|
Nuzu
Nuzi (or Nuzu; Akkadian language, Akkadian Gasur; modern Yorghan Tepe, Iraq) was an ancient Mesopotamian city southwest of the city of Arrapha (modern Kirkuk), located near the Tigris river. The site consists of one medium-sized multiperiod Tell (archaeology), tell and two small single period mounds. History The site showed occupation as far back as the late Uruk period. The city, then named Gasur, was founded in the third millennium during the time of the Akkadian Empire. In the middle of the second millennium the Hurrians gained control of the town and renamed it Nuzi. The history of the site during the intervening period is unclear, though the presence of a few cuneiform tablets from the Old Assyrian Empire indicates that trade with nearby Assur was taking place. After the fall of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni to Ashur-uballit I of the Middle Assyrian Empire, Nuzi went into gradual decline. Note that while the Hurrian period is well known from full excavation of those strata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkuk Governorate
Kirkuk Governorate ( ar, محافظة كركوك, Muḥāfaẓat Karkūk, ku, پارێزگای کەرکووک, Parêzgeha Kerkûkê/Parêzgayi Kerkûk, tr, Kerkük ili) or Kirkuk Province is a governorate in northern Iraq. The governorate has an area of . In 2017 the estimated population was 1,259,561 people. The provincial capital is the city of Kirkuk. It is divided into four districts. The province was named Kirkuk Governorate until 1976, when it was named At-Ta'mim Governorate, meaning "nationalization", referring to the national ownership of the regional oil and natural gas reserves. In 2006, the name "Kirkuk Governorate" was restored. Governorate government *Governor:Rakan Saeed al-Jabouri *Provincial Council Chairman (PCC): Rebwar Talabani Districts Demographics Using census data and other primary and secondary sources, including voter registration rolls and food ration registry, Khalil Fadl Osman traces demographic changes in Kirkuk since the 1920s and investigates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khafajah
Khafajah or Khafaje (Arabic: خفاجة; ancient Tutub, Arabic: توتوب) is an archaeological site in Diyala Province (Iraq). It was part of the city-state of Eshnunna. The site lies east of Baghdad and southwest of Eshnunna. History of archaeological research Khafajah was excavated for 7 seasons in the early 1930s primarily by an Oriental Institute of Chicago team led by Henri Frankfort with Thorkild Jacobsen and Pinhas Delougaz. For two seasons, the site was worked by a joint team of the American Schools of Oriental Research and the University of Pennsylvania. Khafajah and its environment Khafajah lies on the Diyala River, a tributary of the Tigris. The site consists of four mounds, labeled A through D. The main one, Mound A, extends back as far as the Uruk period and contained an oval temple, a temple of the god Sin, and a temple of Nintu. The Dur-Samsuiluna fort was found on mounds B and C. Mound D contained private homes and a temple for the god Sin where the archive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
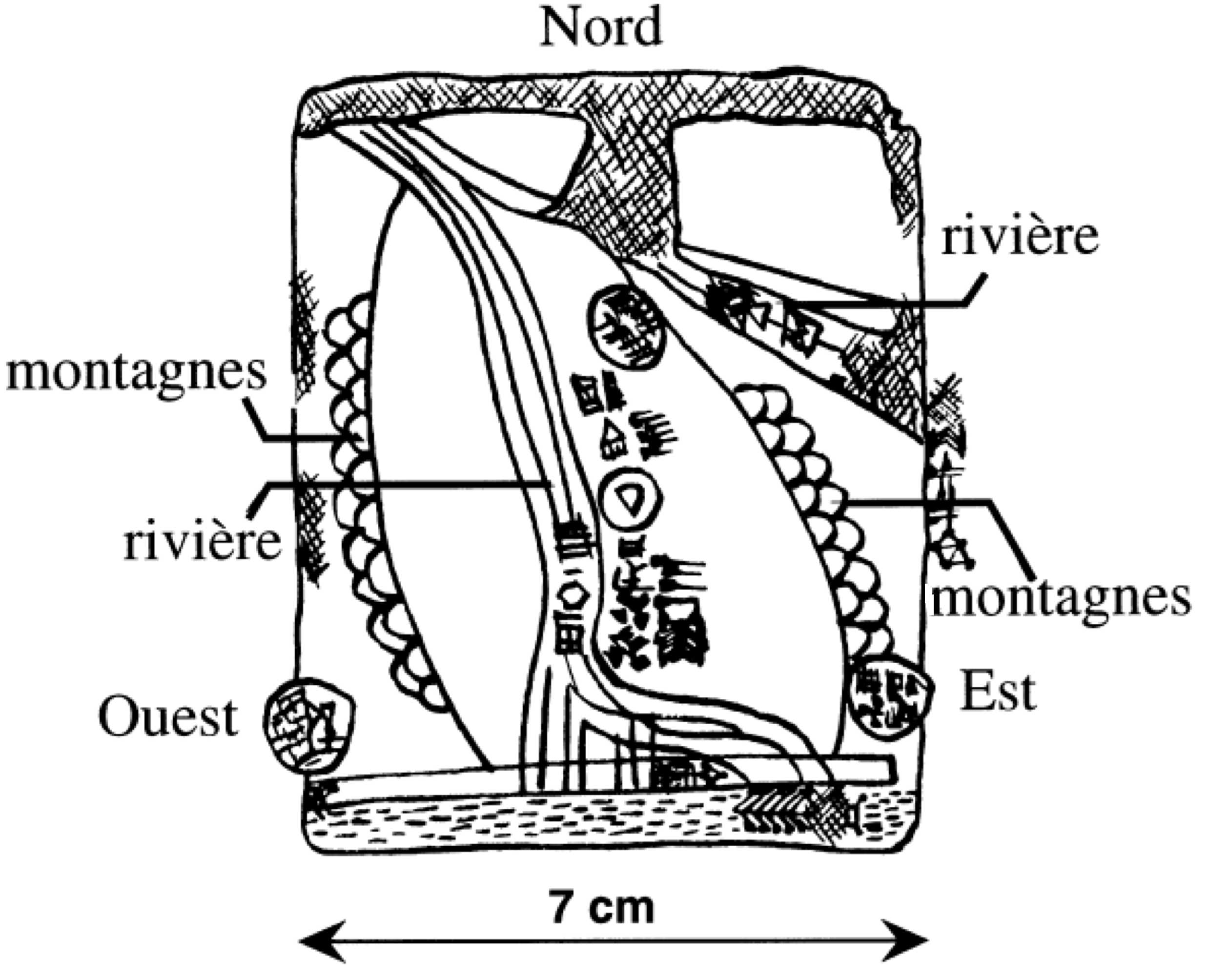
Tell Al-Fakhar
Tell al-Fakhar ( ar, تل الفخار "Pottery Mound") is a '' tell'', or archaeological settlement mound, in Kirkuk Governorate, northeastern Iraq. Excavations were carried out at the site between 1967 and 1969 by the Directorate-General of Antiquities of Iraq. The site measures and is high. Excavations revealed two occupation phases that were dated to the Mitanni/Kassite and Neo-Assyrian periods, or mid-second and early-first millennia BCE. The mid-second millennium phase consisted of a large building, dubbed the "Green Palace", where an archive of circa 800 clay tablets was found. History of research The site was excavated by the Directorate-General of Antiquities of Iraq under the direction of Yasin Mahmoud al-Khalesi during one season in the winter of 1967–1968 lasting from 22 October to 27 January. The excavation was prompted by the fact that the site was threatened by the development of an irrigation project in the region and because illegal digging activities had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern Mesopotamia. The largest and most influential Hurrian nation was the kingdom of Mitanni, its ruling class perhaps being Indo-Aryan speakers. The population of the Hittite Empire in Anatolia included a large population of Hurrians, and there is significant Hurrian influence in Hittite mythology. By the Early Iron Age, the Hurrians had been assimilated with other peoples. The state of Urartu later covered some of the same area. Language The Hurrian language is closely related to the Urartian language, the language of the ancient kingdom of Urartu. Together they form the Hurro-Urartian language family. The external connections of the Hurro-Urartian languages are disputed. There exist various proposals for a genetic relationship to ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning". Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million. The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Semitic Museum
The Harvard Museum of the Ancient Near East (HMANE, previously the Harvard Semitic Museum) is a museum founded in 1889. It moved into its present location at 6 Divinity Avenue in Cambridge, Massachusetts, in 1903. Description From the beginning, HMANE was the home of the Department of Near Eastern Languages and Civilizations, a departmental library, a repository for research collections, a public educational institute, and a center for archaeological exploration. Among the museum's early achievements were the first scientific excavations in the Holy Land (at Samaria in 1907–1912) and excavations at Nuzi in Mesopotamia and Tell el-Khaleifeh in the Sinai, where the earliest alphabet was found. The museum's artifacts include pottery, cylinder seals, sculpture, coins, cuneiform tablets, and Egyptian mummy sarcophagi. Many are from museum-sponsored excavations in Jordan, Iraq, Egypt, Cyprus, Israel, and Tunisia. The museum holds plaster casts of the Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |