|
Old Permic Script
The Old Permic script ( kv, Важ Перым гижӧм, ), sometimes known by its initial 2 characters as Abur or Anbur, is a "highly idiosyncratic adaptation" of the Cyrillic script once used to write medieval Komi (a member of the Permic branch of Finno-Ugric languages). History The script was introduced by a Russian missionary, Stepan Khrap, also known as Saint Stephen of Perm (Степан Храп, св. Стефан Пермский) in 1372. The name ''Abur'' is derived from the names of the first two characters: ''An'' and ''Bur''. The script derived from Cyrillic and Greek, with Komi "Tamga" signs, the latter being similar in the appearance to runes or siglas poveiras because they were created by incisions rather than by usual writing. The inclusion of the latter aided the script to greater acceptance among the medieval Permic speakers of the time. The script was in use until the 17th century, when it was superseded by the Cyrillic script. Abur was also used as cryp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komi Language
The Komi language ( kv, коми кыв, ''komi kyv''), also known as Zyryan, Zyrian or Komi-Zyryan (Komi: коми-зырян кыв, komi-zyrjan kyv),Komi language ''Britannica''. is one of the two regional varieties of the pluricentric Komi language, the other regional variety being Permyak. Komi is natively spoken by the native to the and other parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
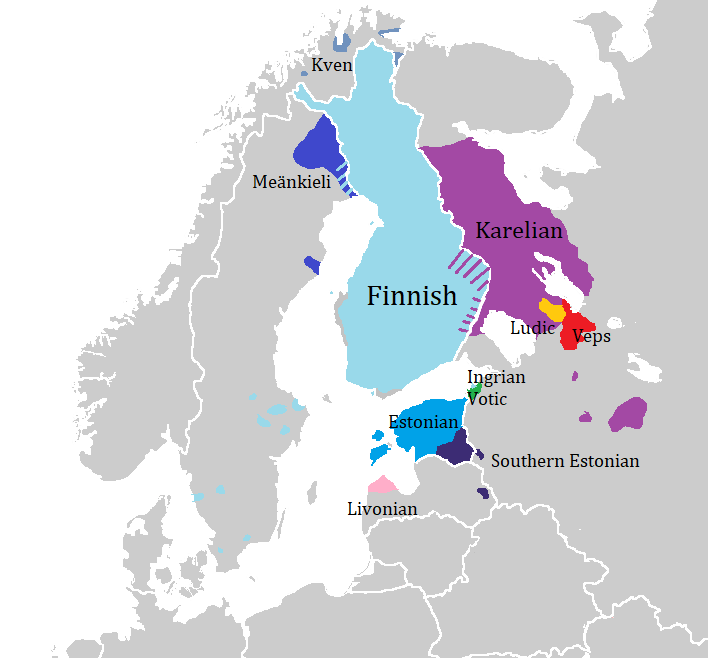
Uralic Languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (which alone accounts for more than half of the family's speakers), Finnish, and Estonian. Other significant languages with fewer speakers are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt, Sami, Komi, and Vepsian, all of which are spoken in northern regions of Scandinavia and the Russian Federation. The name "Uralic" derives from the family's original homeland (''Urheimat'') commonly hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains. Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic, though Finno-Ugric is widely understood to exclude the Samoyedic languages. Scholars who do not accept the traditional notion that Samoyedic split first from the rest of the Uralic family may treat the terms as synonymous. History Homelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabets
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first fully phonemic script, the Proto-Sinaitic script, later known as the Phoenician alphabet, is considered to be the first alphabet and is the ancestor of most modern alphabets, including Arabic, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Latin, and possibly Brahmic. It was created by Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in the Sinai Peninsula (as the Proto-Sinaitic script), by selecting a small number of hieroglyphs commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values of the Canaanite languages. However, Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent consonan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines as of the current version (15.0) 149,186 characters covering 161 modern and historic scripts, as well as symbols, emoji (including in colors), and non-visual control and formatting codes. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread and predominant use in the internationalization and localization of computer software. The standard has been implemented in many recent technologies, including modern operating systems, XML, and most modern programming languages. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Universal Coded Character Set, ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code identical with the other. ''The Unicode Standard'', however, includes more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titlo
Titlo is an extended diacritic symbol initially used in early Cyrillic and Glagolitic manuscripts, e.g., in Old Church Slavonic and Old East Slavic languages. The word is a borrowing from the Greek "", "title" (compare dated English '' tittle'', see tilde). The titlo still appears in inscriptions on modern icons and in service books printed in Church Slavonic. The titlo is drawn as a line over a text. In some styles of writing the line is drawn with serifs, so that it may appear as a zigzag. The usual form in this case is short stroke up, falling slanted line, short stroke up; an alternative resembles a volta bracket: short stroke up, horizontal line, short stroke down. The titlo has several meanings depending on the context: One meaning is in its use to mark letters when they are used as numerals. This is a quasi-decimal system analogous to Greek numerals. A titlo is also used as a scribal abbreviation mark for frequently written long words and also for nouns describing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many Proto-Protestantism, earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the ''Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikael Agricola
Mikael Agricola (; c. 1510 – 9 April 1557) was a Finnish Lutheran clergyman who became the de facto founder of literary Finnish and a prominent proponent of the Protestant Reformation in Sweden, including Finland, which was a Swedish territory at the time. He is often called the "father of literary Finnish". Agricola was consecrated as the bishop of Turku (Åbo) in 1554, without papal approval. He continued the reform of the Finnish church (then a part of the Church of Sweden) along Lutheran lines. He translated the New Testament into Finnish and also produced the prayer book and hymns used in Finland's new Lutheran Church. This work set the rules of orthography that are the basis of modern Finnish spelling. His thorough work is particularly remarkable in that he accomplished it in only three years. He died of sudden illness while returning from a trip during which he assisted in negotiating the Treaty of Novgorod with the Tsardom of Russia. Biography Early life Michael ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at Encyclopædia Britannica The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian and |
Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the Volkhov River just downstream from its outflow from Lake Ilmen and is situated on the M10 federal highway connecting Moscow and Saint Petersburg. UNESCO recognized Novgorod as a World Heritage Site in 1992. The city has a population of At its peak during the 14th century, the city was the capital of the Novgorod Republic and was one of Europe's largest cities. The "Veliky" ("great") part was added to the city's name in 1999. History Early developments The Sofia First Chronicle makes initial mention of it in 859, while the Novgorod First Chronicle first mentions it in 862, when it was purportedly already a major Baltics-to- Byzantium station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birch Bark Letter No
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech-oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 30 to 60 taxonomy of Betula, known taxa of which 11 are on the IUCN Red List, IUCN 2011 Red List of Threatened Species. They are a typically rather short-lived pioneer species widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in northern areas of temperate climates and in boreal climates. Description Birch species are generally small to medium-sized trees or shrubs, mostly of northern temperate and boreal climates. The simple leaf, leaves are alternate, singly or doubly serrate, feather-veined, petiolate and stipulate. They often appear in pairs, but these pairs are really borne on spur-like, two-leaved, lateral branchlets. The fruit is a small samara (fruit), samara, although the wings may be obscure in some species. They differ from the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Hungarian Script
The Old Hungarian script or Hungarian runes ( hu, Székely-magyar rovás, 'székely-magyar runiform', or ) is an alphabetic writing system used for writing the Hungarian language. Modern Hungarian is written using the Latin-based Hungarian alphabet. The term "old" refers to the historical priority of the script compared with the Latin-based one. The Old Hungarian script is a child system of the Old Turkic alphabet. The Hungarians settled the Carpathian Basin in 895. After the establishment of the Christian Hungarian kingdom, the old writing system was partly forced out of use during the rule of King Stephen, and the Latin alphabet was adopted. However, among some professions (e.g. shepherds who used a "rovás-stick" to officially track the number of animals) and in Transylvania, the script has remained in use by the Székely Magyars, giving its Hungarian name . The writing could also be found in churches, such as that in the commune of Atid. Its English name in the ISO 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


.jpg)