|
Nuri Ja'far
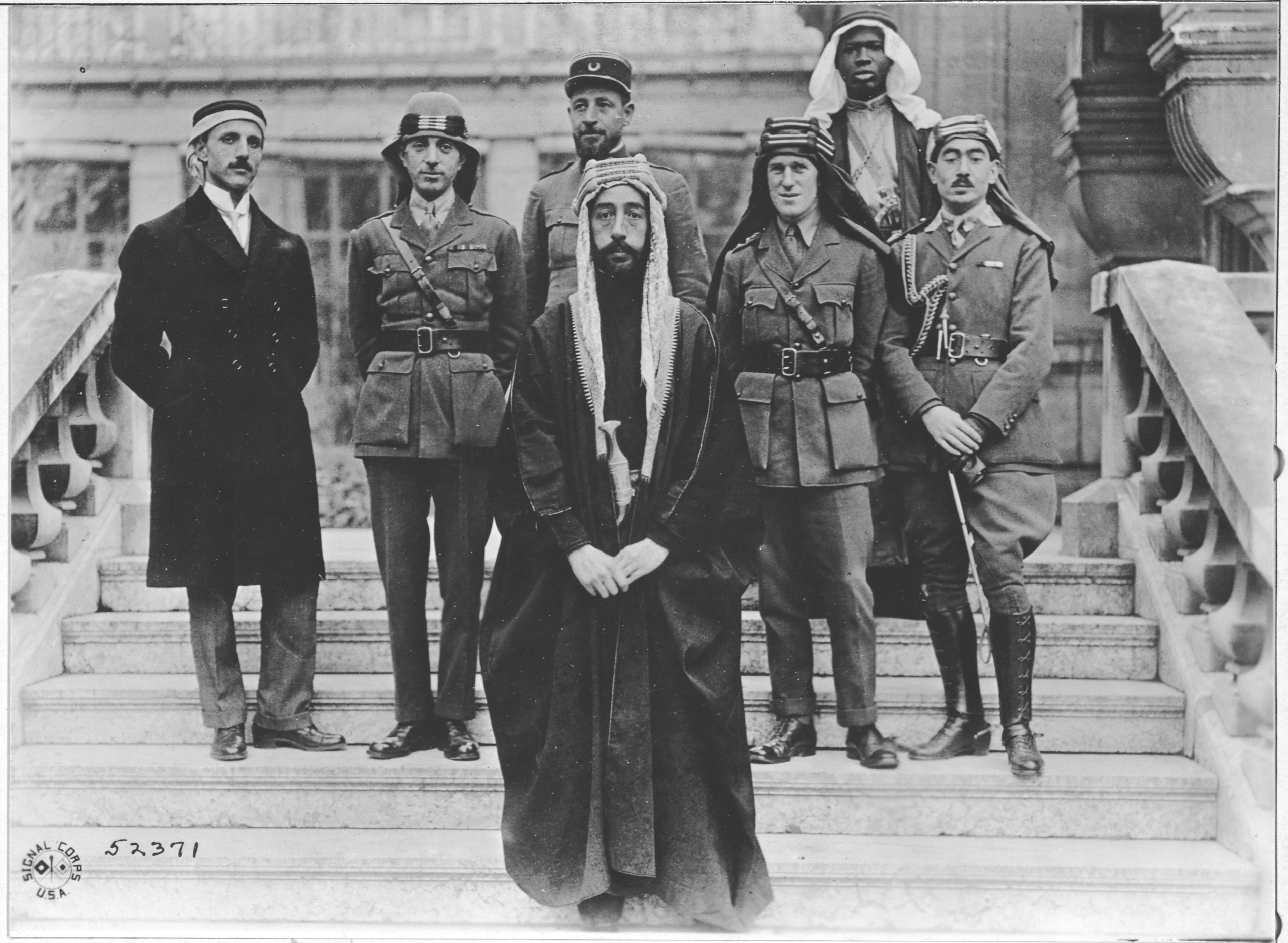
Nuri Ja'far Ali al-Chalabi (), better known as Nuri Ja'far ( ar, نوري جعفر, translit=Nūrī Jaʻfar; 1914 – 7 November 1991), was an Iraqi psychologist, Philosophy of education, philosopher of education, and author. He wrote more than fifty works on pedagogy, psychology, history, philosophy, thought and literature. After graduating from the Higher Teachers' House in Baghdad, he went to the United States, and received a master's degree from Ohio University in 1948 and a Doctor of Philosophy, doctorate in philosophy from the same university in the following year. He was a student of John Dewey and majored in neuropsychology. In his late years, he moved to Libya to teach at the University of Tripoli, until his death. Although Ja'far died in 1991, controversy about his death is continued by biographers. Biography Early years and education Ja'far was born in Al-Qurnah, Basra vilayet. His father, a farmer, and mother, Halimah bint Muhammad Ali Chalabi, were first cousin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Qurna
Al-Qurnah (Kurnah or Qurna, meaning connection/joint in Arabic) is a town in southern Iraq about 74 km northwest of Basra, that lies within the conglomeration of Nahairat. Qurna is located at the confluence point of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to form the Shatt al-Arab waterway. Local folklore holds Qurnah to have been the original site of biblical paradise, the Garden of Eden and location of the Tree of the knowledge of good and evil, Tree of Knowledge. History Local folklore holds Qurnah to have been the site of the Garden of Eden and the location of a city built by general Seleucus I Nicator, Seleucus Nicator I. An ancient tree is celebrated locally and shown to the tourists as the actual Tree of the knowledge of good and evil, Tree of Knowledge of the Bible. The tree died some time ago and replacement trees were planted. The Ezra's Tomb, tomb of Ezra is also described to be nearby and found further upstream on the river Tigris. In 1855, Al Qurnah was the site of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Linguistics
Arabic grammar or Arabic language sciences ( ar, النحو العربي ' or ar, عُلُوم اللغَة العَرَبِيَّة ') is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with the grammar of other Semitic languages. Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic have largely the same grammar; colloquial spoken varieties of Arabic can vary in different ways. The largest differences between classical and colloquial Arabic are the loss of morphological markings of grammatical case; changes in word order, an overall shift towards a more analytic morphosyntax, the loss of the previous system of grammatical mood, along with the evolution of a new system; the loss of the inflected passive voice, except in a few relict varieties; restriction in the use of the dual number and (for most varieties) the loss of the feminine plural. Many Arabic dialects, Maghrebi Arabic in particular also have significant vowel shifts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November 1963 Iraqi Coup D'état
The November 1963 Iraqi coup d'état took place between November 13 and November 18, 1963, when, following internal party divisions, pro-Nasserist Iraqi officers led a military coup within the Ba'ath Party. Although the coup itself was bloodless, 250 people were killed in related actions. The government subsequently lasted until the 17 July Revolution in 1968. Background After seizing Iraqi state power in February 1963, divisions between pro and anti-Nasser Ba'ath leaders, as well as between right and left pan-Arab nationalist Ba'ath leaders led to the first Ba'ath government in Iraq's collapse in November 1963, while 7,000 Iraqi communists remained imprisoned. Qasim's former deputy Abdul Salam Arif (who was not a Ba'athist) was given the largely ceremonial title of President, while prominent Ba'athist general Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr was named Prime Minister. The most powerful leader of the new government was the secretary general of the Iraqi Ba'ath Party, Ali Salih al-Sa'di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arshad Al-Umari
Arshad Pasha al-Umari ( ar, أرشد العمري; 8 April 1888 – 4 November 1978) was an Iraqi statesman from the ancient al-Omari family. Youth Arshad al-Umari was born in Mosul, Iraq on 8 April 1888 when his father was Mayor of Mosul. He obtained his high school degree in 1904 when he was 16 years old. After finishing high school at Mosul he left for Istanbul, the capital of the Ottoman Empire, to complete his studies. He did the trip by horses via Aleppo to the port of Alexandretta on the Mediterranean Sea. Such a trip in those days took about 40 days. From Alexandretta he took the steamer to Istanbul where he was admitted to the Architectural Division of the Royal Engineering College. The teaching staff of the college were professors from Germany, Belgium and Austria. He graduated as an architect in 1908, when he was 21 years old, and was appointed in the Architectural Division of the Municipality of Istanbul. When World War I broke out in 1914 he was conscripted as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuri Al-Said
Nuri Pasha al-Said CH (December 1888 – 15 July 1958) ( ar, نوري السعيد) was an Iraqi politician during the British mandate in Iraq and the Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq. He held various key cabinet positions and served eight terms as the prime minister of Iraq. From his first appointment as prime minister under the British mandate in 1930, Nuri was a major political figure in Iraq under the monarchy. During his many terms in office, he was involved in some of the key policy decisions that shaped the modern Iraqi state. In 1930, during his first term, he signed the Anglo-Iraqi Treaty, which, as a step toward greater independence, granted Britain the unlimited right to station its armed forces in and transit military units through Iraq and also gave legitimacy to British control of the country's oil industry. The treaty nominally reduced British involvement in Iraq's internal affairs but only to the extent that Iraq did not conflict with British economic or military i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
June 1954 Iraqi Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Iraq on 9 June 1954, although they were delayed until 14 June in some areas due to social upheaval.Dieter Nohlen, Florian Grotz & Christof Hartmann (2001) ''Elections in Asia: A data handbook, Volume I'', p101 The Constitutional Union Party remained the largest party in the Chamber of Deputies, winning 50 of the 135 seats, although 53 were won by independents. Despite the government creating obstacles for opposition candidates, they were described as "undoubtedly the freest elections in Iraqi history" in 2001.Nohlen et al, p86 Results Aftermath Due to his concerns about the opposition's strength, Nuri al-Said sought to dissolve the parliament. King Faisal II dissolved the newly elected parliament on 3 August and early elections were held in September. References {{Iraqi elections 1954 06 Iraq Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraqi Parliament
The Council of Representatives ( ar, مجلس النواب, Majlis an-Nuwwāb al-ʿIrāqiyy; ku, ئهنجومهنی نوێنهران, ''Enjumen-e Nûnerên''), usually referred to simply as the Parliament is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Iraq. As of 2020, it comprises 329 seats and meets in Baghdad inside the Green Zone. History The monarchy An elected Iraqi parliament first formed following the establishment of a constitutional monarchy in 1925. The 1925 constitution called for a bicameral parliament whose lower house, the Chamber of Deputies of Iraq or Council of Representatives (''Majlis an-Nuwwab'') would be elected based on universal manhood suffrage. The upper house, the Senate of Iraq (''Majlis al-A`yan'') was appointed by the king. Sixteen elections took place between 1925 and the coup of 1958. On January 17, 1953 elections for the Chamber of Deputies (also known as the National Assembly) took place. Following controversy over the implementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teaching Assistant
A teaching assistant or teacher's aide (TA) or education assistant (EA) or team teacher (TT) is an individual who assists a teacher with instructional responsibilities. TAs include ''graduate teaching assistants'' (GTAs), who are graduate students; ''undergraduate teaching assistants'' (UTAs), who are undergraduate students; ''secondary school TAs'', who are either high school students or adults; and ''elementary school TAs'', who are adults (also known as '' paraprofessional educators'' or ''teacher's aides''). By definition, TAs assist with classes, but many graduate students serve as the sole instructor for one or more classes each semester as a teaching fellow or graduate student instructor, although in some states, such as Florida, they are called "teaching assistants". Graduate and adult TAs generally have a fixed salary determined by each contract period (usually a semester or an academic year); however, undergraduates and high school students are sometimes unpaid and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinar
The dinar () is the principal currency unit in several countries near the Mediterranean Sea, and its historical use is even more widespread. The modern dinar's historical antecedents are the gold dinar and the silver dirham, the main coin of the medieval Islamic empires, first issued in AH 77 (696–697 CE) by Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. The word "dinar" derives from the Latin " ''dēnārius''," a silver coin of ancient Rome, which was first minted about c.211 BCE. The English word "dinar" is the transliteration of the Arabic دينار (''dīnār''), which was borrowed via the Syriac ''dīnarā'', itself from the Latin ''dēnārius''. The Kushan Empire introduced a gold coin known as the ''dīnāra'' into India in the 1st century AD; the Gupta Empire and its successors up to the 6th century adopted the coin. The modern gold dinar is a projected bullion gold coin, not issued as official currency by any state. Legal tender Countries currently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Sinderson
Sir Harry Chapman Sinderson (9 June 1891 – 20 November 1974) was an English medical doctor. He was Doctor to the royal family of Iraq in the period (1923–1946), and founder and first Dean of the College of Medicine University of Baghdad in 1927. Biography Born in Caister, Lincolnshire, Sinderson graduated from the Faculty of Medicine, University of Edinburgh in 1914. He participated in World War I World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ... as an army Doctor. He was posted to Iraq in 1918, and was seconded to the British administration as Deputy Director of Civil Medical Services. In 1919 and 1920, he worked as a surgeon in Hillah and Baghdad, and later was in charge of various hospitals in Baghdad. In 1927, he helped to establish a new medical school in Baghdad, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning". Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million. The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dewey And Nuri Ja'far - 1949
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)