|
Oradea Ghetto
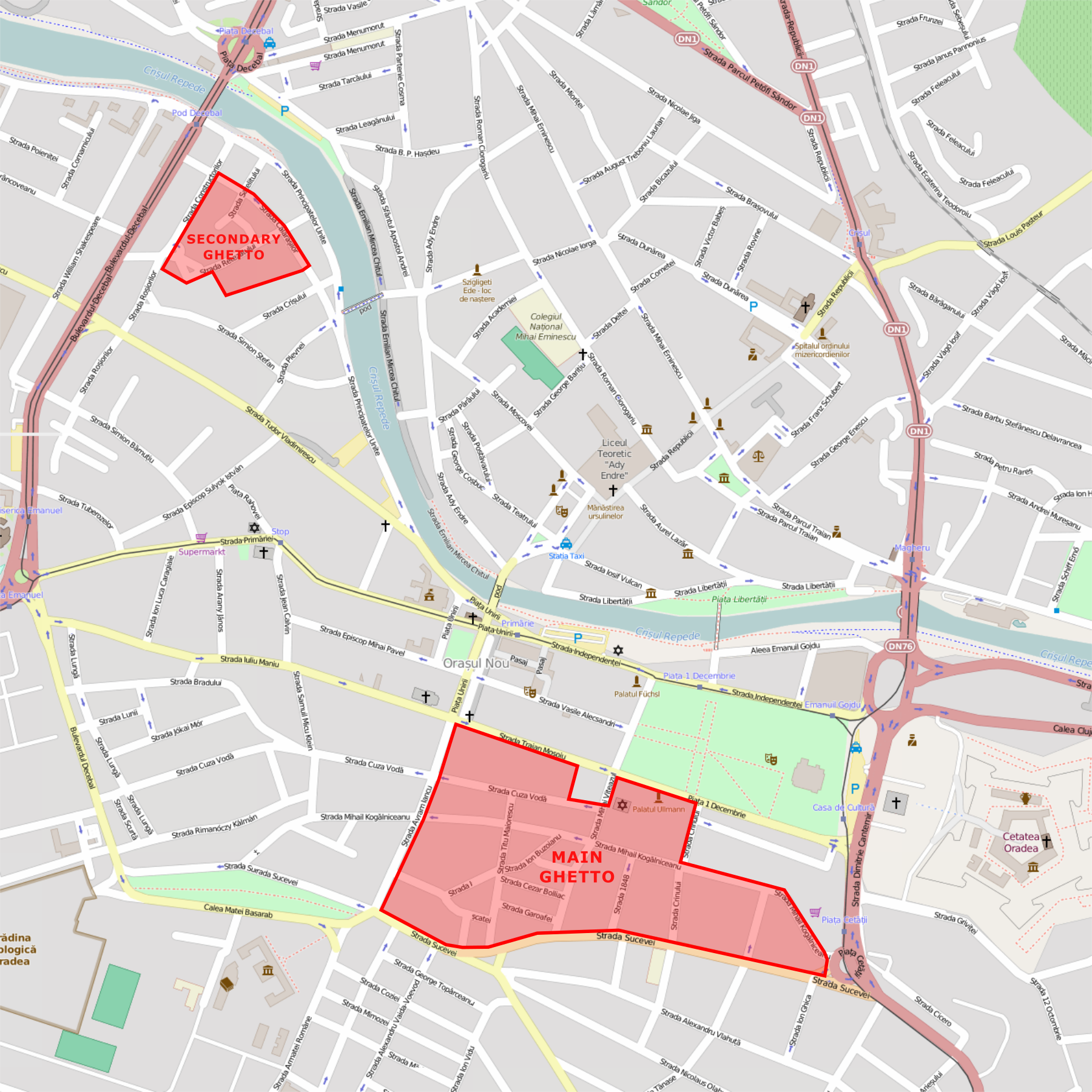
The Oradea ghetto was one of the Nazi-era ghettos for European Jews during World War II. It was located in the city of Oradea ( hu, Nagyvárad) in Bihor County, Transylvania, now part of Romania but administered as part of Bihar County by the Kingdom of Hungary from the 1940 Second Vienna Award's grant of Northern Transylvania until late 1944. The ghetto was active in the spring of 1944, following Operation Margarethe. History Aside from the Budapest ghetto, this was the largest ghetto in Hungary. There were in fact two ghettoes in the city. The first, for Oradea's Jews, numbered 27,000 inhabitants and was situated near the Orthodox synagogue and the Great Square. The second contained nearly 8,000 Jews from the many rural communities of a dozen districts: Aleșd, Berettyóújfalu, Biharkeresztes, Cefa, Derecske, Marghita, Oradea, Săcueni, Sălard, Salonta, Sárrétudvari and Valea lui Mihai. Many Jews from these communities were also placed around the Mezey lumber yard. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oradea Ghetto
The Oradea ghetto was one of the Nazi-era ghettos for European Jews during World War II. It was located in the city of Oradea ( hu, Nagyvárad) in Bihor County, Transylvania, now part of Romania but administered as part of Bihar County by the Kingdom of Hungary from the 1940 Second Vienna Award's grant of Northern Transylvania until late 1944. The ghetto was active in the spring of 1944, following Operation Margarethe. History Aside from the Budapest ghetto, this was the largest ghetto in Hungary. There were in fact two ghettoes in the city. The first, for Oradea's Jews, numbered 27,000 inhabitants and was situated near the Orthodox synagogue and the Great Square. The second contained nearly 8,000 Jews from the many rural communities of a dozen districts: Aleșd, Berettyóújfalu, Biharkeresztes, Cefa, Derecske, Marghita, Oradea, Săcueni, Sălard, Salonta, Sárrétudvari and Valea lui Mihai. Many Jews from these communities were also placed around the Mezey lumber yard. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cefa
Cefa ( hu, Cséffa, ger, Tscheppensdorf) is a commune in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania with a population of 2,272 people (2011). It is composed of three villages: Ateaș (''Atyás''), Cefa and Inand (''Inánd''). It also included five other villages until 2003, when they were split off to form Gepiu and Sânnicolau Român Communes. The oldest attested name of Cefa is ''Chepha'' (1302).Lajos Kiss, ''Földrajzi Nevek Etimológiai Szótára'' A-K, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, 1978, p. 312 References Cefa Cefa ( hu, Cséffa, ger, Tscheppensdorf) is a commune in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania with a population of 2,272 people (2011). It is composed of three villages: Ateaș (''Atyás''), Cefa and Inand (''Inánd''). It also included five other vill ... Localities in Crișana {{Bihor-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debrecen
Debrecen ( , is Hungary's second-largest city, after Budapest, the regional centre of the Northern Great Plain region and the seat of Hajdú-Bihar County. A city with county rights, it was the largest Hungarian city in the 18th century and it is one of the Hungarian people's most important cultural centres.Antal Papp: Magyarország (Hungary), Panoráma, Budapest, 1982, , p. 860, pp. 463-477 Debrecen was also the capital city of Hungary during the revolution in 1848–1849. During the revolution, the dethronement of the Habsburg dynasty was declared in the Reformed Great Church. The city also served as the capital of Hungary by the end of World War II in 1944–1945. It is home of the University of Debrecen. Etymology The city is first documented in 1235, as ''Debrezun''. The name derives from the Turkic word , which means 'live' or 'move' and is also a male given name. Another theory says the name is of Slavic origin and means 'well-esteemed', from Slavic Dьbricinъ or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerződés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It formally ended World War I between most of the Allies of World War I and the Kingdom of Hungary. French diplomats played the major role in designing the treaty, with a view to establishing a French-led coalition of the newly formed states. It regulated the status of the Kingdom of Hungary and defined its borders generally within the #Borders of Hungary, ceasefire lines established in November–December 1918 and left Hungary as a Landlocked country, landlocked state that included , 28% of the that had constituted the pre-war Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Kingdom of Hungary (the Hungarian half of the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian monarchy). The truncated kingdom had a population of 7.6 million, 36% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yad Vashem
Yad Vashem ( he, יָד וַשֵׁם; literally, "a memorial and a name") is Israel's official memorial to the victims of the Holocaust. It is dedicated to preserving the memory of the Jews who were murdered; honoring Jews who fought against their Nazi oppressors and Gentiles who selflessly aided Jews in need; and researching the phenomenon of the Holocaust in particular and genocide in general, with the aim of avoiding such events in the future. Established in 1953, Yad Vashem is located on the western slope of Mount Herzl, also known as the Mount of Remembrance, a height in western Jerusalem, above sea level and adjacent to the Jerusalem Forest. The memorial consists of a complex containing two types of facilities: some dedicated to the scientific study of the Holocaust and genocide in general, and memorials and museums catering to the needs of the larger public. Among the former there are a research institute with archives, a library, a publishing house, and an educational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auschwitz Concentration Camp
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It consisted of Auschwitz I, the main camp (''Stammlager'') in Oświęcim; Auschwitz II-Birkenau, a concentration and extermination camp with gas chambers; Auschwitz III-Monowitz, a labor camp for the chemical conglomerate IG Farben; and dozens of subcamps. The camps became a major site of the Nazis' final solution to the Jewish question. After Germany sparked World War II by invading Poland in September 1939, the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) converted Auschwitz I, an army barracks, into a prisoner-of-war camp. The initial transport of political detainees to Auschwitz consisted almost solely of Poles for whom the camp was initially established. The bulk of inmates were Polish for the first two years. In May 1940, German criminals brought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judenrat
A ''Judenrat'' (, "Jewish council") was a World War II administrative agency imposed by Nazi Germany on Jewish communities across occupied Europe, principally within the Nazi ghettos. The Germans required Jews to form a ''Judenrat'' in every community across the occupied territories. The ''Judenrat'' constituted a form of self-enforcing intermediary, used by the Nazi administration to control larger Jewish communities. In some ghettos, such as the Łódź Ghetto, and in Theresienstadt, the Germans called the councils "Jewish Council of Elders" (''Jüdischer Ältestenrat'' or ''Ältestenrat der Juden''). Jewish communities themselves had established councils for self-government as early as the Middle Ages. The Jewish community used the Hebrew term ''Kahal'' (קהל) or ''Kehillah'' (קהילה), whereas the German authorities generally used the term ''Judenräte''. The Judenräte are notorious today for their collaboration with the Nazi regime, almost always under extreme coerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Transylvania Holocaust Memorial Museum
The Northern Transylvania Holocaust Memorial Museum is located in Șimleu Silvaniei, Sălaj County, Romania, and was opened September 11, 2005. The museum is operated and maintained by the Jewish Architectural Heritage Foundation of New York and Asociația Memoraliă Hebraică Nușfalău (a Romanian NGO), with the support of the Claims Conference, Elie Wiesel National Institute for Studying the Holocaust in Romania, among other philanthropic and pedagogical partners. History The old synagogue of Șimleu Silvaniei (Szilágysomlyó) was erected in 1876. During the height of its use, the synagogue was used for worship and religious ceremonies by Jewish families from the city of Șimleu Silvaniei, as well as surrounding villages such as Giurtelecu Șimleului (Somlyógyőrtelek) and Nușfalău (Szilágynagyfalu). In May/June 1944, when the city was part of Hungary (as a consequence of the territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award), the area's Jewish population was forced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valea Lui Mihai
Valea lui Mihai (; hu, Érmihályfalva) is a town in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania. Geography It is located around 66 km north-east of Oradea, 9 km from the Hungarian border in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania. History In 1312, under Charles I, it was allowed new trade privileges and then in 1459 was also allowed tax benefits privileges for its citizens. Later it was part of the Ottoman Empire, which resulted in its depopulation, but the inhabitants subsequently returned. Thereafter, it was part of the Habsburg monarchy up until the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867. Then it became part of the Kingdom of Hungary within Austria-Hungary. After the breaking-up of Austria-Hungary in 1918/1920, the town became part of Romania. As a result of the Second Vienna Award it became a part of Hungary between 1940 and 1945. Since then it has been part of Romania. It was declared a town on three separate occasions: in 1844, 1930 and 1989, the last time as a result of the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sárrétudvari
Sárrétudvari is a village in Hajdú-Bihar county, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a .... Geography It covers an area of and has a population of 2963 people (2015). Sport References External links * in Hungarian Populated places in Hajdú-Bihar County {{Hajdu-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salonta
Salonta (; hu, Nagyszalonta, italic=no, colloquially , ; ger, Grosssalontha, italic=no; tr, Salanta, italic=no) is a municipiu, city in Bihor County, in the geographical region of Crișana, north-western Romania, near the Hungarian border. Population According to the Demographics of Romania, Romanian census from 2011, the city has a population of 17,042, made up of Hungarians (58.1%), Romanians (38.83%), Romani people, Romani (2.4%), Slovaks 0.4% and others (0.5%). In terms of religion, in year 2002, 51.12% were Reformed Church in Romania, Reformed (Calvinist), 36.46% Romanian Orthodox Church, Romanian Orthodox, 6.56% Roman Catholicism in Romania, Roman Catholic and 5.86% was split between Baptist Union of Romania, Baptists, Romanian Church United with Rome, Greek-Catholic, Romanian Greek-Catholic, Pentecostalism, Pentecostals and other faiths. History The city, a part of the Kingdom of Hungary, was first documented in 1214 under the name of ''Zolonta'' and in 1332 a Papal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sălard
Sălard ( hu, Szalárd) is a commune in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Hodoș (''Jákóhodos''), Sălard, and Sântimreu (''Hegyközszentimre''). The commune is located in the northwestern part of the county, on the banks of the river Barcău. The river Sânnicolau discharges into the Barcău near Sântimreu. Sălard is crossed by national road , which runs from Biharia Biharia ( hu, Bihar) is a commune in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Biharia and Cauaceu (''Hegyközkovácsi''). In 2011 it had 4,205 inhabitants, of whom 85.87% were Hungarians, 12.12% Romanians and 1.73% Roma. H ..., to the southwest, to Chiribiș, to the northeast. The county capital, Oradea, is 27 km to the south. References Communes in Bihor County Localities in Crișana {{Bihor-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |