|
Oxanorbornadiene
Oxanorbornadiene (OND) is a bicyclic organic compound with an oxygen atom bridging the two opposing saturated carbons of 1,4-cyclohexadiene. OND is related to all-carbon bicycle norbornadiene. Synthesis While unsubstituted OND is known, the most useful OND derivatives are dialkyl OND-2,3-dicarboxylates, readily obtainable by a Diels–Alder cycloaddition between furans and acetylenedicarboxylates such as DMAD. Properties OND-2,3-dicarboxylates (thereafter referred to as ''OND'') display unusually high reactivity towards organic azides and thiols. OND–thiol adducts are prone to retro-Diels–Alder fragmentation, which occurs with widely variable rates. Reactions with Azides ONDs react with organic azides to yield a mixture of four products, arising from initial 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition onto either of the two olefins, followed by a retro-Diels–Alder reaction (a cycloelimination reaction) to form 1,2,3-triazoles and furans. The intermediate triazolines avoid detection b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,4-cyclohexadiene
1,4-Cyclohexadiene is an organic compound with the formula C6H8. It is a colourless, flammable liquid that is of academic interest as a prototype of a large class of related compounds called terpenoids, an example being γ-terpinene. An isomer of this compound is 1,3-cyclohexadiene. Synthesis and reactions In the laboratory, substituted 1,4-cyclohexadienes are synthesized by Birch reduction of related aromatic compounds using an alkali metal dissolved in liquid ammonia and a proton donor such as an alcohol. In this way, over reduction to the fully saturated ring is avoided. 1,4-Cyclohexadiene and its derivatives are easily aromatized, the driving force being the formation of an aromatic ring. The conversion to an aromatic system may be used to trigger other reactions, such as the Bergman cyclization The Masamune-Bergman cyclization or Masamune-Bergman reaction or Masamune-Bergman cycloaromatization is an organic reaction and more specifically a rearrangement reaction taking p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olefins
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LUMO
In chemistry, HOMO and LUMO are types of molecular orbitals. The acronyms stand for ''highest occupied molecular orbital'' and ''lowest unoccupied molecular orbital'', respectively. HOMO and LUMO are sometimes collectively called the ''frontier orbitals'', such as in the frontier molecular orbital theory. Gap The energy difference between the HOMO and LUMO is ''the HOMO–LUMO gap''. Its size can be used to predict the strength and stability of transition metal complexes, as well as the colors they produce in solution.Griffith, J. S. and L. E. Orgel"Ligand Field Theory" ''Q. Rev. Chem. Soc.'' 1957, 11, 381–383. As a rule of thumb, the larger a compound's HOMO-LUMO gap, the more stable the compound. Semiconductors The HOMO level is to organic semiconductors roughly what the maximum valence band is to inorganic semiconductors and quantum dots. The same analogy can be made between the LUMO level and the conduction band minimum.Bredas, J,-L"Mind the gap!" ''Mater. Horiz.'' 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HOMO
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans (depending on the species), most notably ''Homo erectus'' and ''Homo neanderthalensis''. The genus emerged with the appearance of '' Homo habilis'' just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus '' Paranthropus'', is probably sister to ''Australopithecus africanus'', which itself had previously split from the lineage of '' Pan'', the chimpanzees. ''Homo erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and, in several early migrations, spread throughout Africa (where it is dubbed ''Homo ergaster'') and Eurasia. It was likely that the first human species lived in a hunter-gatherer society and was able to control fire. An adaptive and successful species, ''Homo erectus'' persisted for more than a million ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzyl Azide
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group () group. Nomenclature In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substituent, for example benzyl chloride or benzyl benzoate. Benzyl is not to be confused with phenyl with the formula . The term benzylic is used to describe the position of the first carbon bonded to a benzene or other aromatic ring. For example, is referred to as a "benzylic" carbocation. The benzyl free radical has the formula . The benzyl cation or phenylcarbenium ion is the carbocation with formula ; the benzyl anion or phenylmethanide ion is the carbanion with the formula . None of these species can be formed in significant amounts in the solution phase under normal conditions, but they are useful referents for discussion of reaction mechanisms and may exist as reactive intermediates. Abbreviations The abbreviation "Bn" denotes benzyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds, whether straight or branched, and which contain no rings of any type, are always aliphatic. Cyclic compounds can be aliphatic if they are not aromatic. Structure Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, joined by single bonds (alkanes), or unsaturated, with double bonds (alkenes) or triple bonds (alkynes). If other elements (heteroatoms) are bound to the carbon chain, the most common being oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and chlorine, it is no longer a hydrocarbon, and therefore no longer an aliphatic compound. The least complex aliphatic compound is methane (CH4). Properties Most aliphatic compounds are flammable, allowing the use of hydrocarbons as fuel, such as methane in Buns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
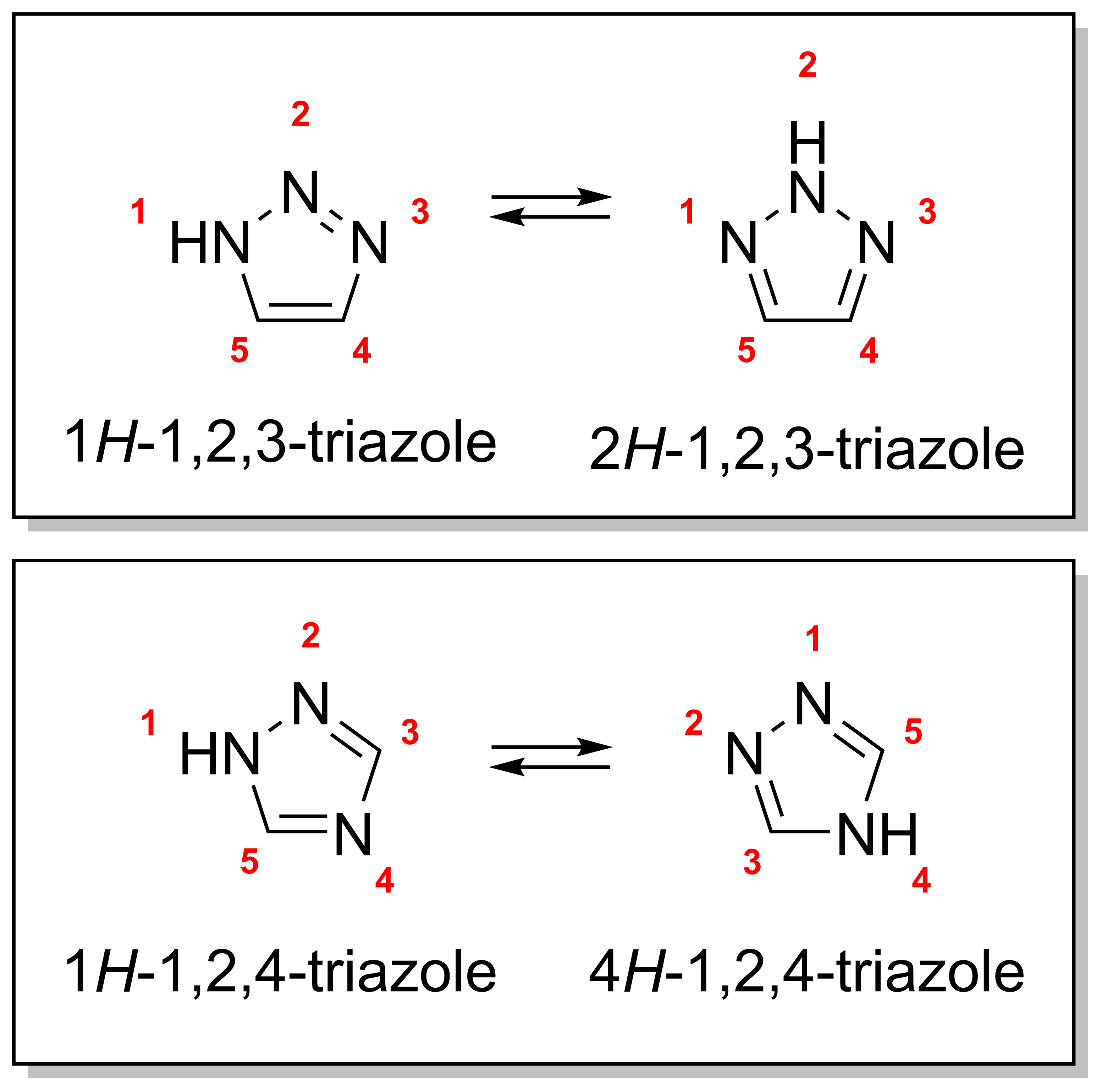
Triazoles
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbornadiene
Norbornadiene is an organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ... and a bicyclic hydrocarbon. Norbornadiene is of interest as a metal-binding ligand, whose complexes are useful for homogeneous catalysis. It has been intensively studied owing to its high reactivity and distinctive structural property of being a diene that cannot isomerization, isomerize (isomers would be anti-Bredt alkenes). Norbornadiene is also a useful Diels–Alder_reaction#The_dienophile, dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. Synthesis Norbornadiene can be formed by a Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and acetylene : Reactions Quadricyclane, a valence isomer, can be obtained from norbornadiene by a photochemical reaction when assisted by a photochemical sensitizer, sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiols
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the "smell of natural gas" is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' (Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate group () bonds very strongly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |