|
Order Of Calatrava
The Order of Calatrava ( es, Orden de Calatrava, pt, Ordem de Calatrava) was one of the four Spanish military orders and the first military order founded in Castile, but the second to receive papal approval. The papal bull confirming the Order of Calatrava was given by Pope Alexander III on September 26, 1164. Most of the political and military power of the order had dissipated by the end of the 15th century, but the last dissolution of the order's property did not occur until 1838. Origins and foundation It was founded at Calatrava la Vieja in Castile, in the twelfth century by St. Raymond of Fitero, as a military branch of the Cistercian family. The etymology of the name of this military order, Calatrava, conveys the meaning: "fortress of Rabah". Rodrigo of Toledo describes the origins of the order: Calatrava is the Arabic name of a castle recovered from the Muslims, in 1147, by the King of Castile, Alfonso VII, called ''el Emperador''. Located in what was then the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Order (society)
A military order ( la, militaris ordo) is a Christian religious society of knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar, the Knights Hospitaller, the Order of Saint James, the Order of Calatrava, and the Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades, both in the Holy Land, the Baltics, and the Iberian peninsula; their members being dedicated to the protection of pilgrims and the defence of the Crusader states. They are the predecessors of chivalric orders. Most members of military orders were laymen who took religious vows, such as of poverty, chastity, and obedience, according to monastic ideals. The orders owned houses called commanderies all across Europe and had a hierarchical structure of leadership with the grand master at the top. The Knights Templar, the largest and most influential of the military orders, was suppressed in the early fourteenth century; only a handful of orders were established and recognized aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
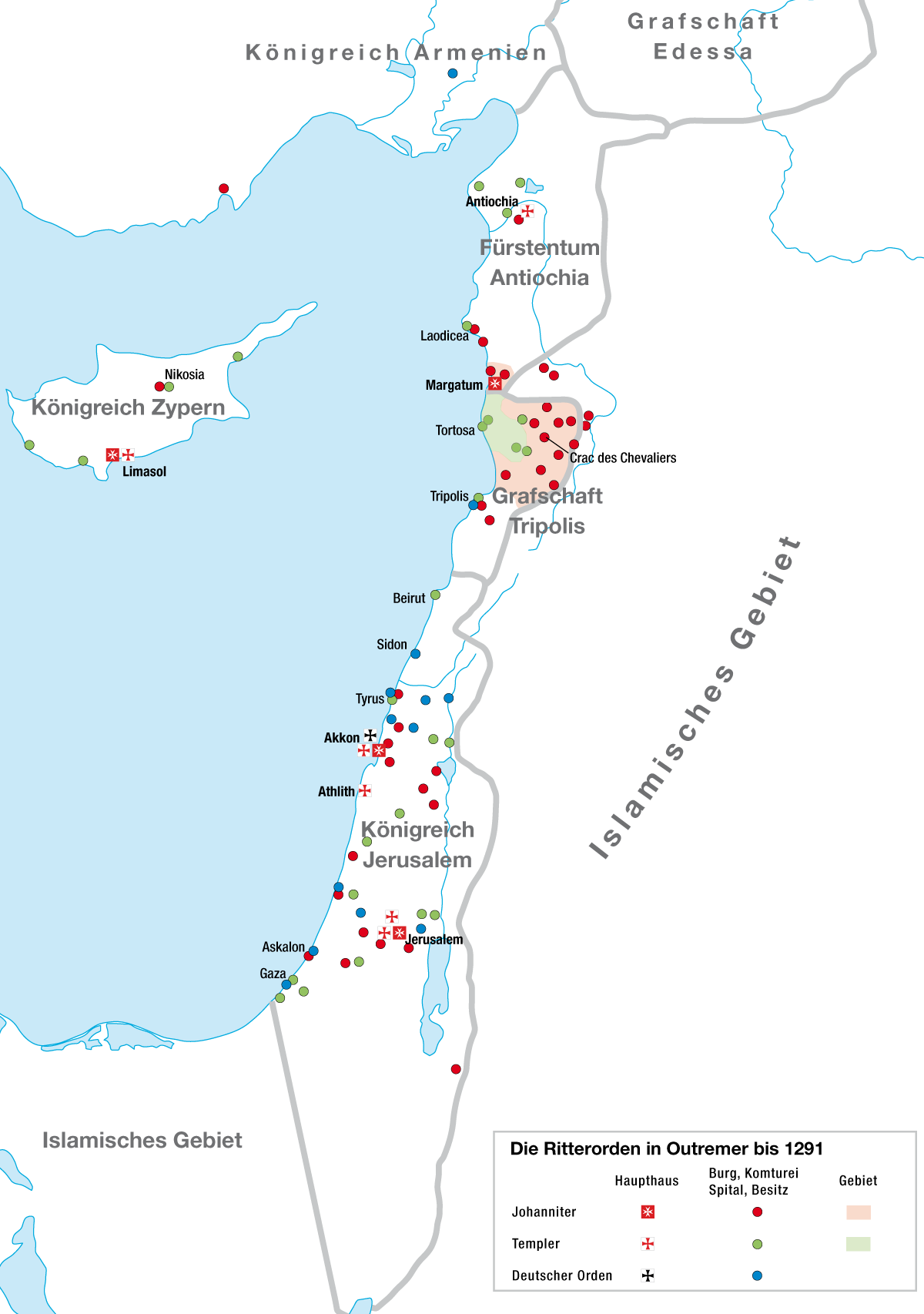
Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross , colors_label = Attire , march = , mascot = Two knights riding a single horse , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = The Crusades, including: , anniversaries = , decorations = , battle_honours = , commander1 = Hugues de Payens , commander1_label = First Grand Master , commander2 = Jacques de Molay , commander2_label = Last Grand Master , commander3 = , commander3_label = , notable_commanders = The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon ( la, Pauperes commilitones Christi Templique Salomonici), also known as the Order of Solomon's Temple, the Knights Templar, or simply the Templars, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almohads
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire founded in the 12th century. At its height, it controlled much of the Iberian Peninsula ( Al Andalus) and North Africa (the Maghreb). The Almohad movement was founded by Ibn Tumart among the Berber Masmuda tribes, but the Almohad caliphate and its ruling dynasty were founded after his death by Abd al-Mu'min al-Gumi. Around 1120, Ibn Tumart first established a Berber state in Tinmel in the Atlas Mountains. Under Abd al-Mu'min (r. 1130–1163) they succeeded in overthrowing the ruling Almoravid dynasty governing Morocco in 1147, when he conquered Marrakesh and declared himself caliph. They then extended their power over all of the Maghreb by 1159. Al-Andalus soon followed, and all of Muslim Iberia was under Almohad rule by 1172. The turning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcañiz
Alcañiz () is a town and municipality of Teruel province in the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. The town is located on the banks of the river Guadalope. Alcañiz is the unofficial capital of the Lower Aragon historical region. It lies some 113 km from Teruel, the provincial capital, and 92 km from Zaragoza, the capital of Aragon. Alcañiz is the capital of the Bajo Aragón comarca and the second city in the province after Teruel. History The current settlement of Alcañiz dates to the Islamic era in Spain. It was captured by the Christian troops of Alfonso I of Aragon in 1119, but was later taken back by the Moors. It was conquered again by count Ramon Berenguer IV of Barcelona in 1157, and again lost, until it was finally recaptured by his son Alfonso II of Aragon. In 1179 the latter gave the town to the military Order of Calatrava. On 23 May 1809 during the Peninsular War, the Battle of Alcañiz was fought between a Spanish force led by General Blake and F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon ( an, Reino d'Aragón, ca, Regne d'Aragó, la, Regnum Aragoniae, es, Reino de Aragón) was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon, in Spain. It should not be confused with the larger Crown of Aragon, which also included other territories — the Principality of Catalonia (which included the former Catalan Counties), the Kingdom of Valencia, the Kingdom of Majorca, and other possessions that are now part of France, Italy, and Greece — that were also under the rule of the King of Aragon, but were administered separately from the Kingdom of Aragon. In 1479, upon John II of Aragon's death, the crowns of Aragon and Castile were united to form the nucleus of modern Spain. The Aragonese lands, however, retained autonomous parliamentary and administrative institutions, such as the Corts, until the Nueva Planta decrees, promulgated between 1707 and 1715 by Philip V of Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitero
Fitero is a town and municipality located in the province and autonomous community of Navarre, northern Spain. The Monastery of Fitero Summary The Monastery of Fitero ( es, italic=yes, Monasterio de Santa María la Real or ''Monasterio de Santa María de Nienzebas'') is a Cistercian monastery located at Fitero, Navarre, Spain, on the banks of the Alhama (river), Alhama river ... is situated here. Monuments Monasterio de Santa María ThMonasterio de Santa Maríais a magnificent complex of buildings mainly in the Romanesque style, which formerly housed the Cistercian Monastery and its dependencies. The monastery is currently a conglomerate of buildings from different periods, built up around the stunning church and the superb chapter house from the Medieval era. The church, which is of cathedral-like proportions, was started in 1179 and completed in 1247. The church is one of the largest and most important buildings constructed by the Cistercian order in Spain, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champagne (historical Province)
Champagne () was a province in the northeast of the Kingdom of France, now best known as the Champagne wine region for the sparkling white wine that bears its name in modern-day France. The County of Champagne, descended from the early medieval kingdom of Austrasia, passed to the French crown in 1314. Formerly ruled by the counts of Champagne, its western edge is about 160 km (100 miles) east of Paris. The cities of Troyes, Reims, and Épernay are the commercial centers of the area. In 1956, most of Champagne became part of the French administrative region of Champagne-Ardenne, which comprised four departments: Ardennes, Aube, Haute-Marne, and Marne. From 1 January 2016, Champagne-Ardenne merged with the adjoining regions of Alsace and Lorraine to form the new region of Grand Est. Etymology The name ''Champagne'', formerly written ''Champaigne'', comes from French meaning "open country" (suited to military maneuvers) and from Latin ''campanius'' meaning "level country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morimond Abbey
Morimond Abbey is a religious complex in Parnoy-en-Bassigny, Haute-Marne department, in the Champagne-Ardenne region of France. It was the fourth of the four great daughter abbeys of Cîteaux Abbey, of primary importance in the spread of the Cistercian Order, along with La Ferté to the south, Pontigny to the west and Clairvaux to the north. History Situated in the diocese of Langres, Morimond was founded in 1115 by Count Odelric of Aigremont and his wife Adeline of Choiseul and settled from Citeaux. The first abbot, known as a "pillar of the Cistercians", was Arnold the German. Thanks to his energy and influence, Morimond grew very rapidly, and established numerous colonies in France, Germany, Poland, Bohemia, Spain, and Cyprus. The only daughter-house in England and Wales was Dore Abbey, founded in 1147. Amongst the best-known were Ebrach Abbey in Germany (1126); Heiligenkreuz Abbey in Austria (1134); and Aiguebelle Abbey in France (1137), which was later restored by the Refo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Gregory VIII
Pope Gregory VIII ( la, Gregorius VIII; c. 1100/1105 – 17 December 1187), born Alberto di Morra, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States for two months in 1187. Becoming Pope after a long diplomatic career as Apostolic Chancellor, he was notable in his brief reign for reconciling the Papacy with the estranged Holy Roman Empire and for initiating the Third Crusade. Early life Alberto di Morra was born about 1105 in Benevento. His father was the nobleman Sartorius di Morra. He became a monk early in life, either as a Cistercian in Laon, or a Benedictine at Monte Cassino. Alberto later joined a new religious order, the Premonstratensian or Norbertine order, probably between the ages of 20–30. He was a canon at St. Martin's Abbey in Laon. He later became a professor of canon law in Bologna. Cardinal In 1156, Pope Adrian IV made him cardinal-deacon of Sant'Adriano, and on 14 March 1158 he became cardinal-priest of San Lorenzo in Lucina. As a papal leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |