854 for reptiles with a very long and slender muzzle, webbed feet and nearly equal teeth. It is currently recognized as a crown group, meaning that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialinae
Gavialinae is a subfamily of large semiaquatic crocodilian reptiles, resembling crocodiles, but with much thinner snouts. Gavialinae is one of the two major subfamilies within the family Gavialidae - the other being the subfamily Tomistominae, which contains the false gharial and extinct relatives. Classification Gavialinae was first proposed by Nopcsa in 1923, and was cladistically defined by Brochu in 2003 as ''Gavialis gangeticus'' (the gharial) and all crocodylians more closely related to it than to ''Tomistoma schlegelii'' (the false gharial). This is a stem-based definition for gavialinae, and means that it includes more basal extinct gavialine ancestors that are more closely related to the gharial than to the false gharial. The false gharial was once thought to be only distantly related to the gharial despite its similar appearance. The false gharial and other tomistomines were traditionally classified within the superfamily Crocodyloidea as close relatives of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialoidea
Gavialoidea is one of three superfamilies of crocodylians, the other two being Alligatoroidea and Crocodyloidea. Although many extinct species are known, only the gharial ''Gavialis gangeticus'' and the false gharial ''Tomistoma schlegelii'' are alive today, with ''Hanyusuchus'' having become extinct in the last few centuries. Extinct South American gavialoids likely dispersed in the mid Tertiary from Africa and Asia. Fossil remains of the Puerto Rican gavialoid '' Aktiogavialis puertorisensis'' were discovered in a cave located in San Sebastián, Puerto Rico and dated to the Oligocene. This individual is thought to have crossed the Atlantic coming from Africa, indicating that this species was able to withstand saltwater. Classification Gavialoidea is cladistically defined as ''Gavialis gangeticus'' (the gharial) and all crocodylians closer to it than to ''Alligator mississippiensis'' (the American alligator) or ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). This is a stem-bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialoidea
Gavialoidea is one of three superfamilies of crocodylians, the other two being Alligatoroidea and Crocodyloidea. Although many extinct species are known, only the gharial ''Gavialis gangeticus'' and the false gharial ''Tomistoma schlegelii'' are alive today, with ''Hanyusuchus'' having become extinct in the last few centuries. Extinct South American gavialoids likely dispersed in the mid Tertiary from Africa and Asia. Fossil remains of the Puerto Rican gavialoid '' Aktiogavialis puertorisensis'' were discovered in a cave located in San Sebastián, Puerto Rico and dated to the Oligocene. This individual is thought to have crossed the Atlantic coming from Africa, indicating that this species was able to withstand saltwater. Classification Gavialoidea is cladistically defined as ''Gavialis gangeticus'' (the gharial) and all crocodylians closer to it than to ''Alligator mississippiensis'' (the American alligator) or ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). This is a stem-bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
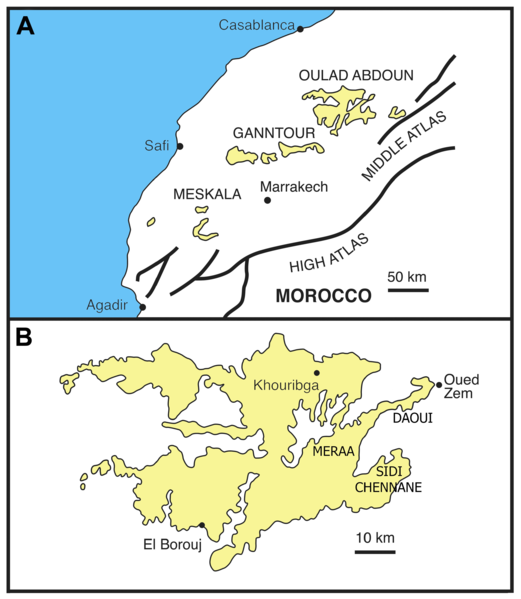
Oulad Abdoun Basin
The Oulad Abdoun Basin (also known as the Ouled Abdoun Basin or Khouribga Basin) is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years. Geography The Oulad Abdoun is located west of the Atlas Mountains, near the city of Khouribga. The Oulad Abdoun phosphate deposits encompass some , an area of . The Oulad Abdoun is the largest and northernmost of Morocco's major phosphate basins, which from northeast to southwest, include the Ganntour, Meskala, and Oued Eddahab (Laayoune-Baa) basins. Paleobiota The Oulad Abdoun Basin stretches from late Cretaceous to the Eocene, and contains abundant marine vertebrate fossils, including sharks, bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Chérifien Des Phosphates
The OCP Group (OCP S.A.) (formerly Office Chérifien des Phosphates) is a Moroccan state-owned phosphate rock miner, phosphoric acid manufacturer and fertilizer producer. Founded in 1920, the company has grown to become the world's largest producer of phosphate and phosphate-based products and it is one of the largest phosphate, fertilizer, Chemicals and Mineral industrial companies in the world by revenue. OCP has access to more than 70% of the world's phosphate rock reserves. Initially a mining company, OCP diversified in 1965 to become a phosphate processor, making it the world's largest and leading fertilizer manufacturers. The company holds a 31% market share of the world phosphate product market. The group employs nearly 23,000 people in Morocco and a number of international subsidiaries. In 2018, its revenues amounted to US$5.884 billion. History Origins The OCP Group was founded in Morocco in 1920 as the Office Chérifien des Phosphates following Royal Decree. Minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomistoma Cairense
''Tomistoma cairense'' is an extinct species of gavialoid crocodilian from the Lutetian stage of the Eocene era. It lived in North East Africa, especially Egypt. Remains of ''T. cairense'' have been found in the Mokattam Formation, in Mokattam, Egypt. ''Tomistoma cairense'' did not have a Maxilla process within their lacrimal gland, whereas all extant (living) crocodilians do. Below is a cladogram based morphological studies comparing skeletal features that shows ''Tomistoma cairense'' as a member of Tomistominae, related to the false gharial: Based on morphological studies of extinct taxa, the tomistomines (including the living false gharial) were long thought to be classified as crocodiles and not closely related to gavialoids. However, recent molecular studies using DNA sequencing have consistently indicated that the false gharial (''Tomistoma'') (and by inference other related extinct forms in Tomistominae) actually belong to Gavialoidea (and Gavialidae). Below is a clad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentisuchus Spenceri
''Kentisuchus'' is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found from England and France that date back to the early Eocene. The genus has also been recorded from Ukraine, but it unclear whether specimens from Ukraine are referable to ''Kentisuchus''. Species The genus ''Kentisuchus'' was erected by Charles Mook in 1955 for the species ''"Crocodylus" toliapicus'', described by Richard Owen, in 1849. William Buckland named ''"Crocodylus" spenceri'' on the basis of a partial skull found from the Isle of Sheppey in Kent, England. In 1888 Richard Lydekker considered ''"C." toliapicus'' synonymous with ''"C." champsoides'' and ''"C." arduini'', named by De Zigno, and reapplied the name ''"C." spenceri'' to all of these species. The genus name ''Kentisuchus'' was constructed only after it was realized that these specimens were clearly distinct from the genus ''Crocodylus'' and that some specimens o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentisuchus Astrei
''Kentisuchus'' is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found from England and France that date back to the early Eocene. The genus has also been recorded from Ukraine, but it unclear whether specimens from Ukraine are referable to ''Kentisuchus''. Species The genus ''Kentisuchus'' was erected by Charles Mook in 1955 for the species ''"Crocodylus" toliapicus'', described by Richard Owen, in 1849. William Buckland named ''"Crocodylus" spenceri'' on the basis of a partial skull found from the Isle of Sheppey in Kent, England. In 1888 Richard Lydekker considered ''"C." toliapicus'' synonymous with ''"C." champsoides'' and ''"C." arduini'', named by De Zigno, and reapplied the name ''"C." spenceri'' to all of these species. The genus name ''Kentisuchus'' was constructed only after it was realized that these specimens were clearly distinct from the genus ''Crocodylus'' and that some specimens o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dollosuchoides Densmorei
''Dollosuchoides'', colloquially known as the Crocodile of Maransart, is an extinct monospecific genus of gavialoid crocodilian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found in the Brussel Formation of Maransart, Belgium and date back to the middle Eocene. The holotype, IRScNB 482, was discovered in 1915 and it was prepared during 1926–1927 by M. Hubert, J. Mehschaert and M. Jean de Kleermaeker, and also in 1927, Louis Dollo had the holotype put on display in the Museum of Natural Sciences and he intended to describe the specimen but he died in 1931 before he was able to describe it and the specimen was eventually referred to '' Dollosuchus'' by Swinton (1937)Swinton, W. E. (1937)The Crocodile of Maransart (Dollosuchus dixoni [Owen]).''Mémoire'' 80: 3–46 until it was moved to its own genus by Brochu (2007). It is currently housed in the Gand Museum in Belgium. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram based morphological studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |