|
Nucleotidase
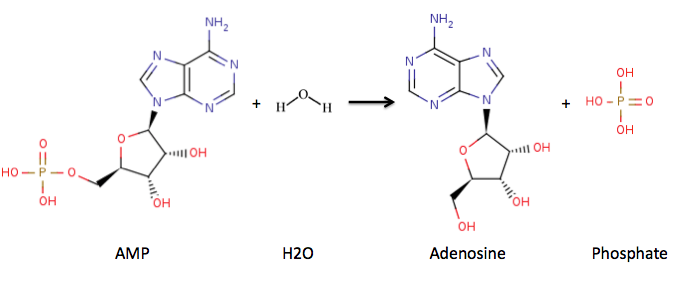
A nucleotidase is a hydrolytic enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a nucleotide into a nucleoside and a phosphate. : A nucleotide + H2O = a nucleoside + phosphate For example, it converts adenosine monophosphate to adenosine, and guanosine monophosphate to guanosine. Nucleotidases have an important function in digestion in that they break down consumed nucleic acids. They can be divided into two categories, based upon the end that is hydrolyzed: * : 5'-nucleotidase - NT5C, NT5C1A, NT5C1B, NT5C2, NT5C3 * : 3'-nucleotidase - NT3 5'-Nucleotidases cleave off the phosphate from the 5' end of the sugar moiety. They can be classified into various kinds depending on their substrate preferences and subcellular localization. Membrane-bound 5'-nucleotidases display specificity toward adenosine monophosphates and are involved predominantly in the salvage of preformed nucleotides and in signal transduction cascades involving purinergic receptors. Soluble 5'-nucleotidases are all known t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5'-nucleotidase
5′-Nucleotidase (EC 3.1.3.5) is an enzyme which catalyzes the phosphorylytic cleavage of 5′-nucleotides. Although originally found in snake venom, the activity of 5'nucleotidase has been described for bacteria and plant cells, and is widely distributed in vertebrate tissue. In mammalian cells the enzyme is predominantly located in the plasma membrane and its primary role is in the conversion of extracellular nucleotides (e.g. 5'-AMP), which are generally impermeable, to the corresponding nucleoside (e.g. adenosine) which can readily enter most cells. Consequently, the enzyme plays a key role in the metabolism of nucleotides. The enzyme has a wide substrate specificity for nucleotides and has been shown to hydrolyze 5'nucleotides rapidly, ribose-5-phosphate slowly, and other phosphate esters extremely slowly (if at all). The enzyme catalyses the following reaction: : a 5′-nucleotide + H2O a nucleoside + phosphate The 5′-nucleotidase-catalyzed reaction of an AMP nucleoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2'-deoxyribose) whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building-blocks of DNA and RNA. List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases The reason for 2 symbols, shorter and longer, is that the shorter ones are better for contexts where explicit disambiguation is superfluous (because context disambiguates) and the longer ones are for contexts where explicit disambiguation is judged to be needed or wise. For example, when discussing long nucleobase sequences in genomes, the CATG symbol system is much preferable to the Cyt-Ade-Thy-Gua symbol system (see ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolase
Hydrolase is a class of enzyme that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases. Esterases cleave ester bonds in lipids and phosphatases cleave phosphate groups off molecules. An example of crucial esterase is acetylcholine esterase, which assists in transforming the neuron impulse into the acetate group after the hydrolase breaks the acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid. Acetic acid is an important metabolite in the body and a critical intermediate for other reactions such as glycolysis. Lipases hydrolyze glycerides. Glycosidases cleave sugar molecules off carbohydrates and peptidases hydrolyze peptide bonds. Nucleosidases hydrolyze the bonds of nucleotides. Hydrolase enzymes are important for the body because they have degra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar ( ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine; it is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix adenylyl-. AMP plays an important role in many cellular metabolic processes, being interconverted to ADP and/or ATP. AMP is also a component in the synthesis of RNA. AMP is present in all known forms of life. Production and degradation AMP does not have the high energy phosphoanhydride bond associated with ADP and ATP. AMP can be produced from ADP: : 2 ADP → ATP + AMP Or AMP may be produced by the hydrolysis of one high energy phosphate bond of ADP: : ADP + H2O → AMP + Pi AMP can also be formed by hydrolysis of ATP into AMP and pyrophosphate: : ATP + H2O → AMP + PPi When RNA is broken down by living systems, nucleoside monophosphates, including adenosine monophosphate, are form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine
Adenosine (symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building blocks of RNA (and its derivative deoxyadenosine is a building block of DNA), which are essential for all life. Its derivatives include the energy carriers adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphate, also known as AMP/ADP/ATP. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is pervasive in signal transduction. Adenosine is used as an intravenous medication for some cardiac arrhythmias. Adenosyl (abbreviated Ado or 5'-dAdo) is the chemical group formed by removal of the 5′-hydroxy (OH) group. It is found in adenosylcobalamin (an active form of vitamin B12) and as a radical in radical SAM enzymes. Medical uses Supraventricular tachycardia In individuals with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify and convert t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Monophosphate
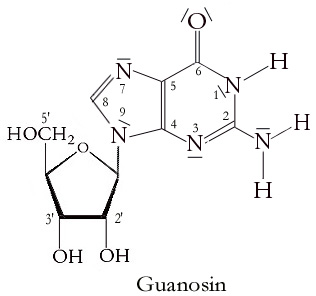
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP), also known as 5′-guanidylic acid or guanylic acid (conjugate base guanylate), is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GMP consists of the phosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine; hence it is a ribonucleoside monophosphate. Guanosine monophosphate is commercially produced by microbial fermentation. As an acyl substituent, it takes the form of the prefix guanylyl-. ''De novo'' synthesis GMP synthesis starts with D-ribose 5′-phosphate, a product of the pentose phosphate pathway. The synthesis proceeds by the gradual formation of the purine ring on carbon-1 of ribose, with CO2, glutamine, glycine, aspartate and one-carbon derivatives of tetrahydrofolate donating various elements towards the building of the ring As inhibitor of guanosine monophosphate synthesis in experimental models, the glutamine analogue DON can be used.''Ahluwalia GS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose ( ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine. Physical and chemical properties Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble in acetic acid, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform. Functions Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. Mechanical digestion takes place in the mouth through mastication and in the small intestine through segmentation contractions. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use. In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells and make up the genetic material. Nucleic acids are found in abundance in all living things, where they create, encode, and then store information of every living cell of every life-form on Earth. In turn, they function to transmit and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus to the interior operations of the cell and ultimately to the next generation of each living organism. The encoded information is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |