|
Nova Scotia Peninsula
The Nova Scotia peninsula is a peninsula on the Atlantic coast of North America. Location The Nova Scotia peninsula is part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada and is connected to the neighbouring province of New Brunswick through the Isthmus of Chignecto. It fronts the open Atlantic Ocean on the south and southeast, the Gulf of Maine to the west, the Bay of Fundy and its sub-basins to the northwest, the Northumberland Strait to the north, and the Strait of Canso to the east. The narrow and deep waters of the Strait of Canso separate the peninsula from Cape Breton Island, the second largest land mass constituting the province of Nova Scotia. In addition to Cape Breton Island, other much smaller islands are geologically associated with the Nova Scotia peninsula, including Boularderie Island, Brier Island, Long Island, Pictou Island, Tancook Island and various smaller islands along the Atlantic coast. Geology The peninsula can be divided into two distinct geological regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Nova Scotia Highlighting The Nova Scotia Peninsula
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictou Island
Pictou Island is a Canadian island located in the Northumberland Strait approximately north of Nova Scotia and south of Prince Edward Island. The island has a length of 9.5 km, a width of 2.5 km and a total area of approximately 12.8 km2. The island is administratively part of Pictou County. The island's highest elevation is above sea level, and its current full-time resident population () stands at 28, with the seasonal population rising and lowering. The island is heavily wooded, with several clearings on the more sheltered south side. There is a small year-round population spread throughout the island, of which the majority make their living by fishing. The island has a public wharf located at the west end and a breakwater for mooring at the east end. There is also a community centre, church, a Pioneer Cemetery, fire department and several lighthouses located on the island. Pictou Island receives no electrical power from the mainland. The residents supply th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney, Nova Scotia
Sydney is a former city and urban community on the east coast of Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada within the Cape Breton Regional Municipality. Sydney was founded in 1785 by the British, was incorporated as a city in 1904, and dissolved on 1 August 1995, when it was amalgamated into the regional municipality. Sydney served as the Cape Breton Island's colonial capital, until 1820, when the colony merged with Nova Scotia and the capital moved to Halifax. A rapid population expansion occurred just after the turn of the 20th century, when Sydney became home to one of North America's main steel mills. During both the First and Second World Wars, it was a major staging area for England-bound convoys. The post-war period witnessed a major decline in the number of people employed at the Dominion Steel and Coal Corporation steel mill, and the Nova Scotia and Canadian governments had to nationalize it in 1967 to save the region's biggest employer, forming the new crown corpora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictou County, Nova Scotia
Pictou County is a county in the province of Nova Scotia, Canada. It was established in 1835, and was formerly a part of Halifax County from 1759 to 1835. It had a population of 43,657 people in 2021, a decline of 0.2 percent from 2016. Furthermore, its 2016 population is only 88.11% of the census population in 1991. It is the sixth most populous county in Nova Scotia. Etymology The origin of the name "Pictou" is obscure. Possible Mi'kmaq derivations include "Piktook" meaning an explosion of gas, and "Bucto" meaning fire, possibly related to the coal fields in the area. It might also be a corruption of Poictou (Poitou), a former province of France. Nicolas Denys named the harbour ''La rivière de Pictou'' in the 1660s. History The area of the modern Pictou County was a part of the Miꞌkmaq nation of Mi'kma'ki (''mi'gama'gi'') at the time of European contact. In the early 1600s France claimed the area as a part of Acadia. By the 1760s, small French settlements existed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debert, Nova Scotia
Debert () (2006 pop: 1,471) is an unincorporated farming community in Nova Scotia, Canada. Located in the central-western part of Colchester County, it is approximately west of Truro. The community has two churches (United Baptist Church and United Church of Canada), Royal Canadian Legion (Branch 106), a skating rink, a community centre, two vehicle repair garages, one convenience store, and a volunteer fire department. Debert is situated near coal and iron ore deposits that were mined in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Debert became a station stop on the Halifax-Montreal mainline of the Intercolonial Railway in the 1870s. This railway line continues to this day under the ownership of Canadian National Railway (CN Rail), with passenger service provided by Via Rail, but without a stop at Debert. Military history During the Second World War Debert was the location of a Canadian Army base named Debert Military Camp and an adjoining Royal Canadian Air Force station named RCA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springhill, Nova Scotia
Springhill is a community located in central Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada. The community was founded as "Springhill Mines." Coal mining led to economic growth, with its incorporation as a town in 1889. The mines in the Springhill coalfield were established in the 19th century, and by the early 1880s were being worked by the Cumberland Coal & Railway Company Ltd. and the Springhill & Parrsboro Coal & Railway Company Ltd. These entities merged in 1884 to form the Cumberland Railway & Coal Company Ltd., which its investors sold in 1910 to the industrial conglomerate Dominion Coal Company Ltd. (DOMCO). All coal mining had ceased in the area by the early 1970s. The community is famous for both the Springhill Mining Disaster and being the childhood home of international recording star Anne Murray, who is honoured by the Anne Murray Centre, a popular tourist attraction. As of 2015 the mine properties, among the deepest in the world, with the No. 2 mine reaching 14,300 fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Hebert, Nova Scotia
River Hebert is a village on the River Hebert in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada.It is approximately 25 kilometres southwest of Amherst. As of 2021 the population was 468. The village and the river are both named after Louis Hébert, a settler from Port Royal in 1604, who navigated the river. Until the late 20th century, coal mining was the major industry in the area, but the last mine closed in 1981. River Hebert is home to 1442 River Hebert Royal Canadian Army Cadet Corps, founded in 1949. River Hebert has one school that is open to students from grades pre-primary to 12, a public library, a medical centre, and it is home to Heritage Models, a tourist attraction that features scale models of local areas of interest, such as the home of Amos Peck "King" Seaman. The Village is also home to a gas station, which was burned down, but has since been replaced. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joggins, Nova Scotia
Joggins is a rural community located in western Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada. On July 7, 2008 a 15-km length of the coast constituting the Joggins Fossil Cliffs was officially inscribed on the World Heritage List.UNESCO portal History The area was known to the as "Chegoggins" meaning place of the large fish weir, a name modified by French and English settlers to Joggins. Situated on the Cumberland Basin, a sub-basin of the Bay of Fund ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland County, Nova Scotia
Cumberland County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. History The name Cumberland was applied by Lieutenant-Colonel Robert Monckton to the captured Fort Beauséjour on June 18, 1755 in honour of the third son of King George II, William Augustus, Duke of Cumberland, victor at Culloden in 1746 and Commander in Chief of the British forces. The Mi'kmaq name for the area was "Kwesomalegek" meaning "hardwood point". Cumberland County was founded on August 17, 1759. When the Township of Parrsboro was divided in 1840, one part was annexed to Cumberland County and the other part annexed to Colchester. The dividing line between Cumberland and Colchester was established in 1840. In 1897, a portion of the boundary line between the Counties of Colchester and Cumberland was fixed and defined. The county thrived in the 19th century with the development of lumbering, shipbuilding and coal mining. Deforestation and rural outmigration in the 20th century led to the abandonment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west. Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the ''Appalachian Highlands'' physiographic division as consisting of 13 provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, St. Lawrence Valley, Appalac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobequid Hills
The Cobequid Mountains, also sometimes referred to as the Cobequid Hills, is a Canadian mountain range located in Nova Scotia in the mainland portion of the province. Geologic history Geologically, the Cobequid Mountains are considered part of the Appalachians. The range stretches from Cape Chignecto in Cumberland County in the west through to Pictou County in the east. The Cobequid Mountains trace their geologic history to the Precambrian and Devonian ages; consequently the mountains are composed of a combination of sediments, granites, and volcanic rock all of which has been crushed and folded by continental drift when this part of Nova Scotia was located at the centre of the Pangea supercontinent. Subsequent erosion over millions of years has resulted in the present-day low range of mountains and rolling hills. The part of northern Nova Scotia which contains the Cobequid Mountains is believed to have been linked with what is now northern Europe. Its collision with a section ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
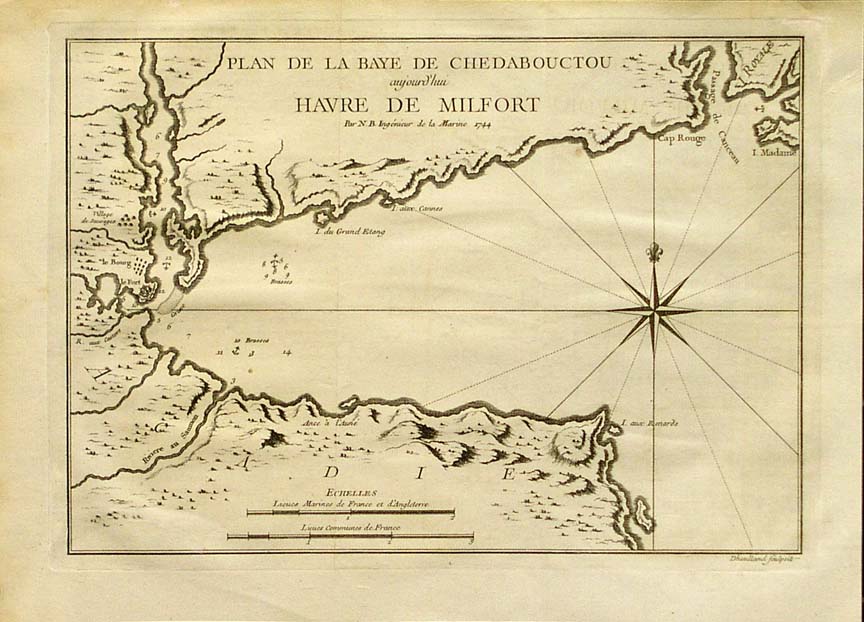
Chedabucto Bay
Chedabucto Bay is a large bay on the eastern coast of mainland Nova Scotia between the Atlantic Ocean and the Strait of Canso next to Guysborough County. At the entrance to Chedabucto Bay is the community of Canso at the head is the community of Guysborough and on the other end is the town of Mulgrave. Geography Chedabucto Bay was formed by the drowning of part of an ancient river system and owes its origin and shape to position of the Chedabucto Fault, which runs across central Nova Scotia from the Bay of Fundy to the Canso peninsula. History Colonial Merchants in La Rochelle, France enjoyed a fishing monopoly in Acadia and formed the Company of Acadia which established a small fortification on Chedabucto Bay named Fort St. Louis. The principal ports were at Chedabucto, which accounted for fifty fishers in 1686. In 1690, Captain Cyprian Southack proceeded to Chedabucto to take Fort St. Louis at the present-day village of Guysborough which, unlike Port-Royal, put up a figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |