|
Outline Of Jakarta
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Jakarta: Jakarta – capital and largest city of Indonesia. Located on the northwest coast of the world's most populous island Java, it is the centre of economics, culture and politics of Indonesia. General reference * Pronunciation: ; * Common English name(s): Jakarta * Official English name(s): Special Capital Region of Jakarta * Common endonym(s): Jakarta * Official endonym(s): Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta * Adjectival(s): * Demonym(s): Jakartan, id, warga Jakarta, orang Jakarta Geography of Jakarta Geography of Jakarta * Jakarta is: ** a city ** a province of Indonesia ** capital of Indonesia * Population of Jakarta: 10,075,310 * Area of Jakarta: 661.5 km2 (255.4 sq mi) Location of Jakarta * Jakarta is situated within the following regions: ** Southern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere *** Asia **** Southeast Asia ***** Maritime Southeast Asia ****** Indonesia (outline) ******* Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Jakarta
The coat of arms of Jakarta is the official symbol of Jakarta, the capital of Indonesia. The coat of arms depicts the National Monument and a gold-and-white paddy and cotton. History Dutch East Indies Prior to the independence of Indonesia, Jakarta was named Batavia. The first coat of arms of Batavia was officially adopted on 8 February 1911. The arms consisted of a red shield with a blue sword surrounded by a brown laurel wreath, supported by lions holding a sword and arrow, above the arms was a normal city crown, and the motto ''Ende Dispereert Niet''. The motto was derived from the arms of the Coen family: ''Ende Dispereert Niet'' (And do not surrender). On 14 January 1929, the color of the shield was changed into orange. A major change to the coat of arms occurred on 22 January 1930, with the shape of the shield being changed, the supporting lions were actually supporting the shield, the crown was changed into a normal city crown and the motto shortened to ''Dispereert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Southeast Asia. The 16th-century term "East Indies" and the later 19th-century term " Malay Archipelago" are also used to refer to Maritime Southeast Asia. In Indonesia, the Old Javanese term "Nusantara" is also used as a synonym for Maritime Southeast Asia. The term, however, is nationalistic and has shifting boundaries. It usually only encompasses Peninsular Malaysia, the Sunda Islands, Maluku, and often Western New Guinea and excludes the Philippines. Stretching for several thousand kilometres, the area features a very large number of islands and boasts some of the richest marine, flora and fauna biodiversity on Earth. The main demographic difference that sets Maritime Southeast Asia apart from modern Mainland Southeast Asia is that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Of Tanjung Priok
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the world's largest and busiest ports, such as Singapore and the Chinese ports of Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancol
Ancol ( nl, Antjol, zh, 安恤) is a coastal lowland area located to the east of Kota Tua Jakarta in northern Jakarta, in Indonesia. The coastal lowland stretched from Kota Tua Jakarta to the west and Tanjung Priok to the east. Today, Ancol contains the main beach resort of Jakarta. Taman Impian Jaya Ancol, the largest integrated tourism area in South East Asia, is located in Ancol. Following the independence of Indonesia, Ancol was made one of the administrative village (''kelurahan'') of Pademangan Subdistrict in North Jakarta. The administrative village Ancol is bounded by Jakarta Bay to the north, Sunda Kelapa harbour to the west and Kali Japat canal to the east. Government The Administrative Village of Ancol has a postal code of 14430. History Pre-colonial period The name Ancol refers to a river located around 3 km east of Sunda Kelapa harbour, and the area surrounding it. The mouth of the Ancol river was located where the area of Putri Duyung Cottage now located. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
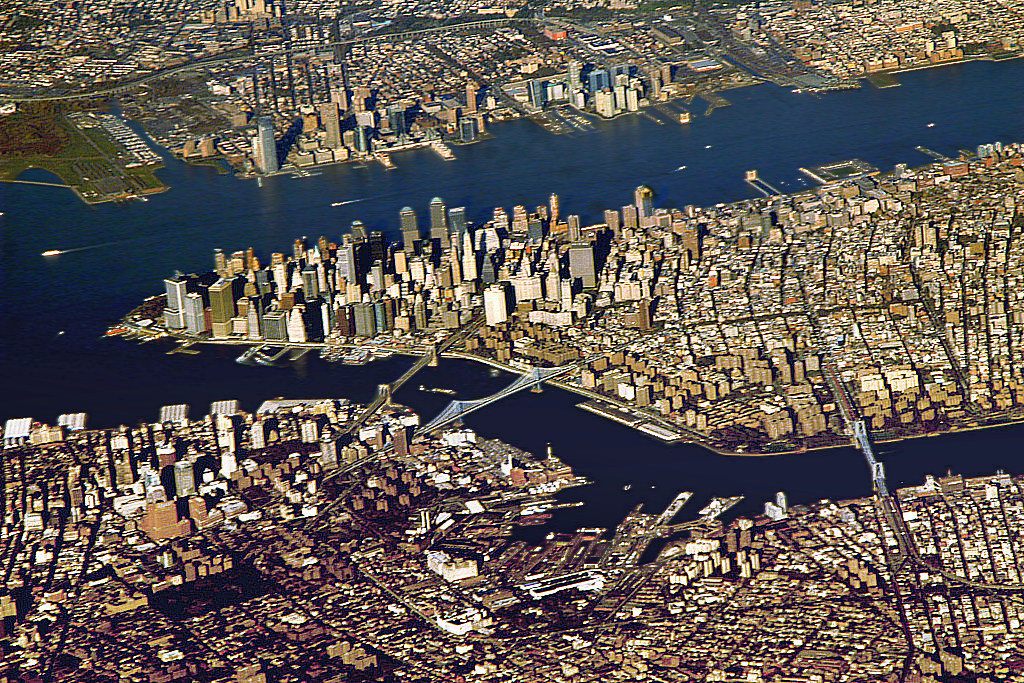
Jakarta Bay
Jakarta Bay ( id, Teluk Jakarta) is a bay north of North Jakarta city. The Thousand Islands (Indonesia), Thousand Islands are located in Jakarta Bay. 13 rivers flow into the bay. The majority of the bay's coastal communities consist of people living below the Poverty threshold, poverty line, in conditions of poor sanitation. Nutrient inputs from agricultural pollution, agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, and wastewater have led to eutrophication, which in turn led to changes in the area's biodiversity. Harmful algal blooms have been observed. References External links TelukJakarta.net Bays of Indonesia Landforms of Jakarta {{jakarta-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
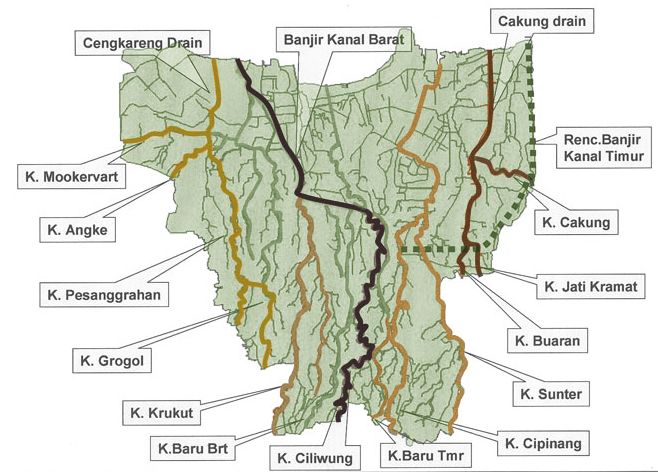
Jakarta Flood Canal
The Jakarta Flood Canal ( id, Kanal Banjir Jakarta) refers to two canals that divert floods from rivers around Jakarta instead of going through the city. This first flood control channel was designed by Hendrik van Breen, an engineer working for the Dutch East Indian ''Department van Burgelijke Openbare Werken'' (BOW—lit. Department of Public Civil Works, currently the Ministry of Public Works and People's Housing), after a big flood hit the city on 13 February 1918. West and East Flood Canal With help of ''Netherlands Engineering Consultants'', the "''Master Plan for Drainage and Flood Control of Jakarta''" was published in December 1973. According to this plan, flood control of Jakarta would revolve around two canals encircling the city. The canals divert the water flowing from the south around the city and into the sea. These canals are known as West Flood Canal (Indonesian: ''Banjir Kanal Barat'') and East Flood Canal (Indonesian: ''Banjir Kanal Timur''). Other measures to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 Jakarta Flood
The 2013 Jakarta flood was a flood in Jakarta, the capital of Indonesia, which, in addition to areas in downtown Jakarta, also affected several other areas surrounding the city, such as West Java and Banten. History Severe floods have been reported to have hit Jakarta in the past, including in 1621, 1654, 1918, 1942, 1976, 1996, 2002 and 2007. An important part of the flooding problem is caused by the fact that a substantial part of Jakarta is low-lying. Around 24,000 ha (about 240 square km) of the main part of Jakarta is estimated to be below sea level. Flooding can become severe if heavy rain happens to coincide with high tides. When this happens, high tides tend to push water into low-lying areas just as the run off from rains in upland areas such as nearby Bogor is flowing down into the Jakarta area. Duration The flood in 2013 began on Tuesday, 15 January 2013, in some parts of the city as a result of heavy rain and waterways clogged with garbage and other kinds of debris. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 Jakarta Flood
The 2007 Jakarta flood was a major flood in Jakarta, the capital of Indonesia and affected several other areas around the city, such as West Java and Banten. The flood, beginning on February 2, 2007 was a result of heavy rain, deforestation in areas south of the city, and waterways clogged with debris. The flood is considered the worst in the last three centuries, including the 1996 and 2002 Jakarta floods, which killed 10 and 25 people respectively. The final official death toll was 80. Causes Meteorological The most significant reason of the disaster is the high rate of rain, since the rainy season in Indonesia starts in December and ends in March. In 2007, the rain intensity reached its peak in February, with the greatest intensity towards the end of the month. Geographical Uncontrolled population growth in urban areas, poor land use planning, and the lack of understanding among city residents and government about floods and its disaster risk are key factors in Jakarta's sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flooding In Jakarta
Flooding in Jakarta occurs on the northwest coast of Java, at the mouth of the Ciliwung River on Jakarta Bay, which is an inlet of the Java Sea and has happened recently in 1996, 1999, 2007, 2013, and 2020. Jakarta geography The area of the Jakarta Special District is 662 km2 of land area and 6,977 km2 of sea area. Jakarta lies in a low, flat basin, averaging above sea level; 40% of Jakarta, particularly the northern areas, is below sea level, while the southern parts are comparatively hilly. Rivers flow from the Puncak highlands to the south of the city, across the city northwards towards the Java Sea; the Ciliwung River, divides the city into the western and eastern principalities. Other rivers include the Pesanggrahan, and Sunter high sea tides. Other contributing factors include clogged sewage pipes and waterways that service an increasing population, in addition to deforestation near rapidly urbanizing Bogor and Depok in Jakarta's hinterland. Jakarta is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of Jakarta
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude/longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme was the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UTC+7
UTC+07:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +07:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as . It is 7 hours ahead of UTC, meaning that when the time in UTC areas is midnight (00:00), the time in UTC+07:00 areas would be 7:00 in the morning. Also known as Indochina Time (ICT) and Western Indonesian Time ( id, Waktu Indonesia Barat, WIB) (in Indonesia), it is used in: As standard time (year-round) ''Principal cities: Medan, Lhokseumawe, Langsa, Garut, Gunungsitoli, Karawang, Jepara, Lubuklinggau, Batam, Pangkal Pinang, Palangkaraya, Pagar Alam, Probolinggo, Pasuruan, Purwakarta, Purwokerto, Pekalongan, Prabumulih, Palembang, Pematangsiantar, Padangsidempuan, Pekanbaru, Padang, Padang Panjang, Pontianak, Pariaman, Payakumbuh, Dumai, Binjai, Bogor, Cimahi, Cirebon, Bukittinggi, Bandar Lampung, Palembang, Jakarta, Bandung, Semarang, Surakarta, Surat Thani, Solok, Sawahlunto, Tanjungpinang, Singkawang, Tebing Tinggi, Sibolga, Sungai Penuh, Sukabumi, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian Western Standard Time
The Indonesian Archipelago geographically stretches across four time zones from UTC+06:00 in Aceh to UTC+09:00 in Papua. However, the Indonesian government recognises only three time zones in its territory, namely: *Western Indonesia Time (WIB) — seven hours ahead ( UTC+07:00) of the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC); *Central Indonesia Time (WITA) — eight hours ahead ( UTC+08:00) of UTC; *Eastern Indonesia Time (WIT) — nine hours ahead ( UTC+09:00) of UTC. The boundary between the Western and Central time zones was established as a line running north between Java and Bali through the provincial boundaries of West and Central Kalimantan. The border between the Central and Eastern time zones runs north from the eastern tip of Indonesian Timor to the eastern tip of Sulawesi. Daylight saving time (DST) is no longer observed anywhere in Indonesia. Current usage In Indonesia, the keeping of standard time is divided into three time zones: These time zones were first observed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |