|
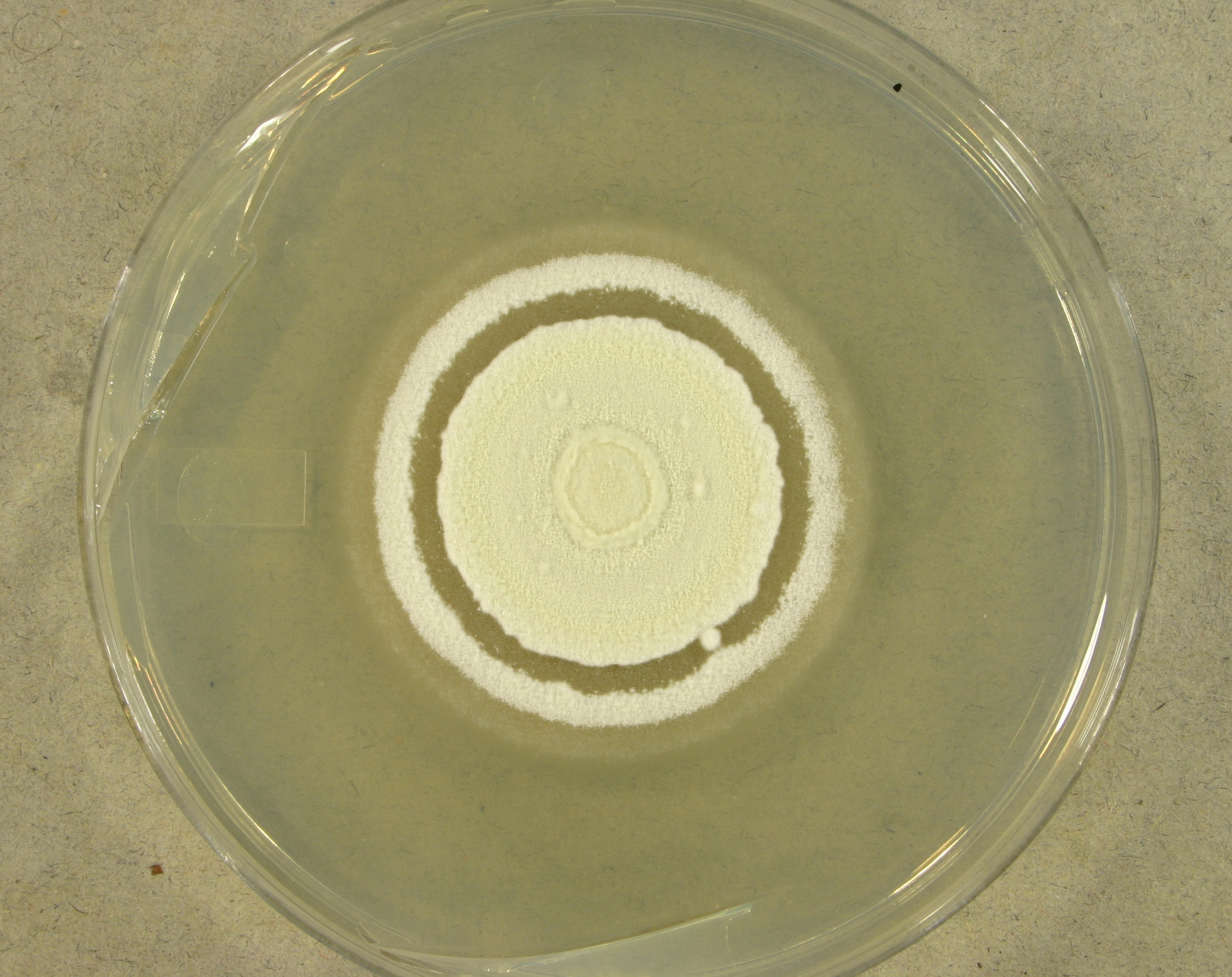
Ophidiomyces Ophiodiicola
''Ophidiomyces ophiodiicola'' is the cause of ophidiomycosis also known as snake fungal disease or SFD in some species of snakes. It is a keratinophilic fungus from the family Onygenaceae of the order Onygenales. ''O. ophiodiicola'' is an emerging pathogen of captive and wild snakes in North America and Europe. Clinical signs include skin swelling, crusts, and nodules of the skin. The mode of transmission is unknown, but is speculated to occur with direct contact between snakes or with the contaminated environment. Currently no treatment for ''O. ophiodiicola'' is available. ''O. ophiodiicola'' was identified by Sigler, Hambleton & Paré in 2013. ''O. ophiodiicola'' is the only species in the genus ''Ophidiomyces''. It was previously known as ''Chrysosporium ophiodiicola'' and is closely related to ''Chrysosporium'' anamorph ''Nannizziopsis vriesii'' (CANV). Taxonomy and naming ''Ophidiomyces ophiodiicola'' was first described as ''Chrysosporium ophiodiicola'' by Josef Guarro a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. The S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesions On Hoplocephalus Bungaroides
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Since lesions can occur anywhere in the body and the definition of a lesion is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, their sizes, their locations, or their causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called ''chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries. Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, a "skin lesion" or a "brain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society For Microbiology
The American Society for Microbiology (ASM), originally the Society of American Bacteriologists, is a professional organization for scientists who study viruses, bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa as well as other aspects of microbiology. It was founded in 1899. The Society publishes a variety of scientific journals, textbooks, and other educational materials related to microbiology and infectious diseases. ASM organizes annual meetings, as well as workshops and professional development opportunities for its members. History ASM was founded in 1899 under the name the "Society of American Bacteriologists." In December 1960, it was renamed the "American Society for Microbiology." Mission ASM's mission is "to promote and advance the microbial sciences." The society seeks to accomplish this mission through: * Publishing highly-cited publications * Running multi-disciplinary meetings * Deploying resources and expertise around the world * Advocating for scientific research * Fost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontiers In Veterinary Science
Frontiers Media SA is a publisher of peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journals currently active in science, technology, and medicine. It was founded in 2007 by Kamila and Henry Markram, and has since expanded to other academic fields. Frontiers is based in Lausanne, Switzerland, with other offices in London, Madrid, Seattle and Brussels. In 2022, Frontiers employed more than 1,400 people, across 14 countries. All Frontiers journals are published under a Creative Commons Attribution License. As of 2022, Frontiers publishes over 185 academic journals, including 48 journals indexed within the Science Citation Index Expanded, and 4 journals indexed within the Social Sciences Citation Index, with a total of 51 journals ranked with an impact factor. Frontiers journals are included in the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). Frontiers is also a member of the Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association (OASPA), a participating publisher and supporter of the Initiative for Op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontiers Media SA
Frontiers Media SA is a publisher of peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journals currently active in science, technology, and medicine. It was founded in 2007 by Kamila and Henry Markram, and has since expanded to other academic fields. Frontiers is based in Lausanne, Switzerland, with other offices in London, Madrid, Seattle and Brussels. In 2022, Frontiers employed more than 1,400 people, across 14 countries. All Frontiers journals are published under a Creative Commons Attribution License. As of 2022, Frontiers publishes over 185 academic journals, including 48 journals indexed within the Science Citation Index Expanded, and 4 journals indexed within the Social Sciences Citation Index, with a total of 51 journals ranked with an impact factor. Frontiers journals are included in the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ). Frontiers is also a member of the Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association (OASPA), a participating publisher and supporter of the Initiative for Op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Experimental Biology
''Journal of Experimental Biology'' (formerly ''The British Journal of Experimental Biology)'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of comparative physiology and integrative biology. It is published by The Company of Biologists. The journal is partnered with Publons and has two-way integration with bioRxiv. ''Journal of Experimental Biology'' is now a hybrid journal and publishes 24 issues a year. Content over six months old is free to read. History ''The'' ''British Journal of Experimental Biology'' was established in Edinburgh in 1923 (''Br. J. Exp. Biol.'': ). It was published by Oliver and Boyd and edited by F. A. E. Crew with an Editorial Board of nine members, including Julian Huxley. When the journal ran into financial trouble, George Parker Bidder II, the founder of The Company of Biologists, rescued it in 1925. Sir James Gray was appointed as the journal's first Editor-in-Chief in 1925 and the journal was renamed ''The Journal of Experimental Biology' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Company Of Biologists
The Company of Biologists is a UK-based charity and not-for-profit publisher that was established in 1925 by George Parker Bidder III with the aim of promoting research and study across all branches of biology. The company publishes currently five scientific journals: ''Development, Disease Models & Mechanisms, Journal of Cell Science, Journal of Experimental Biology, and Biology Open''. As part of its charitable giving, the company awards grants and travelling fellowships to biologists as well as running a series of workshops. The company's current chairman is Professor Matthew Freeman, FRS. Brief history George Parker Bidder III, a prominent zoologist working in Europe during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, founded the Company of Biologists in 1925 in a bid to rescue the ailing journal ''The British Journal of Experimental Biology'' (now ''The Journal of Experimental Biology''), which was founded in 1923 by Julian Huxley, Lancelot Hogben and Frances A. E. Crew. Bidder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
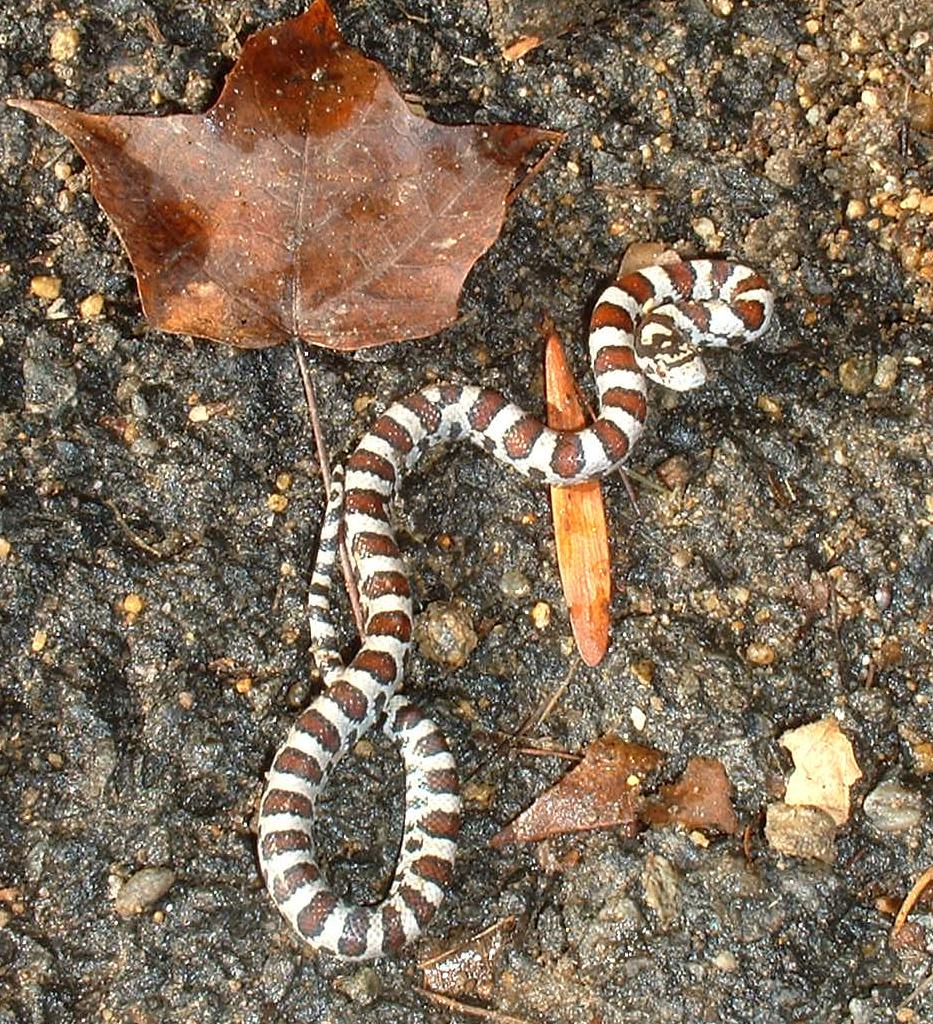
Lampropeltis Triangulum
The milk snake or milksnake (''Lampropeltis triangulum''), is a species of kingsnake; 24 subspecies are currently recognized. ''Lampropeltis elapsoides'', the scarlet kingsnake, was formerly classified as a 25th subspecies (''L. t. elapsoides''), but is now recognized as a distinct species. The subspecies have strikingly different appearances, and many of them have their own common names. Some authorities suggest that this species could be split into several separate species. They are not venomous to humans. Geographic range Milk snakes can be found from the southeastern extreme of Canada through the eastern half of the United States. Habitat Across the wide range of this species, habitat varies. Typically, milk snakes live in forested regions; however, they can also be found in swamps, prairie, farmland, rocky slopes, and sand dunes/beaches. In some situations, milk snakes also migrate seasonally, during the winter they move to higher and drier habitats for hibernation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sistrurus Miliarius
:''Common names: pygmy rattlesnake, eastern pygmy rattlesnake, ground rattlesnake, leaf rattler, death rattler, #Common names, more.''Albert Hazen WWright AH, Anna Allen WWright AA (1957). ''Handbook of Snakes of the United States and Canada''. Ithaca and London: Comstock Publishing Associates, a Division of Cornell University Press. (7th printing, 1985). 1,105 pp. (in two volumes). . (''Sistrurus miliarius'', pp. 1052-1061). ''Sistrurus miliarius,'' commonly called the pygmy rattlesnake, is a species of venomous snake in the subfamily Crotalinae (pit vipers) of the Family (biology), family Viperidae. The species is Endemism, endemic to the Southeastern United States. Three subspecies are currently recognized. Description ''S. miliarius'' is a small species, with adults usually growing to in total length (including tail). The maximum reported total length is (Laurence Monroe Klauber, Klauber, 1972). Snellings and Joseph T. Collins, Collins (1997) reported a specimen of ''S. m. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
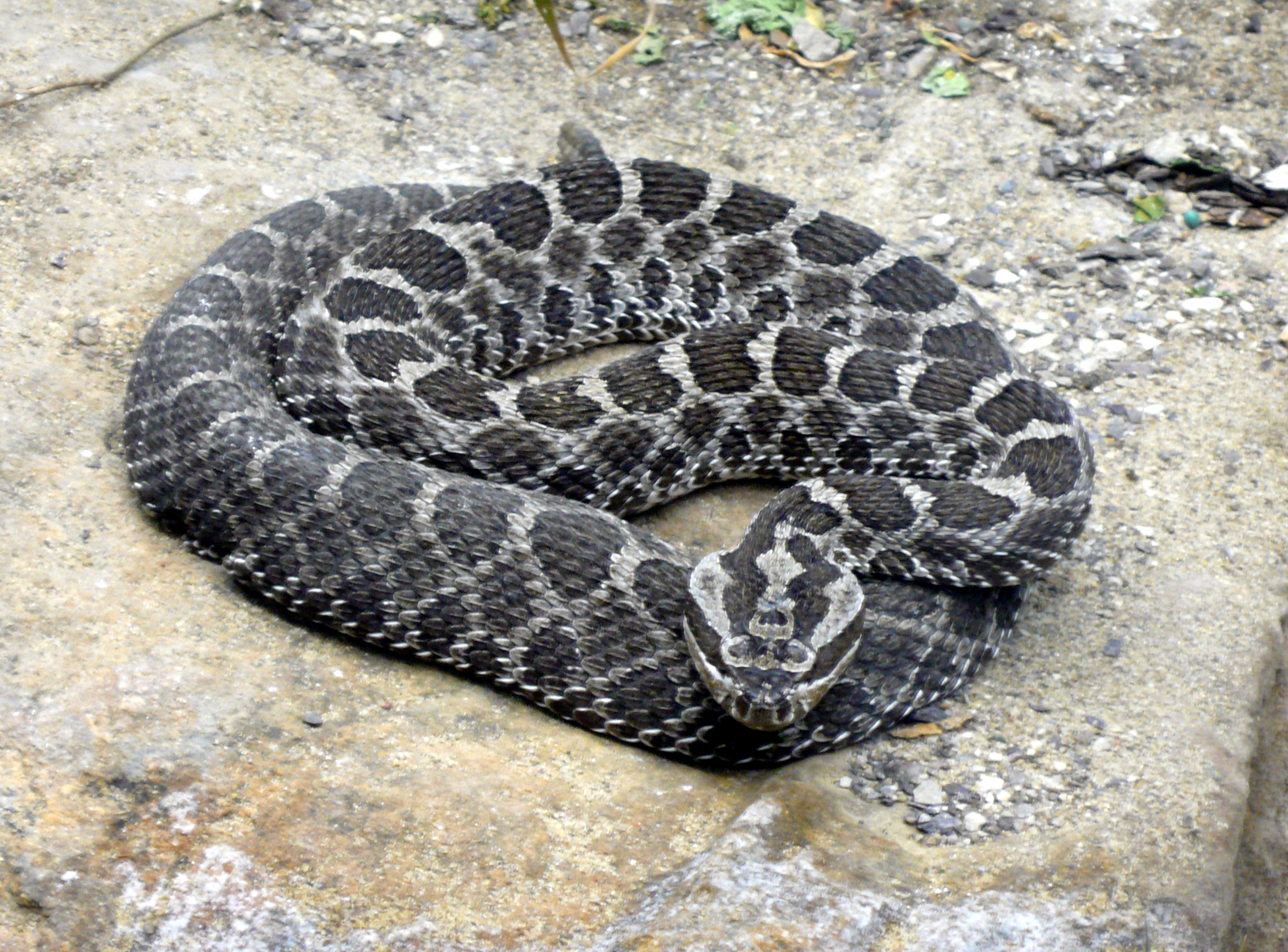
Sistrurus Catenatus
The massasauga (''Sistrurus catenatus'') is a rattlesnake species found in midwestern North America from southern Ontario to northern Mexico and parts of the United States in between. Like all rattlesnakes, it is a pit viper and is venomous. Three subspecies were recognized for more than a century, although research published in 2011 elevated two subspecies ''Sistrurus catenatus catenatus'' and ''Sistrurus catenatus tergeminus'', to full species: the eastern massasauga (''Sistrurus catenatus'') and the western massasauga (''Sistrurus tergeminus'').Kubatko, L.S.; Gibbs, H.L. & Bloomquist, E.W. 2011. ''Inferring Species-Level Phylogenies and Taxonomic Distinctiveness Using Multilocus Data in Sistrurus Rattlesnakes.'' Systematic Biology 60 (4):393–409 The status of the third subspecies was somewhat unresolved and it is tentatively recognized as the desert massasauga (''Sistrurus tergeminus edwardsii'') by some,Powell, Robert, Roger Conant, and Joseph T. Collins. 2016. ''Peterson F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crotalus Horridus
The timber rattlesnake, canebrake rattlesnake, or banded rattlesnake (''Crotalus horridus'') Wright AH, Wright AA (1957). ''Handbook of Snakes of the United States and Canada''. Ithaca and London: Comstock Publishing Associates, a division of Cornell University Press. (7th printing, 1985). 1,105 pp. (in two volumes). . (''Crotalus horridus'', pp. 956–966.) is a species of pit viper endemic to eastern North America. Like all other pit vipers, it is venomous, with a very toxic bite. ''C. horridus'' is the only rattlesnake species in most of the populous Northeastern United States and is second only to its relatives to the west, the prairie rattlesnake, as the most northerly distributed venomous snake in North America. Conant R (1975). ''A Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America, Second Edition''. (First published in 1958). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. xviii + 429 pp. + Plates 1-48. (hardcover), (paperback). (''Crotalus horridus'', pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coluber Constrictor
The eastern racer (''Coluber constrictor'') is a species of nonvenomous snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to North America and Central America. Eleven subspecies, including the nominotypical subspecies, are recognized, which as a group are commonly referred to as the eastern racers. The species is monotypic in the genus ''Coluber''. Geographic range ''C. constrictor'' is found throughout the United States, east of the Rocky Mountains, but it also ranges north into Canada and south into Mexico, Guatemala, and Belize. Description Adult eastern racers can typically vary from in total length (including tail) depending on the subspecies, but a record-sized specimen measured in total length. Conant, Roger (1975). ''A Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America, Second Edition''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. xviii + 429 pp. + Plates 1-48. (paperback). (''Coluber consrictor constrictor'', pp. 178-179 + Plate 26 + Map 139). A typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |