|
Ordered Dithering
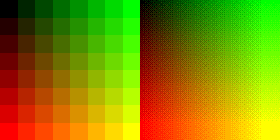
Ordered dithering is an image dithering algorithm. It is commonly used to display a continuous image on a display of smaller color depth. For example, Microsoft Windows uses it in 16-color graphics modes. The algorithm is characterized by noticeable crosshatch patterns in the result. Threshold map The algorithm reduces the number of colors by applying a threshold map to the pixels displayed, causing some pixels to change color, depending on the distance of the original color from the available color entries in the reduced palette. Threshold maps come in various sizes, which is typically a power of two: The map may be rotated or mirrored without affecting the effectiveness of the algorithm. This threshold map (for sides with length as power of two) is also known as an index matrix or Bayer matrix. Arbitrary size threshold maps can be devised with a simple rule: First fill each slot with a successive integer. Then reorder them such that the average distance between two su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenna Ordered Dither
Lenna (or Lena) is a standard test image used in the field of image processing since 1973. It is a picture of the Swedish model Lena Forsén, shot by photographer Dwight Hooker, cropped from the centerfold of the November 1972 issue of ''Playboy'' magazine. The continued use of the image has attracted controversy, on both technical and social grounds, and many journals have discouraged or banned its use. Forsén herself has asked for the image to be retired. The spelling "Lenna" came from the model's desire to encourage the proper pronunciation of her name. "I didn't want to be called ''Lee''na []," she explained. IPA pronunciation of ''Lee''na inserted into the quotation in brackets for clarity. is a common English pronunciation of the name ''Lena''. The quotation reads, "At her suggestion, the editors f Playboyspelled her first name with an extra 'n,' to encourage proper pronunciation. 'I didn't want to be called Leena," she explained.' History Before Lenna, the first u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordered 4x4 Bayer Matrix Dithering
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of different ways * Hierarchy, an arrangement of items that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another * an action or inaction that must be obeyed, mandated by someone in authority People * Orders (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Order'' (album), a 2009 album by Maroon * "Order", a 2016 song from ''Brand New Maid'' by Band-Maid * ''Orders'' (1974 film), a 1974 film by Michel Brault * ''Orders'', a 2010 film by Brian Christopher * ''Orders'', a 2017 film by Eric Marsh and Andrew Stasiulis * ''Jed & Order'', a 2022 film by Jedman Business * Blanket order, purchase order to allow multiple delivery dates over a period of time * Money order or postal order, a financial instrument usually intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithering
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images. Dither is routinely used in processing of both digital audio and video data, and is often one of the last stages of mastering audio to a CD. A common use of dither is converting a grayscale image to black and white, such that the density of black dots in the new image approximates the average gray level in the original. Etymology The term ''dither'' was published in books on analog computation and hydraulically controlled guns shortly after World War II. Though he did not use the term ''dither'', the concept of dithering to reduce quantization patterns was first applied by Lawrence G. Roberts in his 1961 MIT master's thesis and 1962 article. By 1964 dither was being used in the modern sense described in this article. The technique was in use at least as early as 1915, though not under the name ''dither''. In digital p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Depth
Color depth or colour depth (see spelling differences), also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel. When referring to a pixel, the concept can be defined as bits per pixel (bpp). When referring to a color component, the concept can be defined as bits per component, bits per channel, bits per color (all three abbreviated bpc), and also bits per pixel component, bits per color channel or bits per sample (bps). Modern standards tend to use bits per component, but historical lower-depth systems used bits per pixel more often. Color depth is only one aspect of color representation, expressing the precision with which the amount of each primary can be expressed; the other aspect is how broad a range of colors can be expressed (the gamut). The definition of both color precision and gamut is accomplished with a color encoding specification which assigns a digita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers. Genealogy By marketing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Of Two
A power of two is a number of the form where is an integer, that is, the result of exponentiation with number two as the base and integer as the exponent. In a context where only integers are considered, is restricted to non-negative values, so there are 1, 2, and 2 multiplied by itself a certain number of times. The first ten powers of 2 for non-negative values of are: : 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, ... Because two is the base of the binary numeral system, powers of two are common in computer science. Written in binary, a power of two always has the form 100...000 or 0.00...001, just like a power of 10 in the decimal system. Computer science Two to the exponent of , written as , is the number of ways the bits in a binary word of length can be arranged. A word, interpreted as an unsigned integer, can represent values from 0 () to () inclusively. Corresponding signed integer values can be positive, negative and zero; see signed n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale Ordered Dither
Scale or scales may refer to: Mathematics * Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points * Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original * Scale factor, a number which scales, or multiplies, some quantity * Long and short scales, how powers of ten are named and grouped in large numbers * Scale parameter, a description of the spread or dispersion of a probability distribution * Feature scaling, a method used to normalize the range of independent variables or features of data * Scale (analytical tool) Measurements * Scale (map), the ratio of the distance on a map to the corresponding actual distance * Weighing scale, an instrument used to measure mass * Scale (ratio), the ratio of the linear dimension of the model to the same dimension of the original * Spatial scale, a classification of sizes * Scale ruler, a tool for measuring lengths and transferring measurements at a fixed ratio of length * Verni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octet (computing)
The octet is a unit of digital information in computing and telecommunications that consists of eight bits. The term is often used when the term byte might be ambiguous, as the byte has historically been used for storage units of a variety of sizes. The term ''octad(e)'' for eight bits is no longer common. Definition The international standard IEC 60027-2, chapter 3.8.2, states that a byte is an octet of bits. However, the unit byte has historically been platform-dependent and has represented various storage sizes in the history of computing. Due to the influence of several major computer architectures and product lines, the byte became overwhelmingly associated with eight bits. This meaning of ''byte'' is codified in such standards as ISO/IEC 80000-13. While ''byte'' and ''octet'' are often used synonymously, those working with certain legacy systems are careful to avoid ambiguity. Octets can be represented using number systems of varying bases such as the hexadeci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryce Bayer
Bryce Edward Bayer (/ˈbaɪər/; pronounced BYE-er, August 15, 1929 – November 13, 2012) was an American scientist who invented the Bayer filter, which is used in most modern digital cameras. He has been called "the maestro without whom photography as we know wouldn't have been the same." Without his filter, Larry Scarff, a former chairman of the Camera Phone Image Quality Standards Group, told ''The New York Times'' after Bayer's death, "we'd still be getting only black-and-white pictures from our digital cameras." Early life and education Bryce Edward Bayer was born in Portland, Maine, on August 15, 1929, to Alton and Marguerite Willard Bayer. As a boy he tinkered with Brownie (camera), Brownies and other cameras. He graduated in 1947 from Deering High School in Portland, where he spent a good deal of time in the school darkroom. "He, in fact, processed all of the pictures for his high school yearbook," his son David told ''The New York Times'' following Bayer's death. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halftone
Halftone is the reprographic Reprography (a portmanteau of ''reproduction'' and ''photography'') is the reproduction of graphics through mechanical or electrical means, such as photography or xerography. Reprography is commonly used in catalogs and archives, as well as in th ... technique that simulates continuous-tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size or in spacing, thus generating a gradient-like effect.Campbell, Alastair. The Designer's Lexicon. ©2000 Chronicle, San Francisco. "Halftone" can also be used to refer specifically to the image that is produced by this process. Where continuous-tone imagery contains an infinite range of colors or greys, the halftone process reduces visual reproductions to an image that is printed with only one color of ink, in dots of differing size (pulse-width modulation) or spacing (frequency modulation) or both. This reproduction relies on a basic optical illusion: when the halftone dots are small, the human eye inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Noise
In audio engineering, electronics, physics, and many other fields, the color of noise or noise spectrum refers to the power spectrum of a noise signal (a signal produced by a stochastic process). Different colors of noise have significantly different properties. For example, as audio signals they will sound different to human ears, and as images they will have a visibly different texture. Therefore, each application typically requires noise of a specific color. This sense of 'color' for noise signals is similar to the concept of timbre in music (which is also called "tone color"; however, the latter is almost always used for sound, and may consider very detailed features of the spectrum). The practice of naming kinds of noise after colors started with white noise, a signal whose spectrum has equal power within any equal interval of frequencies. That name was given by analogy with white light, which was (incorrectly) assumed to have such a flat power spectrum over the visib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Blur
In image processing, a Gaussian blur (also known as Gaussian smoothing) is the result of blurring an image by a Gaussian function (named after mathematician and scientist Carl Friedrich Gauss). It is a widely used effect in graphics software, typically to reduce image noise and reduce detail. The visual effect of this blurring technique is a smooth blur resembling that of viewing the image through a translucent screen, distinctly different from the bokeh effect produced by an out-of-focus lens or the shadow of an object under usual illumination. Gaussian smoothing is also used as a pre-processing stage in computer vision algorithms in order to enhance image structures at different scales—see scale space representation and scale space implementation. Mathematics Mathematically, applying a Gaussian blur to an image is the same as convolving the image with a Gaussian function. This is also known as a two-dimensional Weierstrass transform. By contrast, convolving by a circle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |