|
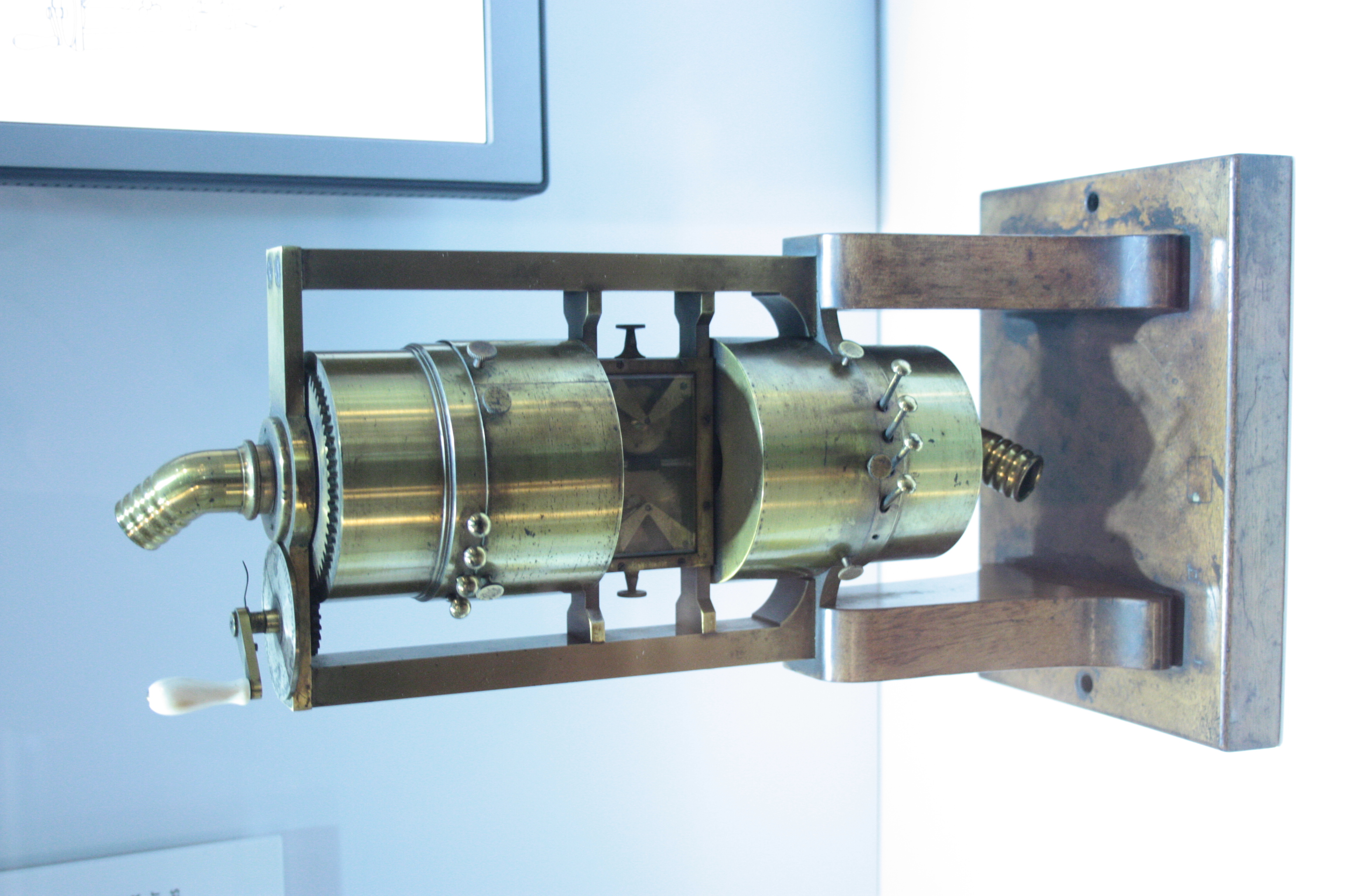
On The Sensations Of Tone
''On the Sensations of Tone as a Physiological Basis for the Theory of Music'' (German ), commonly referred to as ''Sensations of Tone'', is a foundational work on music acoustics and the perception of sound by Hermann von Helmholtz. The first German edition was published in 1863. The English translation by Alexander J. Ellis was first published in 1875 (the first English edition was from the 1870 third German edition; the second English edition from the 1877 fourth German edition was published in 1885; the 1895 and 1912 third and fourth English editions were reprints of the second edition). The editions translated into English contain detailed commentary and notes (titled "Additions by the Translator") by Ellis. Helmholtz declared that he started working on his book in 1854, which concluded in 1862. Helmholtz started publishing on acoustics in 1852. His last article on acoustics was in 1878, reviewing the book by Lord Rayleigh (Theory of Sound). Therefore, Helmholtz published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmholtz Resonator 2
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, is named in his honor. In the fields of physiology and psychology, Helmholtz is known for his mathematics concerning the eye, theories of vision, ideas on the visual perception of space, color vision research, the sensation of tone, perceptions of sound, and empiricism in the physiology of perception. In physics, he is known for his theories on the conservation of energy, work in electrodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, and on a mechanical foundation of thermodynamics. As a philosopher, he is known for his philosophy of science, ideas on the relation between the laws of perception and the laws of nature, the science of aesthetics, and ideas on the civilizing power of scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an Acoustical engineering, acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing (sense), Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perception Of Sound
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of sound perception and audiology—how humans perceive various sounds. More specifically, it is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound (including noise, speech, and music). Psychoacoustics is an interdisciplinary field of many areas, including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science. Background Hearing is not a purely mechanical phenomenon of wave propagation, but is also a sensory and perceptual event; in other words, when a person hears something, that something arrives at the ear as a mechanical sound wave traveling through the air, but within the ear it is transformed into neural action potentials. The outer hair cells (OHC) of a mammalian cochlea give rise to enhanced sensitivity and better frequency resolution of the mechanical response of the cochlear partition. These nerve pulses then travel to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, is named in his honor. In the fields of physiology and psychology, Helmholtz is known for his mathematics concerning the eye, theories of vision, ideas on the visual perception of space, color vision research, the sensation of tone, perceptions of sound, and empiricism in the physiology of perception. In physics, he is known for his theories on the conservation of energy, work in electrodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, and on a mechanical foundation of thermodynamics. As a philosopher, he is known for his philosophy of science, ideas on the relation between the laws of perception and the laws of nature, the science of aesthetics, and ideas on the civilizing power of science. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander J
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander John Ellis
Alexander John Ellis, (14 June 1814 – 28 October 1890), was an English mathematician, philologist and early phonetician who also influenced the field of musicology. He changed his name from his father's name, Sharpe, to his mother's maiden name, Ellis, in 1825 as a condition of receiving significant financial support from a relative on his mother's side. He is buried in Kensal Green Cemetery, London. Biography He was born Alexander John Sharpe in Hoxton, Middlesex to a wealthy family. His father, James Birch Sharpe, was a notable artist and physician who was later appointed Esquire of Windlesham. His mother, Ann Ellis, was from a noble background, but it is not known how her family made its fortune. Alexander's brother James Birch Sharpe junior died at the Battle of Inkerman during the Crimean War. His other brother, William Henry Sharpe, served with the Lancashire Fusiliers after moving north with his family to Cumberland, due to military work. Alexander was educated at Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, movies/videos, moving images, and millions of books. In addition to its archiving function, the Archive is an activist organization, advocating a free and open Internet. , the Internet Archive holds over 35 million books and texts, 8.5 million movies, videos and TV shows, 894 thousand software programs, 14 million audio files, 4.4 million images, 2.4 million TV clips, 241 thousand concerts, and over 734 billion web pages in the Wayback Machine. The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Margenau
Henry Margenau (April 30, 1901 – February 8, 1997) was a German-American physicist, and philosopher of science. Biography Early life Born in Bielefeld, Germany, Margenau obtained his bachelor's degree from Midland Lutheran College, Nebraska before his M.Sc. from the University of Nebraska in 1926, and PhD from Yale University in 1929. World War II Margenau worked on the theory of microwaves and the development of duplexing systems that enabled a single radar antenna both to transmit and receive signals. He also worked on spectral line broadening, a technique used to analyse and review the dynamics of the atomic bombing of Hiroshima. Philosophy and history of science Margenau wrote extensively on science, his works including: ''Ethics and Science'', ''The Nature of Physical Reality'', ''Quantum Mechanics'' and ''Integrative Principles of Modern Thought''. He wrote in 1954 the important introduction for the classic book of Hermann von Helmholtz Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition (OCR), and stored in its digital database.The basic Google book link is found at: https://books.google.com/ . The "advanced" interface allowing more specific searches is found at: https://books.google.com/advanced_book_search Books are provided either by publishers and authors through the Google Books Partner Program, or by Google's library partners through the Library Project. Additionally, Google has partnered with a number of magazine publishers to digitize their archives. The Publisher Program was first known as Google Print when it was introduced at the Frankfurt Book Fair in October 2004. The Google Books Library Project, which scans works in the collections of library partners and adds them to the digital invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Books
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect of all human societies, a cultural universal. While scholars agree that music is defined by a few specific elements, there is no consensus on their precise definitions. The creation of music is commonly divided into musical composition, musical improvisation, and musical performance, though the topic itself extends into academic disciplines, criticism, philosophy, and psychology. Music may be performed or improvised using a vast range of instruments, including the human voice. In some musical contexts, a performance or composition may be to some extent improvised. For instance, in Hindustani classical music, the performer plays spontaneously while following a partially defined structure and using characteristic motifs. In modal jazz th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |