|
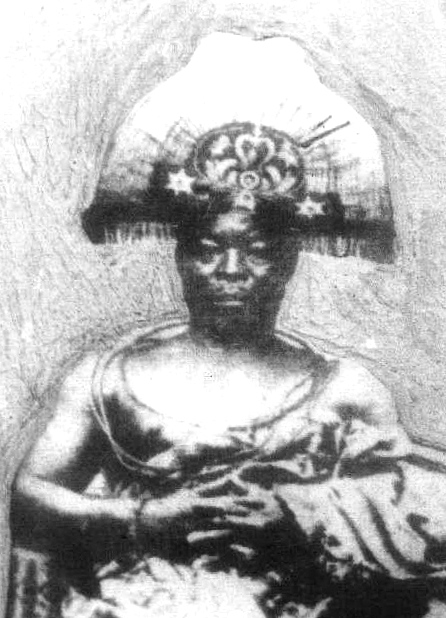
Oba Ewedo
Ewedo, originally known as Prince Efabo, was the fourth Oba of the Kingdom of Benin who reigned from 1255 AD to 1280 AD. He was the only son and successor of Ehenmihen. He is credited with moving the seat of his government from Usama to the present palace site, introducing various gods and laws, and changing the name of the country from Ile or Ile-Ibinu to Ubini (Benin). He also reformed the political and administrative system of the kingdom, established a palace bureaucracy, and expanded the territory and influence of Benin. Background The Kingdom of Benin was one of the oldest and most influential states in West Africa. According to oral tradition, it was founded by the Ogiso (meaning "kings of the sky" or "rulers of heaven") who ruled from a mythical city called Igodomigodo. The Ogiso dynasty lasted for about 31 generations until the last Ogiso, Owodo, was deposed by a group of elders led by Chief Odion. The elders then sent an emissary to Ife, a powerful Yoruba city-sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oba Of Benin
The Oba of Benin is the traditional ruler and the custodian of the culture of the Edo people and all Edoid people. The then Kingdom of Benin (not to be confused with the modern-day and unrelated Republic of Benin, which was then known as Dahomey) has been and continues to be mostly populated by the Edo (also known as Benin ethnic group). In 1897, a British military force, of approximately 1,200 men, under the command of Sir Harry Rawson, mounted the Benin punitive Expedition. The force dispatched in retaliation to the ambush of a British party, at Ugbine village near Gwato, on the 4th January 1897, by a group of Benin soldiers, acting without orders from the Oba; the ambush had led to the deaths of all but two of the British party. The British force captured the capital of the Kingdom of Benin, sacking and burning the city while forcing the Oba of Benin, Ovonramwen, into a six-month exile. The expeditionary force consisted of both indigenous soldiers and British officers b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Royalty
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute more than 42 million people in Africa, are a few hundred thousand outside the continent, and bear further representation among members of the African diaspora. The vast majority of the Yoruba population is today within the country of Nigeria, where they make up 21% of the country's population according to CIA estimations, making them one of the largest ethnic groups in Africa. Most Yoruba people speak the Yoruba language, which is the Niger-Congo language with the largest number of native or L1 speakers. In Africa, the Yoruba are contiguous with the Yoruboid Itsekiri to the south-east in the northwest Niger Delta, Bariba to the northwest in Benin and Nigeria, the Nupe to the north, and the Ebira to the northeast in central Nigeria. To th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba History
The documented history begins when Ọranyan, Oranyan came to rule the Oyo Empire, which became dominant in the early 17th century. The older traditions of the formerly dominant Ile-Ife kingdom are largely orature, oral. Before Oyo Empire The history of the Yoruba people begins in Ife Empire, Ile-Ife(Ife Empire). This kingdom was founded by the deity Oduduwa, who is believed to have created the world. Oduduwa was the first divine king of the Yoruba people. It is said the Yoruba people believe that their civilization began at Ile-Ife where the gods descended to earth. The Ethnic group became popular internationally due to their trading with the Portuguese which gave them guns for their trade. The Yoruba were invaded by the Fulani in the early 1800s, which pushed the people to the South. In the late 1800s, they formed a treaty with the British Empire and were colonized by Britain beginning in 1901. The people who lived in Yorubaland, at least by the seventh century Before Christ, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Nigeria
The history of Nigeria can be traced to the earliest inhabitants whose remains date from at least 13,000 BC through early civilizations such as the Nok culture which began around 1500 BC. Numerous ancient African civilizations settled in the region that is known today as Nigeria, such as the Kingdom of Nri, the Benin Empire, and the Oyo Empire. Islam reached Nigeria through the Bornu Empire between (1068 AD) and Hausa States around (1385 AD) during the 11th century, while Christianity came to Nigeria in the 15th century through Augustinian and Capuchin monks from Portugal. The Songhai Empire also occupied part of the region. From the 15th century, European slave traders arrived in the region to purchase enslaved Africans as part of the Atlantic slave trade, which started in the region of modern-day Nigeria; the first Nigerian port used by European slave traders was Badagry, a coastal harbour. Local merchants provided them with slaves, escalating conflicts among the ethnic group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigerian Traditional Rulers
Nigerian traditional rulers often derive their titles from the rulers of independent states or communities that existed before the formation of modern Nigeria. Although they do not have formal political power, in many cases they continue to command respect from their people and have considerable influence in their community. Though their bearers usually maintain the monarchical styles and titles of their sovereign ancestors, both their independent activities and their relations with the central and regional governments of Nigeria are closer in substance to those of the high nobility of old Europe than to those of actual reigning monarchs. Cited here is a list of traditional rulers in Nigeria. Pre-colonial period Modern Nigeria encompasses lands traditionally occupied by highly diverse ethnic groups with very different languages and traditions. In broad terms, the southeast was occupied mainly by Igbo, the Niger Delta by Edo and Igbo related people, the southwest by Yoruba a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Monarchs In Africa
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Nigerian People
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obas Of Benin
Obas may refer to: People * Beethova Obas (born 1964), Haitian musician * Charles Obas, Haitian painter Places * Obas District Obas District is one of eight districts of the province Yarowilca in Peru. Ethnic groups The people in the district are mainly indigenous citizens of Quechua descent. Quechua is the language which the majority of the population (59.11%) learnt ..., Peru Other * OBAs, Optical Brighteing Agents {{dab, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1280 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igboland
Igboland (Standard ), also known as Southeastern Nigeria (but extends into South-Southern Nigeria), is the indigenous homeland of the Igbo people. It is a cultural and common linguistic region in southern Nigeria. Geographically, it is divided by the lower Niger River into two sections: an eastern (the larger of the two) and a western one. Its population is characterised by the diverse Igbo culture and the speakers of equally diverse Igbo languages. Politically, Igboland is divided into several southern Nigerian states; culturally, it has included several subgroupings, including the Anioma, the Ngwa people, Ngwa, the Aro people, Aro, the Edda people, Ezza, the Ibeku, the Ohuhu people, Ohuhu, the Oboro (Nigeria), Oboro, the Ikwerre people, Ikwerre, the Ogba people, Ogba, the Omuma, the Ohafia, the Oyigbo, the Mbaise, the Isu people, Isu and the Ekpeye. Territorial boundaries Igboland is surrounded on all sides by large rivers, and other southern and central Nigeria indigenous tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oba Oguola
Oba Oguola was a ruler of the Benin Kingdom, reigning from 1280 AD to 1295 AD. His reign was marked by achievements in fortifying the city of Benin, enhancing its defenses, and contributing to the cultural and economic development of the kingdom. Born into the royal family, Oguola's ascent to the throne was prompted by the extended absence of his elder brother, Prince Obuobu, who was engaged in military campaigns. This unorthodox succession was a pragmatic decision by the kingdom's elders and advisors to ensure stability and effective leadership during a critical period. Oba Oguola's commitment to the Benin Kingdom's welfare and security was evident in his initiatives to fortify Benin City, including the construction of the first and second moats. These moats, characterised by their impressive size and strategic design, served as defensive barriers to protect the city from external threats. Furthermore, Oguola played a role in the revival of the ancient guild of brass casting i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |