|
Outline Of Venus
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Venus: Venus – second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. It has the longest rotation period (243 days) of any planet in the Solar System and rotates in the opposite direction to most other planets. It has no natural satellite. It is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. It is the second-brightest natural object in the night sky after the Moon, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows. Because Venus orbits within Earth's orbit it is an inferior planet. Venus is a terrestrial planet and is sometimes called Earth's "sister planet" because of their similar size, mass, proximity to the Sun, and bulk composition. It is radically different from Earth in other respects. It has the densest atmosphere of the four terrestrial planets, consisting of more than 96% carbon dioxide. The atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface is 92 times that of Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnoid (astrogeology)
In astrogeology, an arachnoid is a large geological structure resembling a spider web. They are of unknown origin, and have been found only on the surface of the planet Venus. They appear as concentric ovals surrounded by a complex network of fractures, and can span 200 kilometers. Over 90 arachnoids have been identified on Venus. Arachnoids could be related to volcanos, however it is also possible that different arachnoids are formed by different processes.This article contains text from the Astronomy Picture of the Daybr> As a work of the United States Federal Government, it is in the public domain. One possible explanation is that an upwelling of magma from the interior of the planet pushed up on the surface, causing cracks. An alternate theory concerning their origin is that they are a precursor to Corona (planetary geology), coronae formation. Much of what is known about arachnoids is the result of studies performed by C.B. Dawson and L.S. Crumpler. See also * Chaos te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geological Features On Venus
This is a list of geological features on Venus. Venus is the second planet from the Sun. Venus is classified as a terrestrial planet and it is sometimes called Earth's "sister planet" owing to their similar size, gravity, and bulk composition (Venus is both the closest planet to Earth and the planet closest in size to Earth). The surface of Venus is covered by a dense atmosphere and presents clear evidence of former violent volcanic activity. It has shield and composite volcanoes similar to those found on Earth. Valles Cytherean valleys are called by the Latin term ''valles'', and are named after river goddesses or after words for the planet Venus (including terms for the ''morning star'' or ''evening star'' specifically) in various languages. Undae Undae on Venus refer to dune fields and are named after desert goddesses. Tesserae Tesserae are areas of polygonal terrain. They are named after goddesses in world mythologies. Rupes Scarps on Venus are called rupes and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Venus
Venus is a planet with striking geology. Of all the other planets in the Solar System, it is the one nearest to Earth and most like it in terms of mass, but has no magnetic field or recognizable plate tectonic system. Much of the ground surface is exposed volcanic bedrock, some with thin and patchy layers of soil covering, in marked contrast with Earth, the Moon, and Mars. Some impact craters are present, but Venus is similar to Earth in that there are fewer craters than on the other rocky planets that are largely covered by them. This is due in part to the thickness of the Venusian atmosphere disrupting small impactors before they strike the ground, but the paucity of large craters may be due to volcanic re-surfacing, possibly of a catastrophic nature. Volcanism appears to be the dominant agent of geological change on Venus. Some of the volcanic landforms appear to be unique to the planet. There are shield and composite volcanoes similar to those found on Earth. Given that Venus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Of Venus
The atmosphere of Venus is the layer of gases surrounding Venus. It is composed primarily of supercritical carbon dioxide and is much denser and hotter than that of Earth. The temperature at the surface is 740 K (467 °C, 872 °F), and the pressure is , roughly the pressure found underwater on Earth. The Venusian atmosphere supports opaque clouds of sulfuric acid, making optical Earth-based and orbital observation of the surface impossible. Information about the topography has been obtained exclusively by radar imaging. Aside from carbon dioxide, the other main component is nitrogen. Other chemical compounds are present only in trace amounts. Aside from the very surface layers, the atmosphere is in a state of vigorous circulation. The upper layer of troposphere exhibits a phenomenon of super-rotation, in which the atmosphere circles the planet in just four Earth days, much faster than the planet's sidereal day of 243 days. The winds supporting super-rotation bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
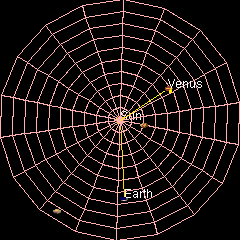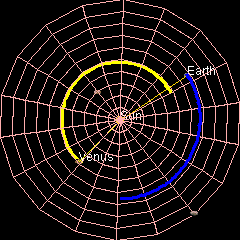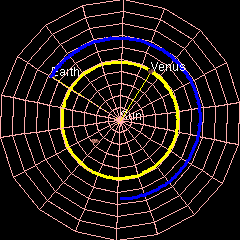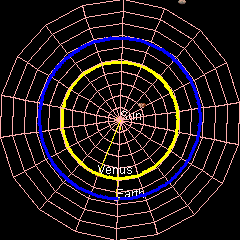
Orbit Of Venus
Venus has an orbit with a semi-major axis of , and an eccentricity of 0.007.Jean Meeus, ''Astronomical Formulæ for Calculators'', by Jean Meeus. (Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell, 1988) 99. Elements by Simon Newcomb The low eccentricity and comparatively small size of its orbit give Venus the least range in distance between perihelion and aphelion of the planets: 1.46 million km. The planet orbits the Sun once every 225 days and travels in doing so,Jean Meeus, ''Astronomical Algorithms'' (Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell, 1998) 238. The formula by Ramanujan is accurate enough. giving an average orbital speed of . Conjunctions and transits When the geocentric ecliptic longitude of Venus coincides with that of the Sun, it is in conjunction with the Sun – inferior if Venus is nearer and superior if farther. The distance between Venus and Earth varies from about 42 million km (at inferior conjunction) to about 258 million km (at superior conjunction). The average period between succes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion Arm
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is across and approximately in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion Bridge, and formerly, the Local Spur and Orion Spur. The arm is named for the Orion Constellation, which is one of the most prominent constellations of Northern Hemisphere winter (Southern Hemisphere summer). Some of the brightest stars and most famous celestial objects of the constellation (e.g. Betelgeuse, Rigel, the three stars of Orion's Belt, the Orion Nebula) are within it as shown on the interactive map below. The arm is between the Carina–Sagittarius Arm (the local portions of which are toward the Galactic Center) and the Perseus Arm (the local portion of which is the main outer-most arm and one of two major arms of the galaxy). Long thought to be a minor structure, namely a "spur" between the two arms mentioned, eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
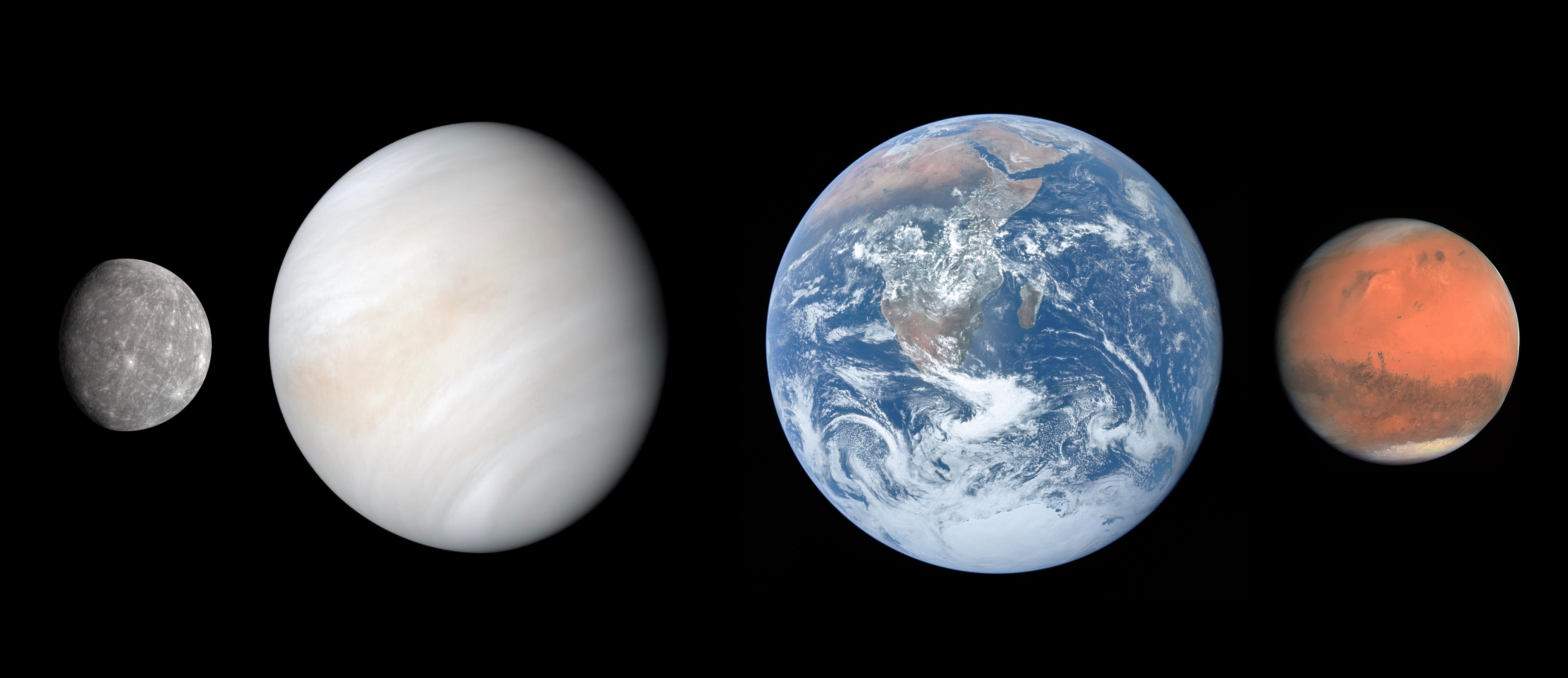
Terrestrial Planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Among astronomers who use the geophysical definition of a planet, two or three planetary-mass satellites – Earth's Moon, Io, and sometimes Europa – may also be considered terrestrial planets; and so may be the rocky protoplanet-asteroids Pallas and Vesta.Emily Lakdawalla et al.What Is A Planet?The Planetary Society, 21 April 2020 The terms "terrestrial planet" and "telluric planet" are derived from Latin words for Earth (''Terra'' and ''Tellus''), as these planets are, in terms of structure, ''Earth-like''. Terrestrial planets are generally studied by geologists, astronomers, and geophysicists. Terrestrial planets have a solid planetary surface, making them substantially different from the larger gaseous plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Planet
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system are substant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Planet
In the Solar System, a planet is said to be inferior or interior with respect to another planet if its orbit lies inside the other planet's orbit around the Sun. In this situation, the latter planet is said to be superior to the former. In the reference frame of the Earth, in which the terms were originally used, the inferior planets are Mercury and Venus, while the superior planets are Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Dwarf planets like Ceres or Pluto and most asteroids are 'superior' in the sense that they almost all orbit outside the orbit of Earth. History These terms were originally used in the geocentric cosmology of Claudius Ptolemy to differentiate as inferior those planets (Mercury and Venus) whose epicycle remained co-linear with the Earth and Sun, and as superior those planets (Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) that did not. In the 16th century, the terms were modified by Copernicus, who rejected Ptolemy's geocentric model, to distinguish a planet's orbit's size in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |