|
O'Connor Engineering Laboratories
Chadwell O'Connor (October 9, 1914 – September 5, 2007) was an American inventor and steam engine enthusiast. He is most remembered as the inventor of an improved fluid-damped tripod head, for which he won Academy Awards in 1975 and 1992. Early life and education Chadwell O'Connor came from a distinguished family. His father, Johnson O'Connor was a well-known psychometrician and pioneer in the study of aptitude testing. His mother died when he was young and his father remarried the MIT-trained architect and educator Eleanor Manning. The family lived in Boston and O'Connor often accompanied his father to his work at the General Electric factory in Lynn, Massachusetts where he acquired an interest in engineering. O'Connor attended the Stevens Institute of Technology and California Institute of Technology where he earned a degree in mechanical engineering. Shortly after graduating, World War II broke out and O'Connor joined Douglas Aircraft where he was in charge of exped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chadwell O'Connor
Chadwell O'Connor (October 9, 1914 – September 5, 2007) was an American inventor and steam engine enthusiast. He is most remembered as the inventor of an improved fluid-damped tripod head, for which he won Academy Awards in 1975 and 1992. Early life and education Chadwell O'Connor came from a distinguished family. His father, Johnson O'Connor was a well-known psychometrician and pioneer in the study of aptitude testing. His mother died when he was young and his father remarried the MIT-trained architect and educator Eleanor Manning. The family lived in Boston and O'Connor often accompanied his father to his work at the General Electric factory in Lynn, Massachusetts where he acquired an interest in engineering. O'Connor attended the Stevens Institute of Technology and California Institute of Technology where he earned a degree in mechanical engineering. Shortly after graduating, World War II broke out and O'Connor joined Douglas Aircraft where he was in charge of expediting a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paddlewheeler
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine that drives paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, where the first uses were wheelers driven by animals or humans. In the early 19th century, paddle wheels were the predominant way of propulsion for steam-powered boats. In the late 19th century, paddle propulsion was largely superseded by the screw propeller and other marine propulsion systems that have a higher efficiency, especially in rough or open water. Paddle wheels continue to be used by small, pedal-powered paddle boats and by some ships that operate tourist voyages. The latter are often powered by diesel engines. Paddle wheels The paddle wheel is a large steel framework wheel. The outer edge of the wheel is fitted with numerous, regularly spaced paddle blades (called floats or buckets). The bottom quarter or so of the wheel travels under water. An e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Award For Documentary Feature
The Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature Film is an award for documentary films. In 1941, the first awards for feature-length documentaries were bestowed as Special Awards to '' Kukan'' and ''Target for Tonight''. They have since been bestowed competitively each year, with the exception of 1946. Copies of every winning film (along with copies of most nominees) are held by the Academy Film Archive. Winners and nominees Following the Academy's practice, films are listed below by the award year (that is, the year they were released under the Academy's rules for eligibility). In practice, due to the limited nature of documentary distribution, a film may be released in different years in different venues, sometimes years after production is complete. 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s 2020s Shortlisted finalists Finalists for Best Documentary Feature are selected by the Documentary Branch based on a preliminary ballot. A se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Living Desert
''The Living Desert'' is a 1953 American nature documentary film that shows the everyday lives of the animals of the desert of the Southwestern United States. The film was written by James Algar, Winston Hibler, Jack Moffitt (uncredited) and Ted Sears. It was directed by Algar, with Hibler as the narrator and was filmed in Tucson, Arizona. The film won the 1953 Oscar for Best Documentary. It is featured in the 2006 DVD ''Walt Disney Legacy Collection Volume 2: Lands of Exploration''. Production ''The Living Desert'' was the first feature-length film in Disney's ''True-Life Adventures'' series of documentaries focusing on zoological studies; the previous films in the series, including the Oscar-winning '' Seal Island'', were short subjects. The documentary was filmed in Tucson, Arizona. Most of the wildlife shown in the film was donated to what would soon become the Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum. The film was inspired by 10 minutes of footage shot by N. Paul Kenworthy, a doct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walt Disney
Walter Elias Disney (; December 5, 1901December 15, 1966) was an American animator, film producer and entrepreneur. A pioneer of the American animation industry, he introduced several developments in the production of cartoons. As a film producer, he holds the record for most Academy Awards earned and nominations by an individual, having won 22 Oscars from 59 nominations. He was presented with two Golden Globe Special Achievement Awards and an Emmy Award, among other honors. Several of his films are included in the National Film Registry by the Library of Congress and have also been named as some of the List of films considered the best, greatest films ever by the American Film Institute. Disney was the first person to be nominated for Academy Awards in six different categories. Born in Chicago in 1901, Disney developed an early interest in drawing. He took art classes as a boy and got a job as a commercial illustrator at the age of 18. He moved to California in the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Minnetonka
Lake Minnetonka (Dakota: ''Mní iá Tháŋka'') is a lake located about west-southwest of Minneapolis, Minnesota. Lake Minnetonka has about 23 named bays and areas. The lake lies within Hennepin and Carver counties and is surrounded by 13 incorporated municipalities. At , it is Minnesota's ninth largest lake. It is a popular spot for local boaters, sailors, and fishermen. History Early history The first people who inhabited the Lake Minnetonka area were indigenous natives who migrated to the region at the end of the last ice age circa 8000 BCE. Later peoples who inhabited the area between 3500 BCE and 1500 CE are commonly referred to collectively as the "Mound Builders" because they constructed large land features serving spiritual, ceremonial, burial, and elite residential functions. The Mound Builder culture reached its apex circa 1150 CE and ceased to exist circa 1500 CE. By the 1700s Lake Minnetonka was inhabited by the Mdewakanton people, a subtribe of the Dak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnehaha (steamboat)
''Minnehaha'' is a steam-powered excursion vessel on Lake Minnetonka in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The vessel was originally in service between 1906 and 1926. After being scuttled in 1926, ''Minnehaha'' was raised from the bottom of Lake Minnetonka in 1980, restored, and returned to active service in 1996. The vessel operated uninterrupted on Lake Minnetonka until 2019. It is currently stored in a maintenance facility in the town of Excelsior. History ''Minnehaha'' was built by the Twin City Rapid Transit Company (TCRT) in 1906 and provided fast and reliable transportation for the residents of Lake Minnetonka during much of the early twentieth century. She ran alongside five identical sister vessels named ''Como'', ''Harriet'', ''Hopkins'', ''Stillwater'', and ''White Bear''. TCRT had commissioned boat builder Royal C. Moore to design these "Express Boats" in 1905. Each were long, wide, drew of water, and were powered by a single coal-fired boiler and triple-expansio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesota Transportation Museum
The Minnesota Transportation Museum (MTM, reporting mark MNTX) is a transportation museum in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. MTM operates several heritage transportation sites in Minnesota and one in Wisconsin. The museum is actively involved in preserving local railroad, bus and streetcar history. MTM was formed in 1962 to save a streetcar that had been built and operated by Twin City Rapid Transit (TCRT) in Minneapolis–St. Paul. Many of the museum's early members were formerly part of the Minnesota Railfans Association, which had organized railfan trips from the 1940s to the 1960s. In 2004–2005, the organization's streetcar operations became the Minnesota Streetcar Museum, with the steamboat ''Minnehaha'', originally built by TCRT in a style similar to its streetcars, becoming a major attraction of the Museum of Lake Minnetonka. Minnehaha Depot After the first streetcar, TCRT 1300, was successfully restored, other projects were examined in the time bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
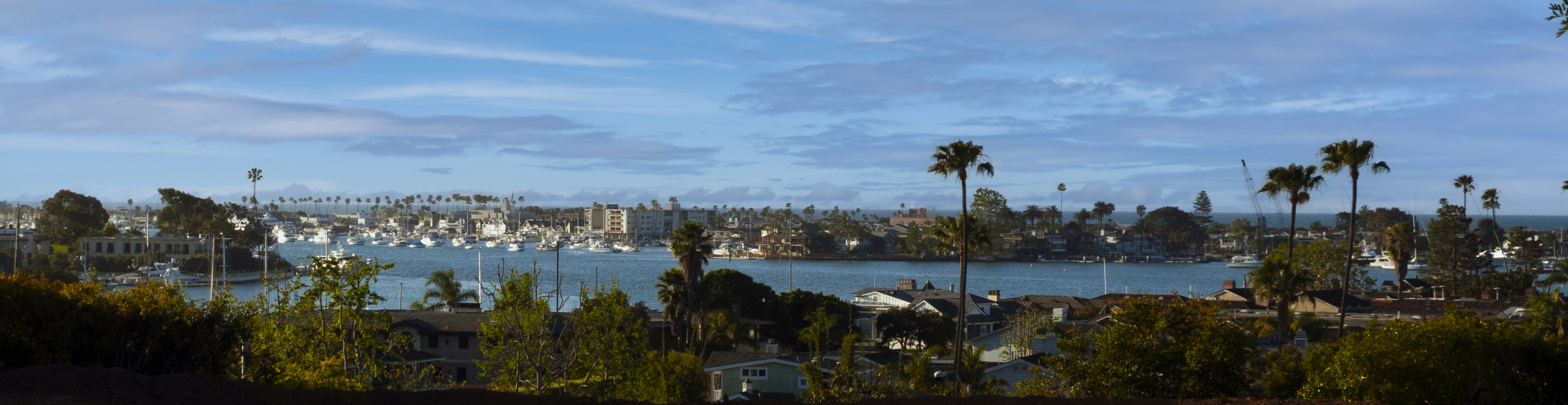
Newport Beach, California
Newport Beach is a coastal city in South Orange County, California. Newport Beach is known for swimming and sandy beaches. Newport Harbor once supported maritime industries however today, it is used mostly for recreation. Balboa Island, Newport Beach, Balboa Island draws visitors with a waterfront path and easy access from the ferry to the shops and restaurants. History The Upper Bay of Newport is a canyon carved by a stream in the Pleistocene period. The Lower Bay of Newport was formed much later by sand brought along by ocean currents, which constructed the offshore beach now recognized as the Balboa Peninsula of Newport Beach. For thousands of years, the Tongva people lived on the land in an extensive, thriving community. The Tongva villages of Genga, California, Genga and Moyongna were located in Newport Beach. Throughout the 1800s, Europeans colonized the land and forcibly removed and assimilated the Tongva. Present-day Newport Beach exists upon the unceded homelands of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ward Kimball
Ward Walrath Kimball (March 4, 1914 – July 8, 2002) was an American animator employed by Walt Disney Animation Studios. He was part of Walt Disney's main team of animators, known collectively as Disney's Nine Old Men. His films have been honored with two Academy Awards for Best Animated Short Film. Outside of his job as an animator, Kimball was a railroad enthusiast as well as a talented jazz trombonist. He founded and led the seven-piece Dixieland band Firehouse Five Plus Two, in which he played the trombone. Early life Kimball was born on March 4, 1914, in Minneapolis. His father was a salesman who traveled widely. He grew up in the Midwest, often residing with his grandparents. Career While Kimball was a brilliant draftsman, he preferred to work on comical characters rather than realistic human designs. Animating came easily to him and he was constantly looking to do things differently. Because of this, Walt Disney called Ward a genius in the book ''The Story of Walt Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
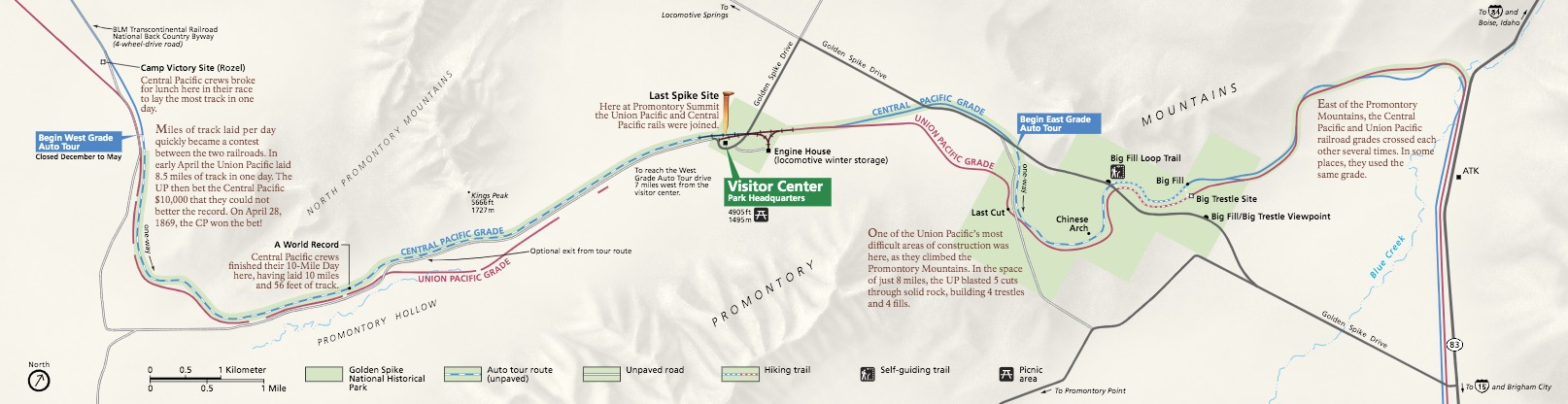
Golden Spike National Historical Park
Golden Spike National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park located at Promontory Summit, north of the Great Salt Lake in east-central Box Elder County, Utah, United States. The nearest city is Corinne, approximately east-southeast of the site. It commemorates the completion of the first Transcontinental Railroad where the Central Pacific Railroad and the first Union Pacific Railroad met on May 10, 1869. The final joining of the rails spanning the continent was signified by the driving of the ceremonial Golden Spike. Background The Golden Spike National Historical Park encompasses . Initially just when it was established in 1957, limited to the area near the junction of the two rail systems, the site was expanded by in 1965 through land swaps and acquisition of approximately a strip of land mostly wide along of the former railroad right-of-way. It reached its present size in 1980. In addition to the Summit site where the rails were joined, the Park in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |